Anesthesia in Orthopedic Surgery
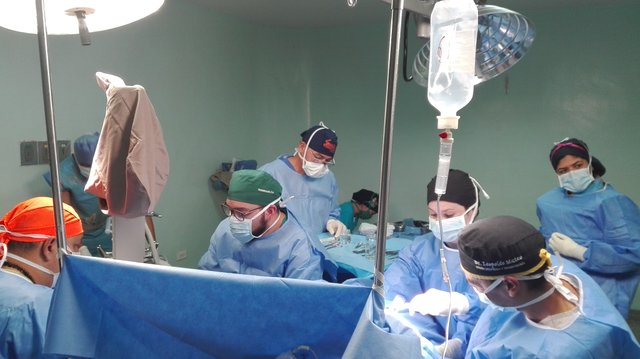
Principles
Anesthesia is a procedure in which we prevent the perception and harmful effects of surgery, a medical procedure, or a painful or uncomfortable exploration. There are different ways to prevent the patient from perceiving the procedure to be performed and, depending on it, as well as the individual, one type of anesthesia or another will be administered, being able to be topical, local, regional or general, depending on whether it affects a small part of the body or the whole body. Also, there are different types of anesthesia depending on whether it is necessary to sleep or not to the patient.
For example, if the patient is nervous or if a minor intervention is required, superficial sedation may be used. Deep sedation will be performed when it is necessary for the patient to be asleep, for example, when the type of procedure requires the patient to be in bed. After this sedation, a powerful stimulus will be necessary to awaken the patient.
General anaesthesia is used to block the consciousness and control the cardiac and respiratory functions and paralyse the muscles, as well as the neurovegetative system that controls tension, blood glucose, etc. It is used for major surgeries.

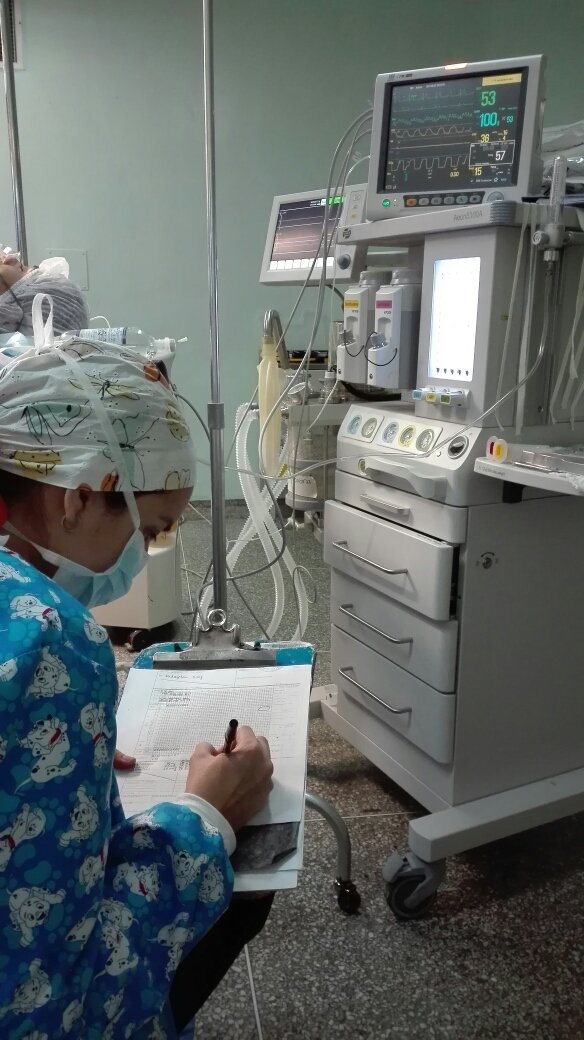
How does anesthesia work?
Anesthesia basically intervenes in the function of a type of neuron (those responsible for consciousness, perception of pain or movement) both in the brain and in the peripheral nerves, decreasing or temporarily cancelling their functions.
It is a safe procedure administered by highly qualified professionals so it is not common that there are complications. The problems can be caused by administering less and the patient suffers while undergoing surgery, or more and that the recovery takes longer or needs complementary support instruments.
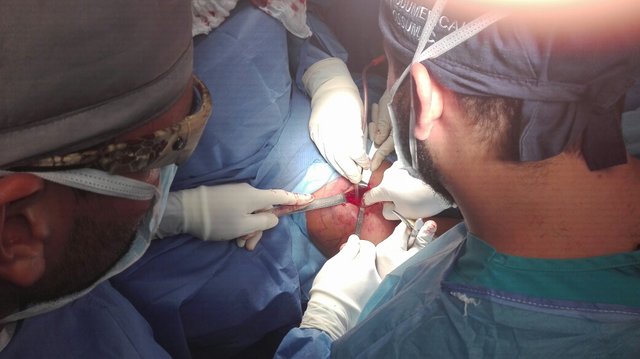
What do they give us to wake us up?
Usually, the drugs we use for anesthesia are anesthetics of short duration on a continuous basis, so it is only necessary to stop administering them for the patient to recover. However, antagonists can also be used, drugs that act on the same receptors as anesthetics (for example, those neurons), displace the anesthetic drug and make it easier for it to stop acting so that the patient wakes up.

