Latest Arxiv Papers In Astrophysics A |2019-04-12
Astrophysics Of Galaxies
Revealing dust segregation in protoplanetary discs with the help of multi-frequency spectral index maps (1904.05251v1)
Yaroslav Pavlyuchenkov, Vitaly Akimkin, Dmitri Wiebe, Eduard Vorobyov
2019-04-10
Dust is known to drift and grow in protoplanetary discs, which results in dust segregation over the disc extent. Maps of the spectral index
are a common tool for studying the dust content in protoplanetary discs. The analysis of observationally derived maps reveals significant gradients of the spectral index, confirming that dust evolves in the disc, but a more detailed information about the dust redistribution is required to make inferences about the early stages of dust growth. We calculated the spectral index maps based on the results of numerical hydrodynamical simulations using the FEOSAD code, which allows studying a long-term dynamics of a self-gravitating viscous disc populated with coagulating, drifting, and fragmenting dust. Here we demonstrate that values of the spectral index estimated for different wavelength intervals within the far-infrared and radio bands reveal the presence of dust grains of various sizes. Specifically, we show that the disc regions with the maximal spectral index in a specific wavelength interval are the regions with the prevalence of dust grains of a specific size. Thus, a set of spectral index maps derived using different wavelength intervals can be used to recover the dust size-distribution over the disc extent.
The Hubble Space Telescope UV Legacy Survey of Galactic Globular Clusters. XIX. A Chemical Tagging of the Multiple Stellar Populations Over the Chromosome Maps (1904.05180v1)
A. F. Marino, A. P. Milone, A. Renzini, F. D'Antona, J. Anderson, L. R. Bedin, A. Bellini, G. Cordoni, E. P. Lagioia, G. Piotto, M. Tailo
2019-04-10
The HST UV Survey of Globular Clusters (GCs) has investigated GCs and their stellar populations. In previous papers of this series we have introduced a pseudo two-color diagram, "chromosome map" (ChM), that maximises the separation between the multiple populations. We have identified two main classes of GCs: Type I (~83% of the objects) and Type II, both hosting two main groups of stars, referred to in this series as first (1G) and second generation (2G). Type II clusters exhibit two or more parallel sequences of 1G and 2G stars in their ChMs. We exploit elemental abundances from literature to assign the chemical composition to the distinct populations as identified on the ChMs of 29 GCs. We find that stars in different regions of the ChM have different composition: 1G stars share the same light-element content as field stars, while 2G stars are enhanced in N, Na and depleted in O. Stars enhanced in Al and depleted in Mg populate the extreme regions of the ChM. We investigate the color spread among 1G stars observed in many GCs, and find no evidence for variations in light elements, whereas either a 0.1 dex Fe spread or a variation in He remain to be verified. In the attempt of analysing the global properties of the multiple populations, we have constructed a universal ChM, which highlights that, though variegate, the phenomenon has some common pattern. The universal ChM reveals a tight connection with Na, for which we have provided an empirical relation. The additional ChM sequences typical of Type II GCs are enhanced in metallicity and, often, in s elements. Omega Cen can be classified as an extreme Type II GC, with a ChM displaying three main streams, each with its own variations in chemical abundances. One of the most noticeable differences is between the lower and upper streams, with the latter (associated with higher He) having higher Fe and lower Li. We publicly release ChMs.
Constraining the Milky Way Halo Potential with the GD-1 stellar stream (1807.05994v2)
Khyati Malhan, Rodrigo A. Ibata
2018-07-16
We use ESA/Gaia astrometry together with SEGUE and LAMOST measurements of the GD-1 stellar stream to explore the improvement on the Galactic gravitational potential that these new data provide. Assuming a realistic universal model for the dark matter halo together with reasonable models of the baryonic components, we find that the orbital solutions for GD-1 require the circular velocity at the Solar radius to be
, and also that the density flattening of the dark halo is
. The corresponding Galactic mass within 20kpc was estimated to be
. Moreover, Gaia's excellent proper motions also allowed us to constrain the velocity dispersion of the GD-1 stream in the direction tangential to the line of sight to be
(95 % confidence limit), confirming the extremely cold dynamical nature of this system.
