• They have two openings on the sides of your head that peek out over the skin just behind your eyes and lead to the inner ear. Since sound travels much faster in the water than in the air, an external ear is not necessary for these big ones, who are also specialists in perceiving low frequency sounds at long distances, so when an animal moves quietly through the water it can be quickly surprised by a shark.
• The sense of smell is the strongest in a shark, its nostrils are located in the nose, just above the mouth, and allow it to detect chemical changes in the water at low concentrations. There is a time lag of approximately half a second between the reception of one nostril and the other, and it is so impressive that by this simple delay the animal will turn in the direction from where it perceived the highest concentration of X substance. This is only talking about chemical changes and their own preservation, but when the subject of the moment is blood, these great fish can detect a few drops of blood in 1 million parts of water, so when an animal is injured will be easy prey of our predator.
• It is to be expected that the taste buds of a shark are on its tongue, but...have you seen a shark with tongue?...They don't have, their taste buds are all over the mouth and pharynx, they look like small buttons with a fine opening where the sensors are specially designed to detect the amount of high energy fat that the prey can provide its organism, and from this decide if it is worthwhile to carry out an expensive digestion process or wait for an upcoming new food. Since the shark's jaws are not independent of each other, literally, they swallow their food and if it is very big they bite it to separate it into pieces... Guys :O I think I am a shark!
• The sense of touch of sharks, in terms of touch, is not very different from ours, although it is obviously sharper. Their skin has very precise sensors that allow them to perceive even weak stimuli caused by contact, pressure, temperature and, probably, they can feel pain.
• When a prey or predator moves in the perception zone of a shark, it produces shocks between the molecules of water that are transferred until running into the skin of our friend, this is called mechanoreception and it is conferred by its lateral line. You will say: Ok niniscool! And what is that? Sharks have sensory cells along their body (from the snout to the caudal fin), which basically consist of cilia that are located under the skin of the shark and connect to the pores of the surface by a gelatinous substance, this leads the electrical impulses received to the brain.
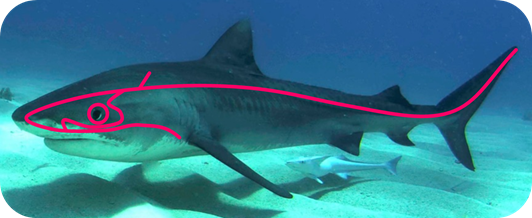 Lateral line
Lateral line
• Lorenzini ampoules are bags filled with a gelatinous substance that are connected to the nervous system, and therefore also to the lateral line of the shark. They are found around his head and lower jaw, and allow him to detect electric fields of possible prey or predators, how?, because all living beings generate one around them with the slightest movement, even with the beat of heart. Some scientists think of the possibility that these excellent predators perceive the Earth's magnetic field and use it as a compass.
 Ampoule of Lorenzini
Ampoule of Lorenzini
Breathing
You've seen that sharks have nostrils, right? but unlike us and many other animals, they don't use it to breathe; instead, they have 5-7 pairs of gills on the sides of their heads. A characteristic of the cartilaginous fish is that they do not have operculae (the organ in charge of making the sea water pass through the gills of the fish when they are at rest), so they are forced to swim constantly so that the water enters the mouth and continues to the gills where the filtration process takes place. Sharks that inhabit the seabed, being quite inactive, have muscles that cause contractions and carry arterial blood to the gills to be oxygenated.
 Gills
Gills
Habitat
The salinity of the water or its temperature are not problems, they have managed to adapt to a wide range of aquatic environments, and although some species prefer shallow and coastal regions, others live in deep water, on the bottom of the ocean and in the open sea, but the most important thing is that their habitat is where the food is. Some species are more adaptable than others.
Mobility
I already mentioned the term swimming bladder, this is a chamber full of gas that fish use to float; since sharks lack it, they use their large livers full of oil to manage their buoyancy, which also allows them to swim up and down in the water column. Sharks living in deep water require more oil, so they have larger livers.
Hunting and Feeding
Most sharks hunt in the afternoon and at night, when they are most active; since some travel great distances to feed and reproduce, they may end up in any ocean basin in the world. Your ideal banquet consists of mollusks, jellyfish, plankton, seals, squid, sea lions, dolphins, turtles, krill, crustaceans, seabirds, etc., all depending on the species of shark that is serving the table. When talking about shark feeding patterns, we find that those who inhabit the seabed developed a lower mouth and others attack shoals of fish in a frenzy; white sharks impress us with their shocking attacks from below to sea lions and seals, while larger sharks such as the Whale Shark and the Pilgrim Shark feed by filter, i.e., they swim across the ocean with their mouth open and filter large amounts of plankton and krill.
