Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences 2|2019-03-18
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Localized Faraday patterns under heterogeneous parametric excitation (1702.02683v2)
Héctor Urra, Juan F. Marín, Milena Páez-Silva, Majid Taki, Saliya Coulibaly, Leonardo Gordillo, Mónica A. García-Ñustes
2017-02-09
Faraday waves are a classic example of a system in which an extended pattern emerges under spatially uniform forcing. Motivated by systems in which uniform excitation is not plausible, we study both experimentally and theoretically the effect of heterogeneous forcing on Faraday waves. Our experiments show that vibrations restricted to finite regions lead to the formation of localized subharmonic wave patterns and change the onset of the instability. The prototype model used for the theoretical calculations is the parametrically driven and damped nonlinear Schr"odinger equation, which is known to describe well Faraday-instability regimes. For an energy injection with a Gaussian spatial profile, we show that the evolution of the envelope of the wave pattern can be reduced to a Weber-equation eigenvalue problem. Our theoretical results provide very good predictions of our experimental observations provided that the decay length scale of the Gaussian profile is much larger than the pattern wavelength.
Unifying vectors and matrices of different dimensions in smooth generalized structures (1701.01281v2)
Vladimir García-Morales
2017-01-05
Physical theories address different numbers of degrees of freedom depending on the scale under consideration. In this work generalized mathematical structures (nonlinear
-embeddings) are constructed that encompass objects with different dimensionality as the continuous scale parameter
is varied. Based on this method, a new approach to compactification in unified physical theories (e.g. supergravity in 10 or 11-dimensional spacetimes) is pointed out. We also show how
-embeddings can be used to connect all cellular automata (CAs) to coupled map lattices (CMLs) and nonlinear partial differential equations, deriving a class of nonlinear diffusion equations. Finally, by means of nonlinear embeddings we introduce CA connections, a class of CMLs that connect any two arbitrary CAs in the limits
and
of the embedding. Applications to biophysics and fundamental physics are discussed.
Two-dimensional composite solitons in Bose-Einstein condensates with spatially confined spin-orbit coupling (1806.04868v4)
Yongyao Li, Xiliang Zhang, Rongxuan Zhong, Zhihuan Luo, Bin Liu, Chunqing Huang, Wei Pang, Boris A. Malomed
2018-06-13
It was recently found that the spin-orbit (SO) coupling can help to create stable matter-wave solitons in spinor Bose-Einstein condensates in the two-dimensional (2D) free space. Being induced by external laser illumination, the effective SO coupling can be applied too in a spatially confined area. Using numerical methods and the variational approximation (VA), we build families of 2D solitons of the semi-vortex (SV) and mixed-mode (MM) types, and explore their stability, assuming that the SO-coupling strength is confined in the radial direction as a Gaussian. The most essential result is identification, by means of the VA and numerical methods, of the minimum size of the spatial confinement for which the 2D system maintains stable solitons of the SV and MM types.
Harmonic Stability of Standing Water Waves (1903.05621v1)
Jon Wilkening
2019-03-13
A numerical method is developed to study the stability of standing water waves and other time-periodic solutions of the free-surface Euler equations using Floquet theory. A Fourier truncation of the monodromy operator is computed by solving the linearized Euler equations about the standing wave with initial conditions ranging over all Fourier modes up to a given wave number. The eigenvalues of the truncated monodromy operator are computed and ordered by the mean wave number of the corresponding eigenfunctions, which we introduce as a method of retaining only accurately computed Floquet multipliers. The mean wave number matches up with analytical results for the zero-amplitude standing wave and is helpful in identifying which Floquet multipliers collide and leave the unit circle to form unstable eigenmodes or rejoin the unit circle to regain stability. For standing waves in deep water, most waves with crest acceleration below
are found to be linearly stable to harmonic perturbations; however, we find several bubbles of instability at lower values of
that have not been reported previously in the literature. We also study the stability of several new or recently discovered time-periodic gravity-capillary or gravity waves in deep or shallow water, finding several examples of large-amplitude waves that are stable to harmonic perturbations and others that are not. A new method of matching the Floquet multipliers of two nearby standing waves by solving a linear assignment problem is also proposed to track individual eigenvalues via homotopy from the zero-amplitude state to large-amplitude standing waves.