MUSE unravels the ionisation and origin of metal enriched absorbers in the gas halo of a z = 2.92 radio galaxy (1904.05114v1)
S. Kolwa, J. Vernet, C. De Breuck, M. Villar-Martin, A. Humphrey, F. Arrigoni-Battaia, B. Gullberg, T. Falkendal, G. Drouart, M. Lehnert, D. Wylezalek, A. Man
2019-04-10
We have used the Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) to study the circumgalactic medium (CGM) of a z = 2.92 radio galaxy, MRC 0943-242 by parametrising its emitting and absorbing gas. In both Ly
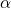
1216 and He II
1640 lines, we observe emission with velocity shifts of
km s
from the systemic redshift of the galaxy. These blueshifted components represent kinematically perturbed gas that is aligned with the radio axis, which we interpret as jet-driven outflows. Three of the four known Ly
absorbers are detected at the same velocity as C IV
and N V
absorbers, proving that the gas is metal enriched more so than previously thought. At the velocity of a strong Ly
absorber with an HI column of
and velocity shift of
km s
we also detect Si II
1260 and Si II
1527 absorption, which suggests that the absorbing gas is ionisation bounded. With the added sensitivity of this MUSE observation, we are more capable of adding constraints to absorber column densities and consequently determining what powers their ionisation. To do this, we obtain photoionisation grid models in \pkg{cloudy} which show that AGN radiation is capable of ionising the gas and producing the observed column densities in a gas of metallicity of Z/Z
0.01 with a nitrogen abundance a factor of 10 greater than that of hydrogen. This metal-enriched absorbing gas, which is also spatially extended over a projected distance of
kpc, is likely to have undergone chemical enrichment through stellar winds that have swept up metals from the interstellar-medium and deposited them in the outer regions of the galaxy's halo.
Optical properties of infrared-bright dust-obscured galaxies viewed with Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam (1803.09951v2)
Akatoki Noboriguchi, Tohru Nagao, Yoshiki Toba, Mana Niida, Masaru Kajisawa, Masafusa Onoue, Yoshiki Matsuoka, Takuji Yamashita, Yu-Yen Chang, Toshihiro Kawaguchi, Yutaka Komiyama, Kodai Nobuhara, Yuichi Terashima, Yoshihiro Ueda
2018-03-27
We report on the optical properties of infrared (IR)-bright dust-obscured galaxies (DOGs) that are defined as (i-[22])_AB > 7.0. Because supermassive black holes (SMBHs) in IR-bright DOGs are expected to be rapidly growing in the major merger scenario, they provide useful clues for understanding the co-evolution of SMBHs and their host galaxies. However, the optical properties of IR-bright DOGs remain unclear because the optical emission of a DOG is very faint. By combining ~ 105 deg^2 images of the optical, near-IR, and mid-IR data obtained from the Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) survey, the VISTA VIKING survey, and the WISE all-sky survey, respectively, 571 IR-bright DOGs were selected. We found that IR-bright DOGs show a redder (g-z)_AB color than other populations of dusty galaxies, such as ultra-luminous IR galaxies (ULIRGs) at a similar redshift, with a significantly large dispersion. Among the selected DOGs, star-formation (SF) dominated DOGs show a relatively red color, while active galactic nucleus (AGN) dominated DOGs show a rather blue color in optical. This result is consistent with the idea that the relative AGN contribution in the optical emission becomes more significant at a later stage in the major merger scenario. We discovered eight IR-bright DOGs showing a significant blue excess in blue HSC bands (BluDOGs). This blue excess can be interpreted as a leaked AGN emission that is either a directly leaking or a scattered AGN emission, as proposed for some blue-excess Hot DOGs in earlier studies.
Earth And Planetary Astrophysics
Near/Far Side Asymmetry in the Tidally Heated Moon (1810.10676v2)
Alice C. Quillen, Larkin Martini, Miki Nakajima
2018-10-25
Using viscoelastic mass spring model simulations to track heat distribution inside a tidally perturbed body, we measure the asymmetry of heating in the crust of a spin synchronous Moon in eccentric orbit about the Earth. With the Moon within a few Earth radii of the Earth, we find that tidal heating per unit area in a lunar crustal shell is asymmetric due to the octupole order moment in the Earth's tidal field and is 10 to 20% higher on its near side than on its far side. Tidal heating reduces the crustal basal heat flux and the rate of magma ocean crystallization. Assuming that the local crustal growth rate depends on the local basal heat flux and the distribution of tidal heating in latitude and longitude, a heat conductivity model illustrates that a moderately asymmetric and growing lunar crust could maintain its asymmetry. Near/far side asymmetric tidal heating could serve as a trigger for uneven lunar crustal growth.
