Understanding Thai Kinship Terminology, Family Structure, Marriage Practices and Culture
Hello It is another day for me to write new article. This time around i will be presenting my research in my Sociology class.
IntroductionThis article aims to presents and evaluates on the different Thai Kinship System, Family structure as well Marriage Practices and its culture. It geared towards understanding Kinship Terminology in Thailand- a Southeast Asian country. It's known for tropical beaches, opulent royal palaces, ancient ruins and ornate temples displaying figures of Buddha.
I address a long hypothesized relationship between the proximity of individuals' dwelling units and their kinship association. Better understanding this relationship is important because of its implications for contact and association among members of a society. This paper is done through purely research of information in the internet as our research approach.
I.Thai Kinship Terminology
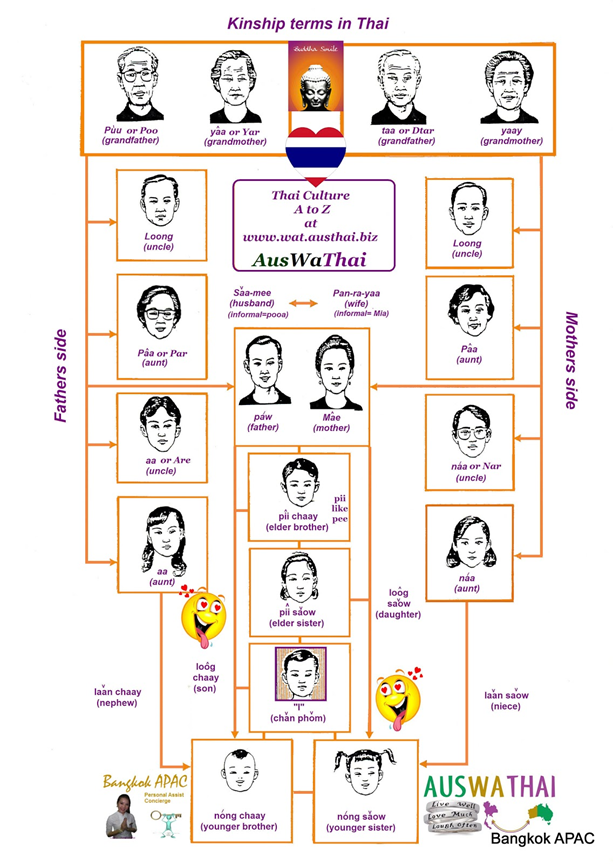
image source
Kinship, system of social organization based on real or putative family ties. The modern study of kinship can be traced back to mid-19th-century interests in comparative legal institutions and philology. In the late 19th century, however, the cross-cultural comparison of kinship institutions became the particular province of anthropology. Thai family usually live in an extended family.
The Kinship system
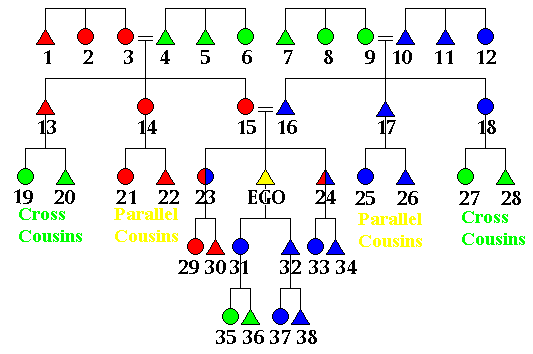
image source
Extends to include newcomers and strangers. A stranger who arrives in the village usually uses kinship terms when he approaches the villagers for help. The use of the terms automatically makes them a relative of all the which takes care.
"Khun"
When strangers meet, the title "khun" will be adopted until a satisfactory relationship develops, at which time kinship terms will be used instead. Age or seniority determines the choice of kinship term. It is interesting to note; however, that kinship terms on the maternal side are more preferable, perhaps because people feel closer to their mother than their father. Once kinship terms are adopted, both parties know that the relationship has reached a satisfactory level. To keep a distance is to ignore , explicitly or implicitly, the other party's attempt to use kinship terms and to maintain the use of the title "khun".
"Teachers"
An extension of the use of kinship terms is the word for "pupil, student, trainee, apprentice and disciple", which is "luuk sit" (learning child). A teacher has the same status and obligation as a parent. This may be a vestige of a tradition in those days when schools were not in existence and those who sought education or training had to live in the home of the teachers. No tuition was asked for but the learners had to help around the house as if they had been one of the younger "yaat".
"Yaat"
To refer to anybody who is, closely as well as remotely, related to them by blood, by marriage or just by association. The closest English equivalent is perhaps the word "relatives." When a newcomer joined the village, they became a new "yaat." Even visitors could be granted a "yaat" status if they wished to be assimilated into the group.
Thai family Structure
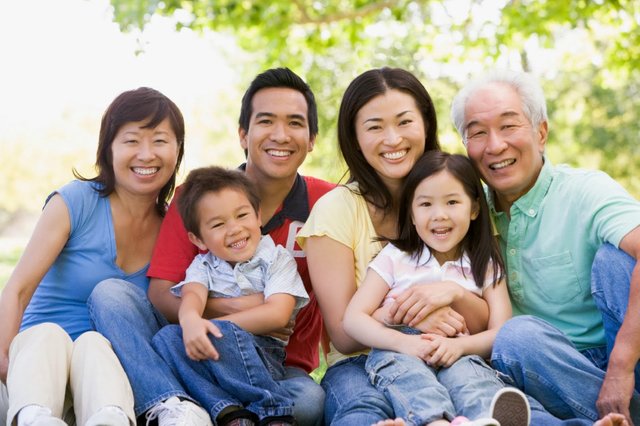

