Heat Exchangers - The "Temperature Manager" of Our Machines
Just some days ago, I saw @gentleshaid's post about a faulty thermostat in his car which led to overheating of his car while driving. His Report was near a perfect one showing how intelligent and adapting he is even without having an engineering background.
The major function of the thermostat is to regulate the flow of coolant to the radiator while the car is trying to attain the operating temperature for the car to start working. So, it helps to regulate the heat transfer in the system by cutting out the working of some components making up the cooling system while the car tries to attain this temperature.
Basically, the radiator is an example of a heat exchanger which helps to cool the automotive engine by transferring the hot fluid flowing in the radiator tubes to the air flowing in the fins (or simply thin plates) attached closely to the tubes.
The radiator hence help to facilitate the exchange of heat between the two fluids (hot water and air) in the system and also help regulate the heat transfer in the engine. The thermostat functions as a sensor of temperature differences in the engine and thus help trigger the heat exchange function of the radiator and other cooling devices.
The major term (or device) playing the key role in the whole story is the "Heat Exchanger" which is what I'd be discussing about today. The concept of heat exchanger involves the transfer of heat from one fluid to another either to cool or heat up a system. Its design and operation can be suited to many fields of application which makes it an important industrial equipment.
So, let's see what it holds..Stay with me
Before I dive into the depth of Heat Exchanger operation and types, I'll first like to give a proper definition of Heat exchanger and why we need it.

So, What are Heat Exchangers?
Heat Exchangers are devices that are used to transfer heat between two fluid existing at different temperatures. In much simpler words, heat exchangers helps to facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids existing at different temperature while keeping them from mixing or coming into contact.
It is a device that allows for heat exchange between mediums existing at different temperatures. These mediums usually consist of two fluids which flow close to each other having a separating wall, usually metals of good heat transfer properties, exisiting between these fluids to avoid mixing or coming in direct contact. They differ from from mixing chambers as they ensure these fluids doesn't come in contact while this heat exchange function is carried out.
The heat transfer in a heat exchanger involves both convection - the heat transfer between fluids and Conduction - the heat transfer between a solid and a fluid. Covection is acheived when the two fluid exchange heat while conduction is experienced between the separating wall conveying the fluids (usually a metal) and the fluid passing through it.

Why do we need these Heat Exchangers?
The concept of Heat exchange is a very important one in flow process industries and finds application in many areas around us. Basically, almost every industry will at a point need a sort of heat regulation in its operation or processes. It could be in form of cooling or heating and this brings the heat exchangers into play.
The Heat exchangers can be used as a component of a cooling system and as well serve the purpose of heating up an element. Many industrial operations tends to involve heat dissipation from machines and other processes being carried out and needs a system to help regulate this heat, either by taking it away or introducing cooling means to neutralize the heat generated.
The Heat exchangers with its variety of design and methods of operation can help facilitate this temperature regulation function. It is an important equipment that has widespread use in different areas such as petroleum refineries, in sewage treatment, power generation, automotive applications, chemical processing, electronics cooling, and even in the air-conditioning and refrigeration.
The design can be suited to the field of application and condition of operation hence why there exists different classification of Heat Exchanger.