Inertial Modes in Near-Spherical Geometries (1904.05221v1)
J. Rekier, A. Trinh, S. A. Triana, V. Dehant
2019-04-10
We propose a numerical method to compute the inertial modes of a container with near-spherical geometry based on the fully spectral discretisation of the angular and radial directions using spherical harmonics and Gegenbauer polynomial expansion respectively. This allows to solve simultaneously the Poincare equation and the no penetration condition as an algebraic polynomial eigenvalue problem. The inertial modes of an exact oblate spheroid are recovered to machine precision using an appropriate set of spheroidal coordinates. We show how other boundaries that deviate slightly from a sphere can be accommodated for with the technique of equivalent spherical boundary and we demonstrate the convergence properties of this approach for the triaxial ellipsoid.
Properties of the Bare Nucleus of Comet 96P/Machholz 1 (1903.10500v2)
Nora L. Eisner, Matthew M. Knight, Colin Snodgrass, Michael S. P. Kelley, Alan Fitzsimmons, Rosita Kokotanekova
2019-03-21
We observed comet 96P/Machholz 1 on a total of 9 nights before and after perihelion during its 2017/2018 apparition. Both its unusually small perihelion distance and the observed fragmentation during multiple apparitions make 96P an object of great interest. Our observations show no evidence of a detectable dust coma, implying that we are observing a bare nucleus at distances ranging from 2.3 AU to 3.8 AU. Based on this assumption we calculated its color, and found average values of g'-r' = 0.50 +/- 0.04, r'-i' = 0.17 +/- 0.03, and i'-z' = 0.06 +/- 0.04. These are notably more blue than those of the nuclei of other Jupiter family and long period comets. Furthermore, assuming a bare nucleus, we found an equivalent nuclear radius of 3.4 +/- 0.2 km with an axial ratio of at least 1.6 +/- 0.1. The lightcurve clearly displays one large peak, one broad flat peak, and two distinct troughs, with a clear asymmetry that suggests that the shape of the nucleus deviates from that of a simple triaxial ellipsoid. This asymmetry in the lightcurve allowed us to constrain the nuclear rotation period to 4.10 +/- 0.03 hours and 4.096 +/- 0.002 hours before and after perihelion, respectively. Within the uncertainties, 96P's rotation period does not appear to have changed throughout the apparition, and we conclude a maximum possible change in rotation period of 130 seconds. The observed properties were compared to those of comet 322P and interstellar object 1I/'Oumuamua in an attempt to study the effects of close perihelion passages on cometary surfaces and their internal structure, and the potential interstellar origin of 96P.
Magnetohydrodynamics in a Cylindrical Shearing Box (1904.05032v1)
Takeru K. Suzuki, Tetsuo Taki, Scott S. Suriano
2019-04-10
We develop a framework for magnetohydrodynamical (MHD) simulations in a local cylindrical shearing box by extending the formulation of the Cartesian shearing box. We construct shearing-periodic conditions at the radial boundaries of a simulation box from the conservation relations of the basic MHD equations. We demonstrate quasi-steady mass accretion, which cannot be handled by the standard Cartesian shearing box model, with an ideal MHD simulation in a vertically unstratified cylindrical shearing box up to 200 rotations with (i) net vertical magnetic flux, (ii) a locally isothermal equation of state, and (iii) a sub-Keplerian equilibrium rotation. Inward mass accretion is induced to balance with the outward angular momentum flux of the MHD turbulence triggered by the magnetorotational instability in a self-consistent manner. We discuss detailed physical properties of the saturated magnetic field, in comparison to the results of a Cartesian shearing box simulation.