image source
Extended Family. In Thailand there is a much stronger company in the family compared to our western culture. Often live several generations under one roof. The parent’s house for example is bequeathed to the youngest daughter, she together with her husband in return accommodate her parents when they are older. The oldest man of a Thai family is the patriarch, the other family members have to act in accordance with his decisions.
In Bangkok every days live adapts more and more to the western developed nations but in the country the old traditions continue to exist almost unchanged. As a tradition a Thai man has to meet the whole family of the bride and get the total consent before he can get engaged. Only then he can propose to her parents for the hand of their daughter. Do both families agree the date for the wedding is fixed. But the date for the wedding is delayed until the groom has finished his apprenticeship. The bride’s parents get bride-money from the groom, a kind of compensation for the upbringing consisting of natural produce or money. Many a time this is returned to the bridal couple on the wedding day. In the country the newly married often stay with their parents until they have the first child.
Marriage Practices
Ideas About Love and Romance in Thai Culture
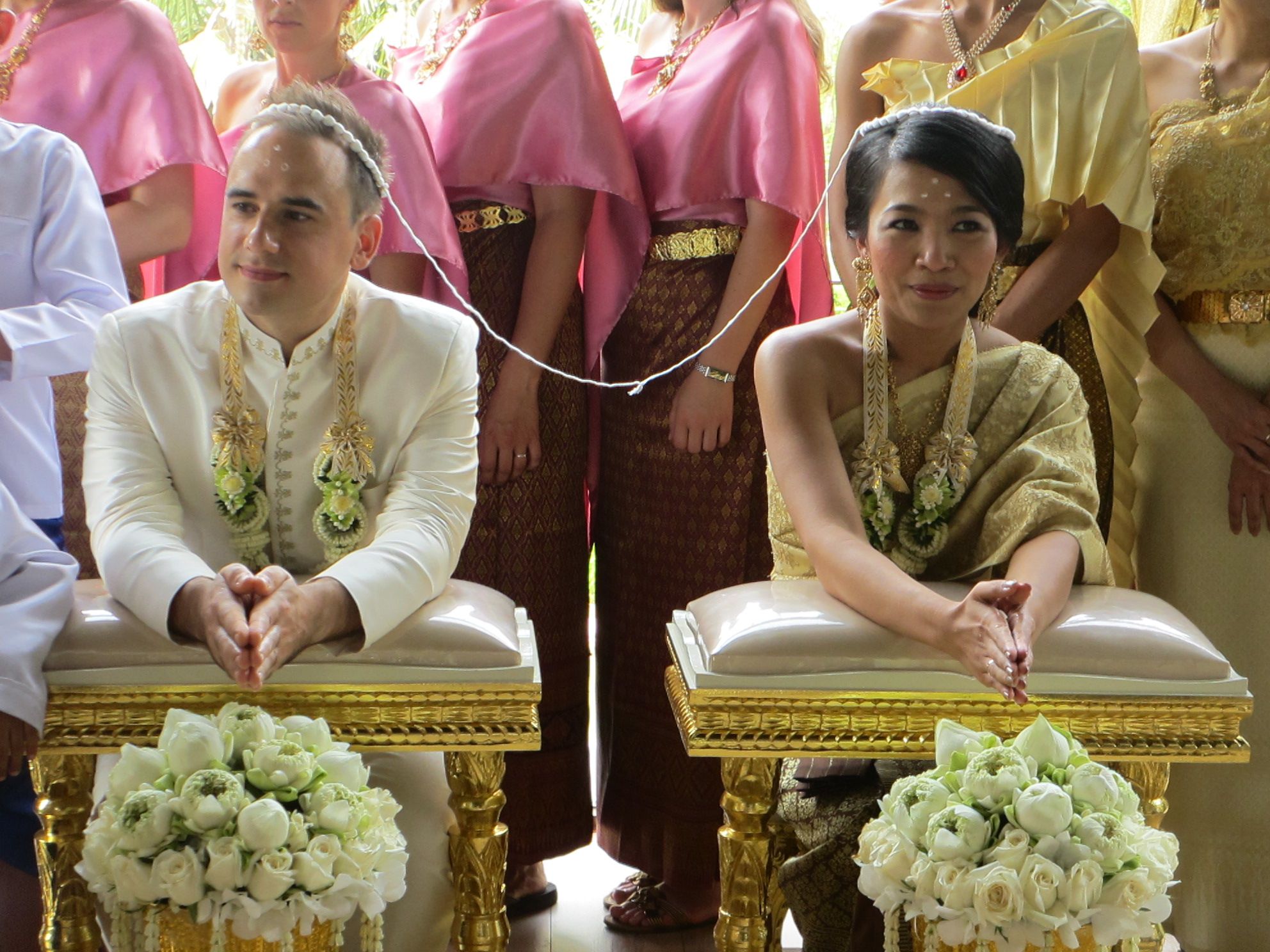

