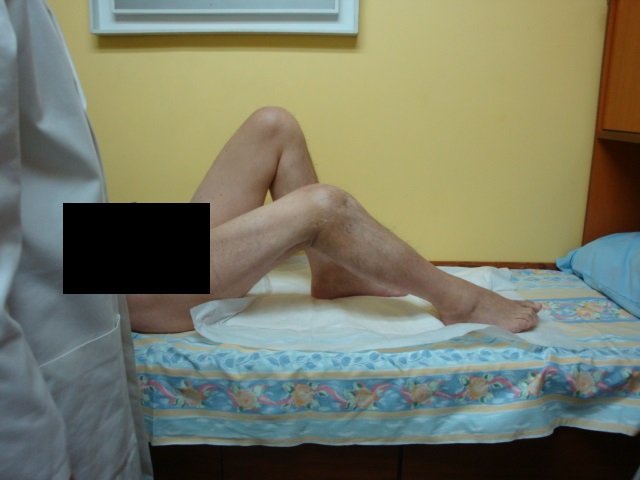
Complex fractures of the tibial diaphysis
Epidemiology
The most common long bone fractures are tibial fractures. It has been estimated that almost half a million new fractures each year with a prevalence of 100,000 unconsolidated cases. Despite arguments that tibial fractures are often difficult to treat, most diaphyseal fractures are for low energy injuries and with a relatively minor degree of soft tissue injury.
An epidemiological study was conducted in Great Britain, and found that 76.5% of fractures were closed, of which 53.6% were of medium complexity. These data show that severe fractures are relatively rare.
Despite the popularity of intramedullary nails to stabilize tibial fractures, specific and relative indications for use with or without reaming remain debated.

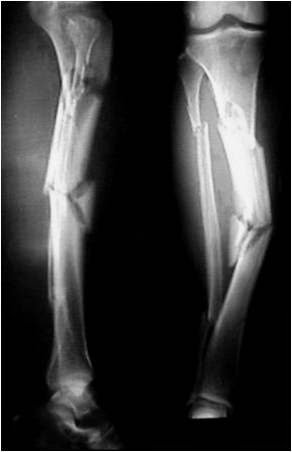
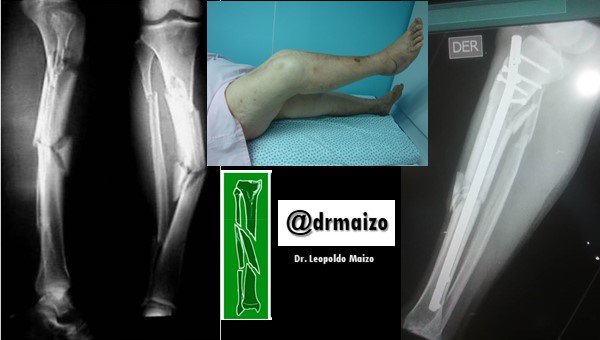
Coomplex fractures of the tibial diaphysis
Segmental fractures of the tibial diaphysis are conditions caused by high-energy trauma. They are usually associated with other soft tissue and bone injuries, which worsen their prognosis and make treatment more difficult.
Nail is especially recommended for closed diaphyseal tibial fractures, with or without soft tissue involvement. Its indications can be extended to some recent fractures of the proximal and distal metaphysis if the locking pins ensure sufficient attachment to the peripheral fragment. Also, after primary treatment with the external fixator, the nail serves to change the treatment.
The nail can be inserted without drilling. Since drilling of the medullary cavity causes considerable additional damage to the cortical circulation as a result of high pressures and temperatures, the technique of locking with drilling is limited to fractures with little soft tissue involvement, however there is still controversy at this point. After proper treatment of soft-tissue injuries, even open fractures of II° and III° degree can be stabilized with the UTN nail.