Transiting Planets near the Snow Line from Kepler. I. Catalog (1904.04980v1)
Hajime Kawahara, Kento Masuda
2019-04-10
We present a comprehensive catalog of cool (period
) transiting planet candidates in the four-year light curves from the prime \kepler\ mission. Most of the candidates show only one or two transits and have largely been missed in the original Kepler Object of Interest catalog. Our catalog is based on all known such candidates in the literature as well as new candidates from the search in this paper, and provides a resource to explore the planet population near the snow line of Sun-like stars. We homogeneously performed pixel-level vetting, stellar characterization with GAIA parallax and archival/Subaru spectroscopy, and light-curve modeling to derive planet parameters and to eliminate stellar binaries. The resulting clean sample consists of 67 planet candidates whose radii are typically constrained to 5%, in which 23 are newly reported. The number of Jupiter-sized candidates (29 with
) in the sample is consistent with the Doppler occurrence. The smaller candidates are more prevalent (23 with
, 15 with
) and suggest that long-period Neptune-sized planets are at least as common as the Jupiter-sized ones, although our sample is yet to be corrected for detection completeness. If the sample is assumed to be complete, these numbers imply the occurrence rate of
planets with
and
per FGK dwarf. The stars hosting candidates with
have systematically higher [Fe/H] than the Kepler field stars, providing evidence that giant planet--metallicity correlation extends to
.
Solar And Stellar Astrophysics
On the origin of the magnetic energy in the quiet solar chromosphere (1904.04464v2)
Juan Martínez-Sykora, Viggo H. Hansteen, Boris Gudiksen, Mats Carlsson, Bart De Pontieu, Milan Gosic
2019-04-09
The presence of magnetic field is crucial in the transport of energy through the solar atmosphere. Recent ground-based and space-borne observations of the quiet Sun have revealed that magnetic field accumulates at photospheric heights, via a local dynamo or from small-scale flux emergence events. However, most of this small-scale magnetic field may not expand into the chromosphere due to the entropy drop with height at the photosphere. Here we present a study that uses a high resolution 3D radiative MHD simulation of the solar atmosphere with non-grey and non-LTE radiative transfer and thermal conduction along the magnetic field to reveal that: 1) the net magnetic flux from the simulated quiet photosphere is not sufficient to maintain a chromospheric magnetic field (on average), 2) processes in the lower chromosphere, in the region dominated by magneto-acoustic shocks, are able to convert kinetic energy into magnetic energy, 3) the magnetic energy in the chromosphere increases linearly in time until the r.m.s. of the magnetic field strength saturates at roughly 4 to 30 G (horizontal average) due to conversion from kinetic energy, 4) and that the magnetic features formed in the chromosphere are localized to this region.
On the minimum mass of neutron stars (1808.02328v2)
Yudai Suwa, Takashi Yoshida, Masaru Shibata, Hideyuki Umeda, Koh Takahashi
2018-08-07
We investigate remnant neutron star masses (in particular, the minimum allowed mass) by performing advanced stellar evolution calculations and neutrino-radiation hydrodynamics simulations for core-collapse supernova explosions. We find that, based on standard astrophysical scenarios, low-mass carbon-oxygen cores can have sufficiently massive iron cores that eventually collapse, explode as supernovae, and give rise to remnant neutron stars that have a minimum mass of 1.17 M
--- compatible with the lowest mass of the neutron star precisely measured in a binary system of PSR J0453+1559.
Evolution of rotation in rapidly rotating early-type stars during the main sequence with 2D models (1904.05219v1)
D. Gagnier, M. Rieutord, C. Charbonnel, B. Putigny, F. Espinosa Lara
2019-04-10
The understanding of the rotational evolution of early-type stars is deeply related to that of anisotropic mass and angular momentum loss. In this paper, we aim to clarify the rotational evolution of rapidly rotating early-type stars along the main sequence (MS). We have used the 2D ESTER code to compute and evolve isolated rapidly rotating early-type stellar models along the MS, with and without anisotropic mass loss. We show that stars with
and masses between
and
reach criticality during the main sequence provided their initial angular velocity is larger than 50% of the Keplerian one. More massive stars are subject to radiation-driven winds and to an associated loss of mass and angular momentum. We find that this angular momentum extraction from the outer layers can prevent massive stars from reaching critical rotation and greatly reduce the degree of criticality at the end of the MS. Our model includes the so-called bi-stability jump of the
relation of 1D-models. This discontinuity now shows up in the latitude variations of the mass-flux surface density, endowing rotating massive stars with either a single-wind regime (no discontinuity) or a two-wind regime (a discontinuity). In the two-winds-regime, mass loss and angular momentum loss are strongly increased at low latitudes inducing a faster slow-down of the rotation. However, predicting the rotational fate of a massive star is difficult, mainly because of the non-linearity of the phenomena involved and their strong dependence on uncertain prescriptions. Moreover, the very existence of the bi-stability jump in mass-loss rate remains to be substantiated by observations.
