Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences 2|2019-03-14
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Symmetry breaking with opposite stability between bifurcated asymmetric solitons in parity-time-symmetric potentials (1903.04953v1)
Jianke Yang
2019-03-12
We report a new type of symmetry-breaking bifurcation of solitons in optical systems with parity-time-symmetric potentials. In this bifurcation, the two bifurcated branches of asymmetric solitons exhibit opposite stability, which contrasts all previous symmetry-breaking bifurcations in conservative and non-conservative systems. We show that this novel symmetry-breaking bifurcation can be exploited to achieve unidirectional propagation of high-intensity light beams in parity-time-symmetric potentials.
Spin-orbit coupled polariton condensates in a radially-periodic potential: Multiring vortices and rotating solitons (1903.04885v1)
Dmitry A. Zezyulin, Yaroslav V. Kartashov, Dmitry V. Skryabin, Ivan A. Shelykh
2019-03-12
We address evolution of a spinor polariton condensate in radially periodic potentials. Such potentials allow for the observation of novel nonlinear excitations and support a variety of dynamically stable soliton states never demonstrated before in polariton condensates, including ring-like solitons with density peaks located in different radial minima of the potential and extended dynamically stable multiring patterns. Among the advantages of the system is that azimuthal modulational instabilities are suppressed due to dominating repulsive interactions between polaritons with the same spin, thereby allowing for the stabilization of radially-symmetric states. The representative feature of this system is that spin-orbit coupling between different spinor components requires them to carry different topological charges. Radially-symmetric states carrying different combinations of topological charges are discussed. Radially symmetric potentials also support stable rotating multipeaked solitons, whose properties unexpectedly depend not only on the magnitude of the rotation velocity, but also on its sign, i.e., on the rotation direction. The latter property is a consequence of spin-orbit coupling which breaks the equivalence between clockwise and counterclockwise rotations. The multiring structures are shown to be robust against unavoidable losses and are therefore amenable to observations with the presently available experimental techniques.
Structured light entities, chaos and nonlocal maps (1901.09274v3)
A. Yu. Okulov
2019-01-26
Spatial chaos as a phenomenon of ultimate complexity requires the efficient numerical algorithms. For this purpose iterative low-dimensional maps have demonstrated high efficiency. Natural generalization of Feigenbaum and Ikeda maps may include convolution integrals with kernel in a form of Green function of a relevant linear physical system. It is shown that such iterative
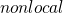
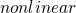
are equivalent to ubiquitous class of nonlinear partial differential equations of Ginzburg-Landau type. With a Green functions relevant to generic optical resonators these
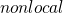
emulate the basic spatiotemporal phenomena as spatial solitons, vortex eigenmodes breathing via relaxation oscillations mediated by noise, vortex-vortex and vortex-antivortex lattices with well defined periodic location of vortex cores.
Topological insulators in longitudinally driven waveguides: Lieb and Kagome lattices (1804.09880v2)
Mark J. Ablowitz, Justin T. Cole
2018-04-26
Topological insulators are studied via tight-binding approximations of longitudinally driven photonic lattices with three lattice sites per unit cell. Two cases are considered in detail: Lieb and Kagome lattices. The lattice is decomposed into three sublattices each of which are allowed move independently of one another. Emphasis is placed on periodic driving induced by laser-etched helical coils along the direction of propagation. The linear Floquet bands are constructed for various inter-sublattice rotation patterns such as: different radii, different frequency, phase offset and quasi one-dimensional motion. Depending on the nature of the band structure, bulk spectral bands with nonzero Chern number are found to support topologically protected edge states which can move unidirectionally. In this case, the modes move scatter-free around defects due to underlying topological protection. Intriguing mode dynamics are found including bi-directional topological modes and bulk-edge leakage i.e. excitation of bulk modes at a defect for edge modes with dispersion frequencies nearby the bulk bands. Finally, certain nonlinear edge modes are also found to propagate unidirectionally and scatter-free around lattice defects.