Classifications of Heat Exchangers?
A Simple heat exchanger is made of two concentric tubes of different diameters. The smaller tube carries one of the fluids while the other fluid flows through the space between the two tubes - the annular space. The heat is thus exchanged as the fluid in the annular space run over that in the smaller tube through conduction and convection.
As earlier noted, Heat Exchanger is a widely applied flow device. Different applications require different design and configuration of the heat transfer equipment thus why its types fall under different classifications which include; Flow Arrangement, Type of Construction, Heat Exchange Process, and Physical State of Fluid.
The major basis of classification of Heat Exchanger is upon the type of flow arrangement of the exchange tubes and are of three types namely;
- Parallel Flow Heat Exchangers
- Counter Flow Heat Exchangers
- Cross Flow Heat Exchangers
Parallel Flow Heat Exchanger (by @mrbreeziewrites)
It is usually referred to as a surface heat exchanger because of the separating wall and requires a large surface area for heat transfer. The latter makes it is less used in industrial applications. Examples of parallel flow heat exchanger include oil heaters, oil coolers, and water heaters.
Counter Flow Heat Exchanger (by @mrbreeziewrites)
The temperature difference in this type of flow arangement remains more or less constant as the fluids move in opposite direction. It gives a maximum heat transfer per surface area and this makes it a well-used type of flow arrangement in heating or cooling of fluids.
Cross Flow Heat Exchanger (by @mrbreeziewrites)
This kind of flow arrangement is a common and involves arrangement of fins closely to some tube bundles. The tubes usually carry the fluid to be cooled or heat up while the other fluid flow in the fin across the tube. This is the type of fluid arrangement in car radiators and the cooling units of a refrigerator.
Another major basis for classifying Hest Exchanger is the type of construction and arrangement of the tubes. The types of Heat Exchangers under this classification are the:
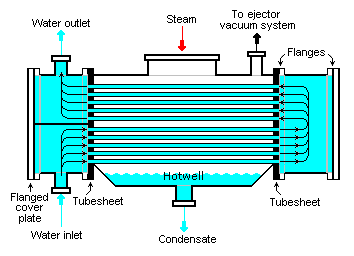
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger from Wikimedia Commons - Public Domain
The tubes can be plain or longitudinally tubes carrying the fluid to be heated or cooled while the other fluid is allowed to flow freely inside the shell over the tubes thus exchanging heat through convection with the fluid in the tube.
The Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger is mostly used for high pressure and high-temperature application for their robust shape. This property, however, limits their use in aircraft and automobiles as they are considered too large and of big weight. Typically, they usually have their ends connected to plenums - also called water boxes, through the holes in the tube sheets and the tube stack (or bundle) are usually bent in a U-shape.
In their design, a lot of design parameters needs be considered to achieve a suitable and functioning equipment. Some of the major ones include the tube diameter, length, thickness, corrugation, pitch and the Baffle design which are used to direct the flow through the tube. and prevent them from sagging.
The Shell and tube heat exchangers are by far the most used in industries for their robust size and ruggedness. They are able to work in extreme conditions and can be assembled with different types of materials like brass and copper.
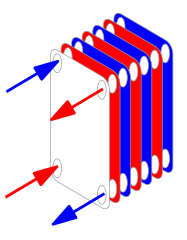
Plate Heat Exchanger from WikimediaCommons - CC by SA 3.0 (Authored by R. Castelnuovo and modified by Krzysztof Zajączkowski)
The flow passages are placed at the edges of the plates and the hot and cold fluids are made to flow in alternate passages thus allowing each cold stream to be surrounded by two streams of hot fluid. The flow arrangement ensures an effective heat transfer.
The stacked plates are more effective than the shell and tube types in some given space for it has a lower volume and cost. Its ability to serve for low temperature and low-pressure fluids unlike high-pressure fluids of the shell and tube design makes it more applicable to more simple devices. It is usually used in HVAC applications and in a closed loop system like the refrigerators.
On the basis of nature of heat exchange process, the Heat exchangers can be classified as:
The direct contact heat exchangers, also called open heat exchangers, are ones in which there is direct contact between the fluids in the process of heat exchange. This heat exchangers are employed in conditions where the direct mixing of the fluids are harmless or desirable. Common examples of their application is seen in Jet Condensers, Feed Heaters, and Cooling Towers.
The Indirect Heat exchangers, on the other hand, are characterized by the presence of a separating wall between the fluids while the heat exchange is being carried out. This class of heat exchanger are of two types;
The Regenerators are the indirect contact type of Heat Exchangers whereby the fluids i.e the hot and cold fluids passes alternately through a space containing some solid particles that provides a sink and a source for heat flow. Some regenerators operate periodically whereby the solid particles hold the hot fluid and later deliver it to the cold fluid when needed while some regenerators work continously by allowing the hot fluid rotate round the cold fluid via some passages.
A common example of regenerators are the Internal Combustion Engines, Gas Turbine, and Furnaces (Air heater of the blast furnace and glass melting furnaces)
The Recuperators on the other hand are indirect contact heat exchangers whereby the heat exchanging fluids are on either side of a dividing wall. The dividing wall in this case is usually in form of a pipe or tube. They are usually employed when the fluids exchanging heat must not mix and the flow is usually a steady type. They are suitable for stationary plants and are the type existing in Radiators, Superheaters, Milk Chillers, and Oil Coolers.
On the basis of Physical State of fluid during exchange, the heat exchangers can be classified as Evaporators and Condensers.
In Condensers, the condensing fluid (the hot fluid) maintains a constant temperature during the heat exchange process while the cold fluid's temperature increases gradually as it moves from the inlet to the outlet. In Evaporators, the hot fluid loses its temperature from the inlet to outlet while the boiling fluid i.e. the cold fluid, remain at a constant temperature.