The Hubble Space Telescope UV Legacy Survey of Galactic Globular Clusters. XIX. A Chemical Tagging of the Multiple Stellar Populations Over the Chromosome Maps (1904.05180v1)
A. F. Marino, A. P. Milone, A. Renzini, F. D'Antona, J. Anderson, L. R. Bedin, A. Bellini, G. Cordoni, E. P. Lagioia, G. Piotto, M. Tailo
2019-04-10
The HST UV Survey of Globular Clusters (GCs) has investigated GCs and their stellar populations. In previous papers of this series we have introduced a pseudo two-color diagram, "chromosome map" (ChM), that maximises the separation between the multiple populations. We have identified two main classes of GCs: Type I (~83% of the objects) and Type II, both hosting two main groups of stars, referred to in this series as first (1G) and second generation (2G). Type II clusters exhibit two or more parallel sequences of 1G and 2G stars in their ChMs. We exploit elemental abundances from literature to assign the chemical composition to the distinct populations as identified on the ChMs of 29 GCs. We find that stars in different regions of the ChM have different composition: 1G stars share the same light-element content as field stars, while 2G stars are enhanced in N, Na and depleted in O. Stars enhanced in Al and depleted in Mg populate the extreme regions of the ChM. We investigate the color spread among 1G stars observed in many GCs, and find no evidence for variations in light elements, whereas either a 0.1 dex Fe spread or a variation in He remain to be verified. In the attempt of analysing the global properties of the multiple populations, we have constructed a universal ChM, which highlights that, though variegate, the phenomenon has some common pattern. The universal ChM reveals a tight connection with Na, for which we have provided an empirical relation. The additional ChM sequences typical of Type II GCs are enhanced in metallicity and, often, in s elements. Omega Cen can be classified as an extreme Type II GC, with a ChM displaying three main streams, each with its own variations in chemical abundances. One of the most noticeable differences is between the lower and upper streams, with the latter (associated with higher He) having higher Fe and lower Li. We publicly release ChMs.
Off-centre carbon burning in He-accreting carbon-oxygen white dwarfs (1904.05130v1)
Chengyuan Wu, Bo Wang
2019-04-10
The carbon-oxygen white dwarf (CO WD) + He star channel is one of the promising ways for producing type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) with short delay times. Recent studies found that carbon under the He-shell can be ignited if the mass-accretion rate of CO WD is higher than a critical rate (about 2 * 10^-6 Msun/yr), triggering an inwardly propagating carbon flame. Previous studies usually supposed that the off-centre carbon flame would reach the centre, resulting in the formation of an oxygen-neon (ONe) WD that will collapse into a neutron star. However, the process of off-centre carbon burning is not well studied. This may result in some uncertainties on the final fates of CO WDs. By employing MESA, we simulated the long-term evolution of off-centre carbon burning in He-accreting CO WDs. We found that the inwardly propagating carbon flame transforms the CO WDs into OSi cores directly but not ONe cores owing to the high temperature of the burning front. We suggest that the final fates of the CO WDs may be OSi WDs under the conditions of off-centre carbon burning, or explode as iron-core-collapse SNe if the mass-accretion continues. We also found that the mass-fractions of silicon in the OSi cores are sensitive to the mass-accretion rates.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @astrophysics
Keeping everyone inform.
Hello astrophysics, welcome to Partiko, an amazing community for crypto lovers! Here, you will find cool people to connect with, and interesting articles to read!
You can also earn Partiko Points by engaging with people and bringing new people in. And you can convert them into crypto! How cool is that!
Hopefully you will have a lot of fun using Partiko! And never hesitate to reach out to me when you have questions!
Cheers,
crypto.talk
Creator of Partiko
You got a 60.26% upvote from @brupvoter courtesy of @astrophysics!