Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences 2|2019-04-11
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Temporal dissipative solitons in time-delay feedback systems (1901.03524v2)
Serhiy Yanchuk, Stefan Ruschel, Jan Sieber, Matthias Wolfrum
2019-01-11
Localized states are a universal phenomenon observed in spatially distributed dissipative nonlinear systems. Known as dissipative solitons, auto-solitons, spot or pulse solutions, these states play an important role in data transmission using optical pulses, neural signal propagation, and other processes. While this phenomenon was thoroughly studied in spatially extended systems, temporally localized states are gaining attention only recently, driven primarily by applications from fiber or semiconductor lasers. Here we present a theory for temporal dissipative solitons (TDS) in systems with time-delayed feedback. In particular, we derive a system with an advanced argument, which determines the profile of the TDS. We also provide a complete classification of the spectrum of TDS into interface and pseudo-continuous spectrum. We illustrate our theory with two examples: a generic delayed phase oscillator, which is a reduced model for an injected laser with feedback, and the FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron with delayed feedback. Finally, we discuss possible destabilization mechanisms of TDS and show an example where the TDS delocalizes and its pseudo-continuous spectrum develops a modulational instability.
Dynamics of a class A nonlinear mirror mode-locked laser (1904.04127v1)
Andrei G. Vladimirov, Anton V. Kovalev, Evgeny A. Viktorov, Natalia Rebrova, Guillaume Huyet
2019-04-08
Using a delay differential equation model we study theoretically the dynamics of a unidirectional class-A ring laser with a nonlinear amplifying loop mirror. We perform linear stability analysis of the CW regimes in the large delay limit and demonstrate that these regimes can be destabilized via modulational and Turing-type instabilities, as well as by an instability leading to the appearance of square-waves. We investigate the formation of square-waves and mode-locked pulses in the system. We show that mode-locked pulses are asymmetric with exponential decay of the trailing edge in positive time and faster-than-exponential (super-exponential) decay of the leading edge in negative time. We discuss asymmetric interaction of these pulses leading to a formation of harmonic mode-locked regimes.
Subcritical transition to turbulence in wall-bounded flows: the case of plane Poiseuille flow (1904.03739v1)
Paul Manneville, Masaki Shimizu
2019-04-07
In wall-bounded flows, the laminar regime remain linearly stable up to large values of the Reynolds number while competing with nonlinear turbulent solutions issued from finite amplitude perturbations. The transition to turbulence of plane channel flow (plane Poiseuille flow) is more specifically considered via numerical simulations. Previous conflicting observations are reconciled by noting that the two-dimensional directed percolation scenario expected for the decay of turbulence may be interrupted by a symmetry-breaking bifurcation favoring localized turbulent bands. At the other end of the transitional range, a preliminary study suggests that the laminar-turbulent pattern leaves room to a featureless regime beyond a well defined threshold to be determined with precision.
Evolution of wave pulses in fully nonlinear shallow-water theory (1903.01667v2)
S. K. Ivanov, A. M. Kamchatnov
2019-03-05
We consider evolution of wave pulses with formation of dispersive shock waves in framework of fully nonlinear shallow-water equations. Situations of initial elevations or initial dips on the water surface are treated and motion of the dispersive shock edges is studied within the Whitham theory of modulations. Simple analytical formulas are obtained for asymptotic stage of evolution of initially localized pulses. Analytical results are confirmed by exact numerical solutions of the fully nonlinear shallow-water equations.
Travelling Waves in Monostable and Bistable Stochastic Partial Differential Equations (1904.03037v1)
Christian Kuehn
2019-04-05
In this review, we provide a concise summary of several important mathematical results for stochastic travelling waves generated by monostable and bistable reaction-diffusion stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs). In particular, this survey is intended for readers new to the topic but who have some knowledge in any sub-field of differential equations. The aim is to bridge different backgrounds and to identify the most important common principles and techniques currently applied to the analysis of stochastic travelling wave problems. Monostable and bistable reaction terms are found in prototypical dissipative travelling wave problems, which have already guided the deterministic theory. Hence,we expect that these terms are also crucial in the stochastic setting to understand effects and to develop techniques. The survey also provides an outlook, suggests some open problems, and points out connections to results in physics as well as to other active research directions in SPDEs.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
Rogue breather modes: Topological sectors, and the `belt-trick', in a one-dimensional ferromagnetic spin chain (1807.01867v2)
O. R. Rahul, S. Murugesh
2018-07-05
We present explicit solutions for breather soliton modes of excitation in the one-dimensional Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain. We identify a characteristic geometrical feature of these breather modes wherein a helicoidal configuration of spins is continuously transformed to one which differs from the initial helicoid by a total twist of
2'. This is a curious manoeuvre popularly known as thebelt trick', an illustration of the simple connectedness of thegroup manifold, and its rotation period
. We show that this effectively splits the configuration space of the ferromagnetic chain in one-dimension into two topological sectors, distinguished by their total twist -- either
0', or1'. Further, the energy lower bound of the two sectors is separated by a finite gap varying inversely with the size of the lattice.
Matrix product solution to the reflection equation associated with a coideal subalgebra of 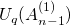 (1812.03767v5)
(1812.03767v5)
Atsuo Kuniba, Masato Okado, Akihito Yoneyama
2018-12-10
We present a new solution to the reflection equation associated with a coideal subalgebra of
in the symmetric tensor representations and their dual. Elements of the
matrix are expressed by a matrix product formula involving terminating
-hypergeometric series in
-boson generators. At
, our result reproduces a known set-theoretical solution to the reflection equation connected to the crystal base theory.
N=2 supersymmetric extensions of relativistic Toda lattice (1904.03996v1)
Anton Galajinsky
2019-04-08
N=2 supersymmetric extensions of both the periodic and non-periodic relativistic Toda lattices are built within the framework of the Hamiltonian formalism. A geodesic description in terms of a non-metric connection is discussed.
Rationally weighted Hurwitz numbers, Meijer  -functions and matrix integrals (1904.03770v1)
-functions and matrix integrals (1904.03770v1)
M. Bertola, J. Harnad
2019-04-07
The quantum spectral curve equation associated to KP
-functions of hypergeometric type serving as generating functions for rationally weighted Hurwitz numbers is solved by generalized hypergeometric series. The basis elements spanning the corresponding Sato Grassmannian element are shown to be Meijer
-functions, or their asymptotic series. Using their Mellin integral representation, the
-function, evaluated at the trace invariants of an externally coupled matrix, is expressed as a matrix integral.
New developments of the methodology of the Modified method of simplest equation with application (1904.03481v1)
Nikolay K. Vitanov
2019-04-06
We discuss an extension of the modified method of simplest equation for obtaining exact analytical solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. The extension includes the possibility for use of: (i) more than one simplest equation; (ii) relationship that contains as particular cases the relationship used by Hirota \cite{hirota} and the relationship used in the previous version of the methodology; (iii) transformation of the solution that contains as particular case the possibility of use of the Painleve expansion; (iv) more than one balance equation. The discussed version of the methodology allows: obtaining multi-soliton solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations if such solutions do exist and obtaining particular solutions of nonintegrable nonlinear partial differential equations. Examples for the application of the methodology are discussed.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.
You got a 54.55% upvote from @brupvoter courtesy of @complexcity!