Selection of Heat Exchangers?
The selection of Heat Exchangers can be daunting to engineers as it depends on several factors which are mostly interrelated. Favoring one over the other could lead to a lag in another. But, the field of application and the type of heat exchange desired ultimately decides which factor is the more important than another. In the selection of a Heat Exchanger, the following factors play a major role:
- Heat Transfer Rate
- Cost
- Pumping Power
- Size and Weight
- Type
- Material
The most important feature of a Heat exchanger is its Heat Transfer rate. It actually defines the function of a Heat exchanger and should be the first thing to consider when selecting a heat exchanger for a particular application. A Heat Exchanger must be capable of transferring heat a specified rate enough to achieve the desired temperature change in the fluids exchanging heat. Without this standard feature, a heat exchanger is considered useless.
The Cost is the second big factor that comes into the engineer's mind when selecting a heat exchanger. As much as we want a good machine, we must also look at our pockets so as to ensure that we choose the equipment relative to the cost and efficiency. More than the initial cost, we must look at the operational and maintenance cost before selecting the equipment so as to balance the whole selection process and future costs.
The Pumping Power of a Heat Exchanger is one of the factors that determine its cost of operation. The operating cost of a Heat Exchanger is expressed as the product of the pumping power of the heat exchanger and the operating hour of the equipment. So, a machine with optimal pumping power in its area of application should be considered when selecting a heat exchanger.
As noted while discussing the Shell and Tube heat exchanger, size and weight of the heat exchanger determines where it would find the application and must be one of the leading factors in heat exchanger selection. The size and weight of the heat exchanger disqualify it from some particular application. Engineers during selection thus must pay attention to the equipment size and weight.
The type of heat exchanger is also a significant factor that must be considered when choosing a heat exchanger. The type of fluid, size and weight, and phase changes possessed by the heat exchanger determines its application and suitability in some areas. For instance, a plate heat exchanger is best for cooling a liquid by another liquid.
The Material of the heat exchanger also determines where and how a heat exchanger can be used. When selecting a heat exchanger, the material with which it is made determines to great extent its application. Especially where temperature is very harsh, materials that can withstand such conditions must be chosen for such area. A corrosive environment also plays a major role in the need for material consideration for heat exchanger selection as it could prove costly if it is not catered for during the initial selection stage.

Common examples of Heat Exchangers application
The heat exchangers as we might have noted are widespread in terms of application. But as complex as the name might look, Heat exchangers are so basic in design and appearance. In many machines around us, there exists a heat exchanger structure that we might not know of.

Condenser of a Refrigerator from Wikimedia Commons - CC by SA 3.0 (Authored by Juan de Vojníkov)
Another common one is the Automotive Radiator that I've been mentioning. The fin and tube equipment usually in the front of our cars is an example of a heat exchanger that help regulate the heat transfer in the engine. The radiator cools the hot fluid from the engine running through the radiator tubes by means of air running across the tubes through the fins.
Milk Chillers on pasteurising plants, condensers and boilers in Steam plant, Air preheaters and air-conditioner's condensing and evaporating units are also common examples of equipments using the mechanism of heat exchangers to deliver their functions.