Vortex soliton in a cold atomic gas via electromagnetically induced transparency (1903.03433v1)
Shun-fang Chen, Ya-Wei Guo, Qi Guo, Dong Zhao, Milivoj R. Belić, Yuan Zhao, Si-liu Xu
2019-03-08
We investigate the formation and propagation of vector vortex solitons (VS) and unipolar soliton (US) in a cold atomic gas with Bessel lattices (BLs). The system we consider is a cold, coherent atomic gas with a tripod or multipod level configuration. Dueing to the giant enhancement of Kerr nonlinearity contributed by electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT), a vector weak vortex soliton can be effectively formed with ultraslow propagating velocity. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the characteristics of 2D VS and US can be controlled and manipulated via adjusting BLs. The results predicted here may be used to design all-optical switching at very low light level.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
Asymptotics for the Sasa--Satsuma equation in terms of a modified Painlevé II transcendent (1903.04857v1)
Lin Huang, Jonatan Lenells
2019-03-12
We consider the initial-value problem for the Sasa-Satsuma equation on the line with decaying initial data. Using a Riemann-Hilbert formulation and steepest descent arguments, we compute the long-time asymptotics of the solution in the sector
,
constant. It turns out that the asymptotics can be expressed in terms of the solution of a modified Painlev'e II equation. Whereas the standard Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann-Hilbert problem, this modified Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann--Hilbert problem.
Boundary matrices for the higher spin six vertex model (1903.00274v2)
Vladimir V. Mangazeev, Xilin Lu
2019-03-01
In this paper we consider solutions to the reflection equation related to the higher spin stochastic six vertex model. The corresponding higher spin
-matrix is associated with the affine quantum algebra
. The explicit formulas for boundary
-matrices for spins
are well known. We derive difference equations for the generating function of matrix elements of the
-matrix for any spin
and solve them in terms of hypergeometric functions. As a result we derive the explicit formula for matrix elements of the
-matrix for arbitrary spin. In the lower- and upper- triangular cases, the
-matrix simplifies and reduces to simple products of
-Pochhammer symbols.
Search for CAC-integrable homogeneous quadratic triplets of quad equations and their classification by BT and Lax (1806.08511v2)
Jarmo Hietarinta
2018-06-22
We consider two-dimensional lattice equations defined on an elementary square of the Cartesian lattice and depending on the variables at the corners of the quadrilateral. For such equations the property often associated with integrability is that of "multidimensional consistency" (MDC): it should be possible to extend the equation from two to higher dimensions so that the embedded two-dimensional lattice equations are compatible. Usually compatibility is checked using "Consistency-Around-a-Cube" (CAC). In this context it is often assumed that the equations on the six sides of the cube are the same (up to lattice parameters), but this assumption was relaxed in the classification of Boll \cite{Boll2011}. We present here the results of a search and classification of homogeneous quadratic triplets of multidimensionally consistent lattice equations, allowing different equations on the three orthogonal planes (hence triplets) but using the same equation on parallel planes. No assumptions are made about symmetry or tetrahedron property. The results are then grouped by subset/limit properties, and analyzed by the effectiveness of their B"acklund transformations, or equivalently, by the quality of their Lax pair (fake or not).
The Construction of the mKdV Cyclic Symmetric 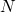 -soliton Solution by the Bäcklund Transformation (1805.09637v3)
-soliton Solution by the Bäcklund Transformation (1805.09637v3)
Masahito Hayashi, Kazuyasu Shigemoto, Takuya Tsukioka
2018-05-24
We study group theoretical structures of the mKdV equation. The Schwarzian type mKdV equation has the global M"{o}bius group symmetry. The Miura transformation makes a connection between the mKdV equation and the KdV equation. We find the special local M"{o}bius transformation on the mKdV one-soliton solution which can be regarded as the commutative KdV B"{a}cklund transformation can generate the mKdV cyclic symmetric
-soliton solution. In this algebraic construction to obtain multi-soliton solutions, we could observe the addition formula.
The Static Elliptic 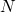 -soliton Solutions of the KdV Equation (1812.09685v2)
-soliton Solutions of the KdV Equation (1812.09685v2)
Masahito Hayashi, Kazuyasu Shigemoto, Takuya Tsukioka
2018-12-23
Regarding
-soliton solutions, the trigonometric type, the hyperbolic type, and the exponential type solutions are well studied. While for the elliptic type solution, we know only the one-soliton solution so far. Using the commutative B"{a}cklund transformation, we have succeeded in constructing the KdV static elliptic
-soliton solution, which means that we have constructed infinitely many solutions for the
-function type differential equation.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.