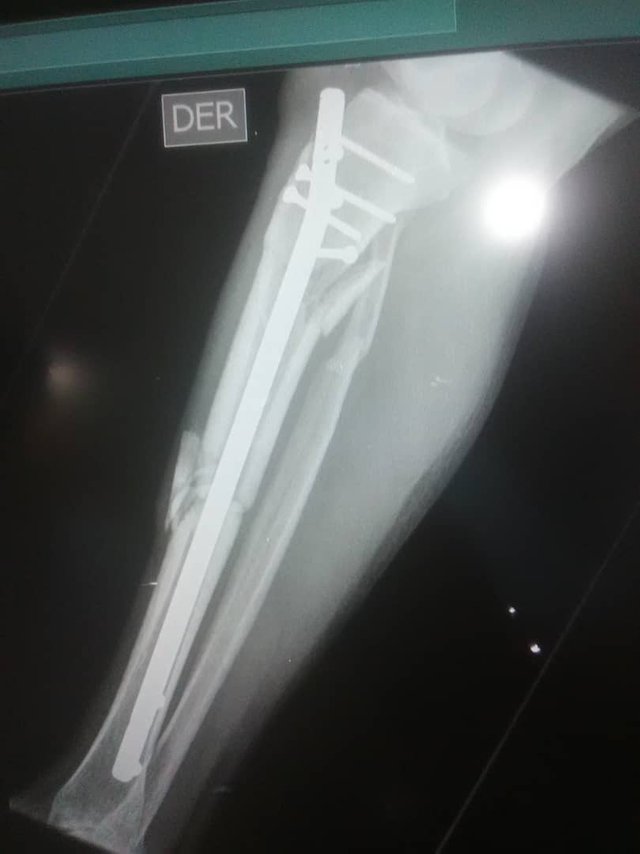
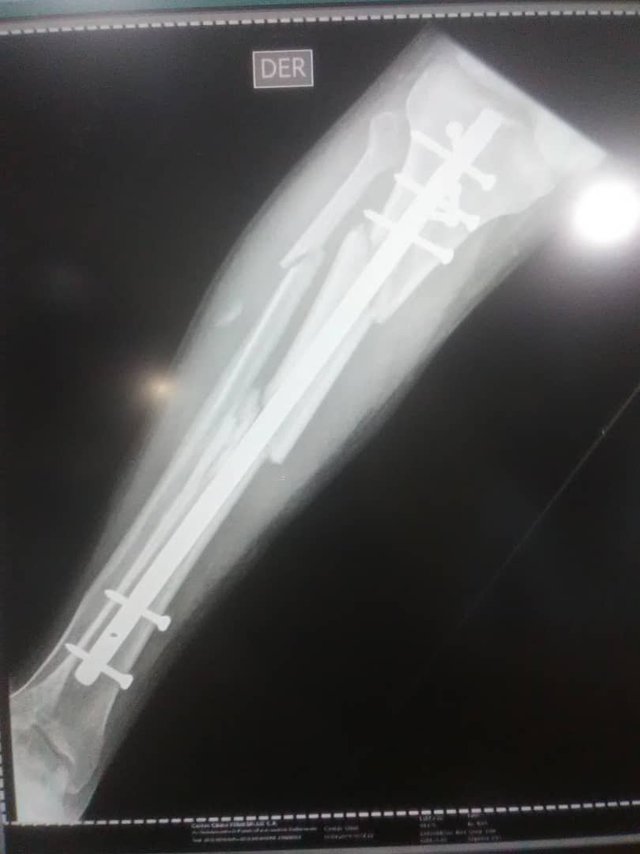
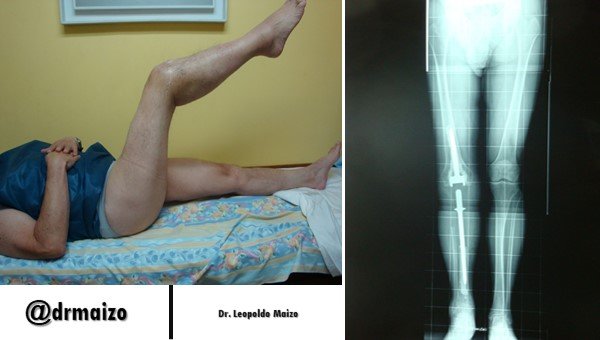
Surgical Goal
The goal of surgical treatment includes, a proper joint, correct alignment, restoration of the joint mechanism of the knee and ankle as well as their normal activity as soon as possible.
Numerous laboratory studies have examined the biological effects of intramedullary drilling and the insertion of fitted nails. Supporters of unreamed nails make severe criticism of this technique. Skipping the milling makes the procedure quicker and easier.
The average hospitalization time is somewhat high considering that due to the type of lesions the antibiotic treatment should not be very prolonged (maximum 3 days) according to world acceptance and no additional handling of soft tissues has to be performed.
Due to the above we can consider this method as an excellent choice for the surgical treatment of diaphyseal tibial fractures.
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon

Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)