Do you know that Heat Exchangers also exist in our Body?
Well, heat exchanger aren't so complex as you think. Just think of any system where heat is exchange and you will see the principle of Heat exchanger playing a role...
So, what if I told you that you NOSE is a heat Exchanger? Yes, your nose is a Heat Exchanger!
Ok, let's look at it together. How does the nose operates? The air inhaled is usually quite hotter compared to what we exhale. The nose basically help warm the air being inhaled while it cools that that we exhale. We can observe this by comparing the coldness of the air we breathe out and that from the mouth. We'll notice that the one from the nose is quite cooler than that from the mouth.
Also, there exist a mesh of vein surrounding the arteries to the testes called the Pampiniform Plexus that cools the blood going to the testes while it warms that leaving the testes.
Another place where heat exchanger exist is in Birds, fishes and marine mammals. Counter flow heat exchange is said to naturally occur in these animals with the arteries close to skin carrying warm blood usually intertwine with those carrying cold blood. Wading Birds also use this heat exchange process to reduce heat loss from their body by dipping their legs inside water.

Conclusion
The notion of Heat Exchangers is a very important and widely existing in many aspects of our life. The process of heat transfer will always pop up in some part of our daily activities as there is always changes in temperature across many places we find ourselves.
A simple Heat exchanger basically help exchange of Heat between fluids existing at different temperature by providing a means of exchanger or a sort of separation between these fluids, hence, aiding heat transfer.
Together we have seen different classifications and types of heat exchangers available to us for use. The feature each heat exchanger possesses determines its field of application and plays a big role in its selection for the particular applications.
Heat exchangers are quite essential and helps a lot in flow process industries to facilitate heat regulation and thus operating conditions of machines and environments.
I appreciate your time here. Thanks for Reading.

References
- R. K. Rajput "Textbook of Heat and Mass Transfer in SI Units". Revised Edition
- Y. A. Cengel "Textbook of Heat Transfer". 2nd Edition
- J. P. Holman "Textbook of Heat Transfer". 10th Edition
- Codecogs | Types of Heat Exchangers
- Setxind | How the Heat exchanher works
- Wikipedia | Heat Exchangers

If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details.


Heat exchangers find a lot of industrial applications. You will always find them in one form or the other in any production industry. I particularly have encountered many shell and tube heat exchangers in my training days at Egbin Power plc.
The boiler, condenser, and regenerators (drain coolers, feed water heaters etc.) are all types of shell and tube heat exchanger. They handle enormous amounts of pressure and temperature and any breakdown of one is a breakdown to a whole generating unit.
Nice input sir!
Oh, you're well exposed. That's awesome.
They are quite dynamic and widespread in use indeed.
Thanks for the additional information. I appreciate your time here.
My pleasure.
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! @wafrica is now following you! ALWAYs follow @wafrica and use the wafrica tag!
Nice post.
You've proven to be a good writer always. I really enjoyed the Article on Heat Exchangers. Keep it up sir.
Thanks for the kind words. I appreciate your time here.
A comprehensive one here on heat exchangers. It exists in many aspect of Life.. Thanks for impacting this. Kudos!
Thanks for coming around too.
I remember writing something on heat exchangers few weeks ago.. The heat exchangers are wonderful especially with their working principle.
Yes, they are. Thanks for dropping by!
You are welcome
I sure could use one of these heat exchangers right now, I'm so cold.
HEs are life savers, it's nice to have learnt more about them from you.
Keep writing , I will keep learning.
Lol, you need a space heater.
Glad I could impart. Thanks for stopping by. You're appreciated.
You are most welcome.
The knowledge of heat e xcahngers would make us understand how cooling systems work..
Welldone on this piece
Exactly. Thanks for dropping by.
Well articulated! The concept exists in almost anything that requires heating, combustion or cooling. The same arrangement used in cars (radiators) can also be found in large generating plants. Those fins (thin pipes) increase the contact area for the other fluid (usually air) to take away the heat as fast as possible before the cooled water is returned to the engine
Wow! I appreciate your additional contributions..You said it well, the fins allow for more contact area hence improving the effective heat coefficient.
Thanks for dropping by...I appreciate your time here.
you welcome
💪
Having read @gentleshaid’s post and now reading yours. I’ll say I’ve learned a lot already.
Good work man. You have done well yet again
Glad I could impart. I appreciate your time here buddy..You're an authority yourself
Thanks for dropping by
This is a great and well detailed reaction to @gentleshaid's post. Your vast knowledge and enormous contribution can never be overlooked. Keep it up man.
I'm flattered hearing this from a boss...I appreciate your time here.
Thanks for dropping by
It's my pleasure!