image source
According to the Encyclopedia of Sexuality: Thailand: “ Most cultures glorify and idolize romance between men and women, and Thai people are no exception. Themes of quests for eternal love and the consequences of passion - ecstasy, aspirations, heartbreaks, jealously, elopements, and deaths - abound in the Thai folklore, literature, and music. Borrowed from the karma concept, people explain an unexpected, overwhelming infatuation in metaphysical terms: They were meant for each other because of destiny (bu-phay vassana) or they had made merit together in previous lives. [Source: Encyclopedia of Sexuality: Thailand (Muang Thai) by Kittiwut Jod Taywaditep, M.D., M.A., Eli Coleman, Ph.D. and Pacharin Dumronggittigule, M.Sc., late 1990s;
According to the Encyclopedia of Sexuality: Thailand: “ Most cultures glorify and idolize romance between men and women, and Thai people are no exception. Themes of quests for eternal love and the consequences of passion - ecstasy, aspirations, heartbreaks, jealously, elopements, and deaths - abound in the Thai folklore, literature, and music. Borrowed from the karma concept, people explain an unexpected, overwhelming infatuation in metaphysical terms: They were meant for each other because of destiny (bu-phay vassana) or they had made merit together in previous lives. [Source: Encyclopedia of Sexuality: Thailand (Muang Thai) by Kittiwut Jod Taywaditep, M.D., M.A., Eli Coleman, Ph.D. and Pacharin Dumronggittigule, M.Sc., late 1990s;
Traditional Thai Wedding
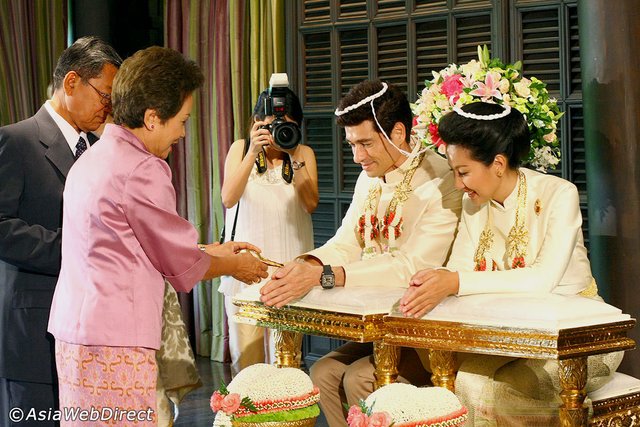

image source
- Choosing the Date
- Wedding Invitations
- Engagement Ceremony
- Paying Homage to the Bride’s Ancestors
- Making Merit
- Buddhist Blessing and Merit Making
- Khan Maak Procession
- Doors Ceremony/Gate Ceremony
- Sai Monkhon
- Shell Ceremony – ‘Rod Nam Sang’
- White Thread Ceremony – ‘Phiti Bai Sri Su Kwan’
- Sai Sin
- Evening Party
- Preparing Bridal Bed
- Sinsod
Buddhists have never been big on marriage and wedding ceremonies. In the past a young man who wanted to marry a young women moved in with her family and worked for her family for a period of around two years. If all went well he was given permission to marry the young woman. Even today, in many cases, only wealthy and middle class families have weddings. Other couples simply live together until they are considered married. Honeymoons habe traditionally not been a custom in Thailand.
During the two-year “bride service,” the young man usually lived in a separate dwelling and attended a local monastery and served there as a monk for at least a few months. When his monk service was finished the man was regarded as morally prepared for marriage. Often, after that the young man began building a house for himself and his bride that would be furnished by his father-in-law.
Thai Culture