Anesthesia in Orthopedic Surgery
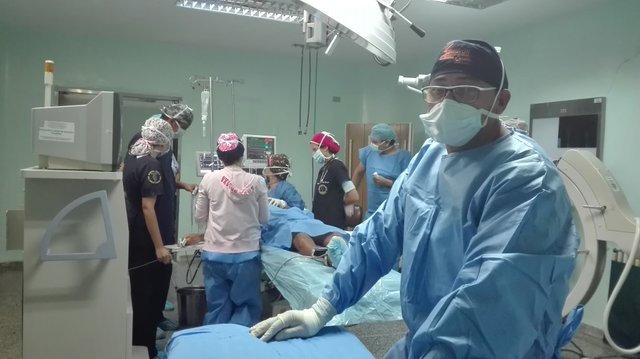
The preoperative requirements for anaesthesia in orthopaedic and traumatological surgery are: to inform about regional anaesthesia techniques and discuss their risk-benefit ratio in order to propose an anaesthetic protocol that satisfies the patient; to inform about the use of transfusion and to obtain informed consent; to inform about the thromboembolic risk and its preventive measures; and to inform about the infectious risk. It is also necessary to carry out the necessary complementary assessments depending on the surgery and the characteristics of the patient, to verify the compatibility of the treatments with the surgery planned to plan the necessary interruptions or therapeutic relays, to propose specific treatments (erythropoietin, antibiotics) and, sometimes, to reconsider in detail with the surgeon the possibility of minor functional surgery due to the not inconsiderable anaesthetic implications in an unstable or high-risk patient. Perioperative behaviour includes: the implementation of regional anaesthesia techniques for the pre- and post-operative period for the purpose of analgesia and early rehabilitation and the prevention or treatment of post-operative complications, now well known in major orthopaedic surgery. For example, invasive monitoring is an easy way to establish continuous monitoring of blood pressure and biological parameters. Postoperative behaviour includes, in the first place, the optimal management of pain with the implementation of standards of continuous surveillance by nursing teams and the use of combination therapies (locoregional, systemic analgesia), the search for, detection and treatment of complications (thromboembolic, haemorrhagic, infectious). Postoperative "early rehabilitation" points in several directions, some of them in evaluation: better postoperative analgesia; reduction of thromboembolic (new molecules), infectious (new forms of prevention) and hemorrhagic (blood substitutes) induced risks, and assessment of patient characteristics: nutritional and cognitive aspects in the elderly, co-morbidities and new treatments (rheumatoid arthritis, for example).
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon


Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)
Makes me cringe thinking about surgery; however, I am very thankful for skilled anesthesiologists.
Posted using Partiko iOS
It's true, without the anesthesiologists we surgeons could not perform almost any procedure. A big hug, my friend.
This project is being supported by @Fundition the next-generation, decentralized, peer-to-peer crowdfunding and collaboration platform, built on the Steem blockchain.
Read the full details of Fundition Fund program
Learn more about Fundition by reading our purplepaper
Join a community with heart based giving at its core
Fundition is a non profit project, by supporting it with delegation you are supporting 200+ projects.
50SP100SP200SP500SP1000SP2000SP5000SP10000SP