Static structures of strained carbon chains:DFT-modeling vs classical modeling of the chain with Lennard-Jones potential (1903.05423v1)
George Chechin, Victoria Lapina
2019-03-13
We proved earlier that in the strained monoatomic chains with Lennard-Jones potential there can exist an equilibrium static bi-structure, which corresponds to N - 1 equal short interatomic bonds and one long bond with inversion in its center (N is the number of atoms of the chain). In the present work, we investigate with the aid of the density functional theory (DFT modeling) similar structures that can exist in the strained carbon chains. In contrast to the Lennard-Jones model, the bi-structures in this case are inhomogeneous (they have short bonds of different lengths) and appear abruptly when the strain exceeds a certain critical value
as a result of a hard bifurcation of the equilibrium state (an analogue of the first-order phase transition). Such a bifurcation is associated with two different parts of potential, in which the Lennard-Jones forces can be quite small (this is the vicinity of the potential minimum and the potential tail) and, therefore, the forces acting on the particle between the long and short bonds can be equal. Since practically all interatomic potentials possess such features, the above bifurcation is universal, i.e. it must occur for any monoatomic chain. We have studied in detail the properties of the above structures, in particular, the behavior of their parameters with increasing N. With the help of DFT-modeling, the electron density of the above structures near the bifurcation point is investigated.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
KP theory, plabic networks in the disk and rational degenerations of M--curves (1801.00208v2)
Simonetta Abenda, Petr G. Grinevich
2017-12-30
We complete the program of Ref. [3,5] of connecting totally non-negative Grassmannians to the reality problem in KP finite-gap theory via the assignment of real regular divisors on rational degenerations of M-curves for the class of real regular multi-line soliton solutions of KP II equation whose asymptotic behavior has been combinatorially characterized by Chakravarthy, Kodama and Williams. We use the plabic networks in the disk introduced by Postnikov to parametrize positroid cells in totally nonnegative Grassmannians. The boundary of the disk corresponds to the rational curve associated to the soliton data in the direct spectral problem, and the bicolored graph is the dual of a reducible curve G which is the rational degeneration of a regular M-curve whose genus g equals the number of faces of the network diminished by one. We assign systems of edge vectors to the planar bicolored networks. The system of relations satisfied by them has maximal rank and may be reformulated in the form of edge signatures.. We prove that the components of the edge vectors are rational in the edge weights with subtraction free denominators and provide their explicit expressions in terms of conservative and edge flows. The edge vectors rule the value of the KP wave function at the double points of G, whereas the signatures at the vertices rule the position of the divisor in the ovals. We prove that the divisor satisfies the conditions of Dubrovin-Natanzon for real finite-gap solutions: there is exactly one divisor point in each oval except for the one containing the essential singularity of the wave function. The divisor may be explicitly computed using the linear relations at the vertices of the network. We explain the role of moves and reductions in the transformation of both the curve and the divisor for given soliton data, and apply our construction to some examples.
Lens Generalisation of  -functions for the Elliptic Discrete Painlevé Equation (1810.12103v2)
-functions for the Elliptic Discrete Painlevé Equation (1810.12103v2)
Andrew P. Kels, Masahito Yamazaki
2018-10-29
We propose a new bilinear Hirota equation for
-functions associated with the
root lattice, that provides a "lens" generalisation of the
-functions for the elliptic discrete Painlev'e equation. Our equations are characterized by a positive integer
in addition to the usual elliptic parameters, and involve a mixture of continuous variables with additional discrete variables, the latter taking values on the
root lattice. We construct explicit
-invariant hypergeometric solutions of this bilinear Hirota equation, which are given in terms of elliptic hypergeometric sum/integrals.
Quantum Critical Dynamics of a Heisenberg-Ising Chain in a Longitudinal Field: Many-Body Strings versus Fractional Excitations (1903.05492v1)
Zhe Wang, M. Schmidt, A. Loidl, Jianda Wu, Haiyuan Zou, Wang Yang, Chao Dong, Y. Kohama, K. Kindo, D. I. Gorbunov, S. Niesen, O. Breunig, J. Engelmayer, T. Lorenz
2019-03-13
We report a high-resolution terahertz spectroscopic study of quantum spin dynamics in the antiferromagnetic Heisenberg-Ising spin-chain compound BaCo
V
O
as a function of temperature and longitudinal magnetic field. Confined spinon excitations are observed in an antiferromagnetic phase below
K. In a field-induced gapless phase above
T, we identify many-body string excitations as well as low-energy fractional psinon/antipsinon excitations by comparing to Bethe-Ansatz calculations. In the vicinity of
, the high-energy string excitations are found to be dynamically dominant over the fractional excitations.
Exact 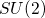 symmetry and
symmetry and  -pairing ground states in interacting fermion models with spin-orbit coupling (1901.06914v2)
-pairing ground states in interacting fermion models with spin-orbit coupling (1901.06914v2)
Kai Li
2019-01-21
We generalize the
-pairing theory in Hubbard models to the ones with spin-orbit coupling (SOC). Despite the broken
spin symmetry, the
pairing reveals an
pseudospin symmetry in our spin-orbit coupled Hubbard model. In particular, we find that our exact results can be applied to a variety of spin-orbit coupled systems, whose noninteracting limit can be a Dirac semimetal, a Weyl semimetal, a nodal-line semimetal, and a Chern insulator. We then focus on a Dirac-semimetal Hubbard model with additional interactions and establish the stability regions in parameter space where the
-pairing states as well as charge-density-wave states can be constructed as exact ground states. The basic idea of the exact solution is to make the Hamiltonian frustration-free in some parameter regions. Our work uncovers an exact
symmetry and establishes the exact superconducting ground states in spin-orbit coupled interacting systems, which may shed new light on the physics of strongly correlated systems with SOC.
Asymptotics for the Sasa--Satsuma equation in terms of a modified Painlevé II transcendent (1903.04857v1)
Lin Huang, Jonatan Lenells
2019-03-12
We consider the initial-value problem for the Sasa-Satsuma equation on the line with decaying initial data. Using a Riemann-Hilbert formulation and steepest descent arguments, we compute the long-time asymptotics of the solution in the sector
,
constant. It turns out that the asymptotics can be expressed in terms of the solution of a modified Painlev'e II equation. Whereas the standard Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann-Hilbert problem, this modified Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann--Hilbert problem.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.
Congratulations @complexcity! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!