 White Shark Attacking Baby Seal
Filter feed. Whale Shark
White Shark Attacking Baby Seal
Filter feed. Whale Shark
Pairing and Reproduction
The sexual maturity of sharks comes slowly in comparison to other species of fish, about 12 to 15 years old, so it is difficult for them to recover after a decline in their population; observing the mating of these animals you may wonder if they are copulating or fighting, as it is often wild and cause non-lethal injuries. Sharks usually live alone, so the game begins when the female releases chemicals into the water that attract the male; once the male finds the female he begins to swim in circles around her to let him know that he is ready and in a moment the bites and cuts that are usually caused mostly by the male, who holds the female with his jaw until the fertilization takes place, begin. The gestation period is between 9 and 12 months, and in many species only 1-2 offspring are given at a time, which begin a life independent of their parents shortly after birth. Shark reproduction can be viviparous (where the shark is born formed), oviparous (where the egg hatches and the shark born) or oviparous (where the egg hatches inside the mother's womb and the shark develops there until it is born). There are also sharks in captivity that have achieved asexual reproduction.
 Mating and Viviparous Reproduction
Shark egg
Mating and Viviparous Reproduction
Shark egg
Depredadores
Small sharks can be preyed upon by large fish and giant octopus, while large sharks have few, but dangerous, predators; one as natural as the killer whale and another as unnecessary as man. Talking about how human activity directly affects sharks, we find clandestine fishing, whose purposes can be commercial (restaurants, seafood, accessories, etc.) or mere fun and sport. Leaving aside the cruelty with which, for the most part, these animals are mutilated and thrown to die on the seabed, the ecological imbalance caused by these activities is alarmingly striking. Without the maximum aquatic predators, we are destroying the nature of the sea.
 Illegal trade in shark fins
Orca attacks Tiger Shark
Illegal trade in shark fins
Orca attacks Tiger Shark
Types
There are just over 370 different species of sharks across the globe that represent the top of the oceans' food chains and regulate the populations of species found beneath them. Among the smaller sharks are the Dwarf Shark and the Spiny Dogfish, whose lengths reach a maximum of 19-20cm and 21cm, respectively. Among the largest sharks are the Whale Shark and the Pilgrim Shark, whose lengths reach a maximum of 15m and 12.3m, respectively. The fastest sharks are the Mako Shark and the Blue Shark. The largest mouth belongs to the Whale Shark and the longest tail to the Fox Shark, whose upper lobe is the same length as its body. So each specie has differentiating characteristics that make them more agile in some aspects than in others.
 Tiger Shark
Hammerhead Shark
Tiger Shark
Hammerhead Shark
Attacks on people
The truth is that if we investigate on this subject, shark attacks, without taking away how terrifying it must be for the victims, are overestimated, to think that we are the favorite snack of these animals or that it is the main cause of death in a country, is something exaggerated; even if the latter would true somewhere in the world, it would be good to ask oneself what humans are doing that makes sharks feel so curious as to come closer to take a look. Some instinctive reasons why a shark can attack you, me or anyone are: the agitation of the water or splashes, colors that contrast with the marine tones of the beach or any where and the use of bright jewelry in the water, similarities in the silhouette or movement between us and their prey (sea lions or seals) at certain times, unconsciously invade their safety zones, etc... If we think about each of these causes, we see that their motives are the same as we all have in front of the unknown or what we do not understand: curiosity, error of identity and territoriality. Most of the victims survive, and once bitten (and tasted) they are not what these fish expected and release them. Currently diving with sharks in various parts of the world, without any protection and without accidents, so (and I do not say this lightly) it is possible that sharks and humans are in the same place without major problem.
 Diving with sharks
Diving with sharks
Guys, I hope you liked this article very much, it was my passion for nature and an attraction I feel for these animals since I was a little girl that inspired me to know them better and make them known to you. See you in the next article, it's a date!
Big hug. God bless you. 

















Congratulations @niniscool! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!