photo source
Thailand is a hierarchical society in which thanks to the believe in the Karma the social status of the people is untouched. A person who has a high social position has acquired this in its previous lives. The important one has to look after his subordinates (for example workers or employees) and his less moneyed relatives. In return he receives respect, obedience, thankfulness and loyalty. The social position and the age is decisive for the behaviour of the Thais among one another. Generally the oldest or socially highest ranking person receives the most respect. Many details in behaving among one another depends on the social status and /or the age of the people attending. This is reflected in the family, the circle of friends and in the working life. It also explains the believe in authority, favoritism and the partly undemocratic structures in the Thai society. Thus every Thai makes an effort to knot an big harmonic net of relations. For example the important are not over bothered as by this a relation could be destroyed which one day could become important.

photo source
Much of Thailand’s culture comes from the ethnic Thai people. One of the most important influences on Thai culture has been Buddhism. Many of the traditions and beliefs of the people in Thailand stem directly from Buddhist principles. Hinduism has also made important contributions to Thai culture, and the close links between Thailand and India can be seen in art, literature, and in many Thai customs. The cultures of nearby Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, and China have also played an important role in forming the traditions of Thailand, as have indigenous belief systems such as Animism.
Values

photo source
Thai culture is deeply influenced by religion. With around 95% of the country being Theraveda Buddhist, the belief system and values of Buddhism play a huge role in day-to-day life. Throughout the country, the most important values that Thai people hold to are respect, self-control, and a non-confrontational attitude. Losing face by showing anger or by telling a lie is a source of great shame for Thai people.
In general, displays of emotion in public are viewed in a very negative light. No matter how frustrated or upset a person might feel, he or she will always strive to maintain a positive and friendly attitude, a sense of humor, and a smile.

photo source
Respect for elders and for those in higher social positions is also important. Hierarchies of social status characterize nearly every interaction. Children are expected to respect their parents and teachers. The young must show deference to the elderly. Those with highly prestigious positions in society, such as doctors, important public figures, and monks are almost revered.
Family is central to Thai life. Although many newly-married couples will set up their own households, it is not uncommon for extended family to live with them. Often, grandparents, cousins, aunts, and uncles will all live in the same household and help to raise children and provide for the family. Children are expected to show great respect for their parents, and they maintain close ties, even well into adulthood.
Thank you fro reading! i hope you have learned and see the glimpse of another culture <3
-Zam
Bibliography
Cavanagh,R.2016. Traditional Thai Wedding.Retrieved October 26,2017 from http://learnthaiwithmod.com/2013/09/thai-tradition-wedding-ceremony/
Thai Visa. April 27, 2016.Marriage in Thailand, Thai customes and Rituals.Retrieved November 3, 2017 fromhttp://www.th4u.com/thai_marriage.htm
Hays,Jeffrey.2013. Marriage,Love, Wdding in Thailand:Sinsot, Nine Monks, Dating and Divorce.Retreived October 28,2017 from http://factsanddetails.com/southeast-asia/Thailand/sub5_8c/entry-3221.html
Becker Lexikon, Martin Luttherjohann.2002. Thailand’s Society, Family Structures, the Wai - Thailand's traditional Reception, Leisure Time and Thailand’s Cuisine. Retrieved October 4, 2017 Fromhttp://www.kochangvr.com/thailandssociety/familystructures.htm
Rabibhadana A.1984. Kinship, marriage and the Thai social system.Retrieved October 09, 2017 from http://www.popline.org/node/416854
Aus Wa Thai Community. Kinship In Thailand. Retrieved October 06, 2017 fromhttp://www.wat.austhai.biz/Home/thai-culture/kinship-terms
Tomasa.2010. Thailand: Kinship System. Retrieved Ocober 30, 2017 from https://quizlet.com/3118084/thailand-kinship-system-flash-cards/

You have been upvoted by the @sndbox-alpha! Our curation team is currently formed by @jeffbernst, @bitrocker2020, @jrswab & @teachblogger . We are seeking posts of the highest quality and we deem your endeavour as one of them. If you want to get to know more, feel free to check our blog.