The Ingredients : Sugar (Part 3)

In this post i would like to specify the benefit and the risk of over consuming sugar intake on our daily life.
- The Effect of Added Sugar
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that comes in many different forms. In its simplest form it is called a monosaccharide and includes:
Glucose (occurs naturally in fruits and plant juices)
Fructose (occurs naturally in fruits, some root vegetables, cane sugar and honey)
Galactose (combines with glucose to form lactose)
The major sources of added sugars are regular soft drinks, sugars, candy, cakes, cookies, pies and fruit drinks (fruit punch), dairy desserts and milk products (ice cream, sweetened yogurt and sweetened milk); and other grains (cinnamon toast and honey-nut waffles).
therefore It is the added sugar that gives no beneficial nutrients (just energy) and in excess can impact on our health. The World Health Organization guideline is that "added sugar" should make up no more than 10% of our daily intake. However, with sugar being used in many of our foods these days it is easy to lose track of how much "added" sugar you are eating in a day.
- According to the American Heart Association (AHA),
recommends limiting the amount of added sugars you consume to no more than half of your daily discretionary calories allowance. For most American women, that’s no more than 100 calories per day, or about 6 teaspoons of sugar. For men, it’s 150 calories per day, or about 9 teaspoons. The AHA recommendations focus on all added sugars, without singling out any particular types such as high-fructose corn syrup.
To put that into perspective, one 12-oz can of Coke contains 140 calories from sugar, while a regular-sized Snickers bar contains 120 calories from sugar.
In contrast, the US dietary guidelines advise people to limit their intake to less than 10% of their daily calorie intake. For a person eating 2,000 calories per day, this would equal 50 grams of sugar, or about 12.5 teaspoons.
.jpg)
-- Benefit of Sugar
Sugar Can Provide an Immediate Burst of Energy
Glucose is the body’s primary source of fuel, and it comes from the breakdown of sugar. Sucrose contains a fructose molecule and a glucose molecule. The body splits the molecules apart, and insulin helps transport the glucose to cells where it’s instantly metabolized and converted into energy. Without glucose we wouldn’t have stamina for doing our daily activity.Sugar can store Energy for later use
Sugar can provide energy beyond the immediate boost. After glucose is converted into energy for immediate use, the body will store some of the glucose as an energy reserve for later. The process is called glycogenesis. the important thing about the glycogenesis process is that it allows us to go extended periods without eating . It’s worth noting, however, to still be mindful of your intake because when glucose exceeds storage capacity it’s converted into fat.Sugar Can Provide an Instant Mood Boost
It should come as no surprise that sugar makes us happy. sugar activates the pleasure center of our brain and causes a rush of dopamine. This will produce an immediate euphoric feeling.

The Risk of consuming to much sugar
sugar can be addictive
Brain depends on glucose (sugar) for immediate energy. Without glucose, the brain would struggle to work properly. In particular, it appears that the hypothalamus (small of brain that help releasing hormones) plays a role in sugar cravings and addiction. For some people, the cravings may cause them to eat or crave certain foods more than they should, and it could encourage them to make poor dietary choices.
this is how our brain react when we consuming sugar compare with cocaine
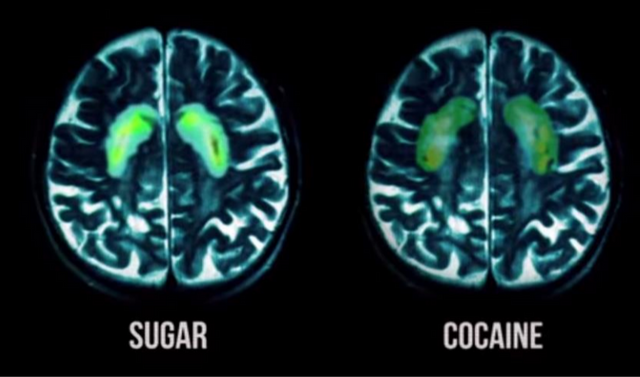
Insulin become Resistance
A lot of people are quick to state that sugar can cause diabetes. While there is a bit of truth to this, sugar addiction may have other consequences. Your body releases insulin in response to sugar in your blood, which occurs shortly after a meal (this is why you may feel sluggish after eating). As the day goes on, your body becomes less sensitive to the insulin your body releases. This is true even in people who are not diabetic, but it’s As a result, you become insulin resistant, which is associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity.sugar causes bad teeth
Sugar disturbs the sensitive balance of phosphorus, calcium & magnesium. All three are needed for strong teeth & bones. If for example phosphorus is depleted by eating too much refined sugar, calcium cannot be assimilated, even though it might be present in your diet. So refined sugar does indeed cause bad teeth, but the cause is not primarily bacteria interacting with the sugar, but a de-mineralization of the teeth due to a lack of important nutrients.Skin aging faster
Sugar attaches to proteins in your bloodstream and creates harmful molecules called “AGEs,” or advanced glycation end products. These molecules do exactly what they sound like they do: age your skin. They have been shown to damage collagen and elastin in your skin -- protein fibers that keep your skin firm and youthful. The result? Wrinkles and saggy skin.Cause Heart disease
When you eat excess sugar, the extra insulin in your bloodstream can affect your arteries, part of your body’s circulatory system. It causes their walls to grow faster than normal and get tense, which adds stress to your heart and damages it over time. This can lead to heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.

Source articles and photos :
https://bit.ly/2Cm8ZIj (heart.org)
https://bit.ly/2HeIFAQ (healthline.com)
https://bit.ly/2REb9pY (the1thing.com)
https://bit.ly/2Tm54Th (canpweb.org)
https://bit.ly/2C42wiF (sweetdefeat.com)
https://bit.ly/2CdvhcX (ncbi.nlm.gov)
https://bit.ly/2Hk8xvd (medicalnewstoday.com)
https://bit.ly/2TcG6GE ( thedolcediet.com)
https://bit.ly/2Uizfrv (gazettereview.com)
https://bit.ly/1QYclkH (naturaljuicejunkie.com)
https://bit.ly/2NGcQlz (sciencedaily.com)
Great write-up @jumps. I just saw you over on Ed Privat’s page, I decided to come check you out—I’m glad I did. My wife is currently fighting a stomach infection, she’s been on a zero sugar (of any kind) eating kick since November, last year.
Sugar has made its way into everything we consume whereas we thought it was the basics like soda and candy—quite the contrary. It’s in everything!
Eh, I just recently signed on with @artzone as a curator, in my opinion, informative research study is an #art and, if you would change one of your tags to #artzone and continue to use the artzone tag, I’ll continue to keep an eye out for you.
Happy steeming @jumps, I’ll see you around.
@splatz. Make that three. Ok.. I’m done for this am.
thank you for the kind word mate.. i will try out to use the #artzone tag regarding to your recommendation.
ps : i dont know about splatz but thanks for the splatz.. lol
3 - Splatz and your out!! Ha ha ha A little slow but I am here. Commencing the splattering of this Steemian
source
Rewarding Your Original Work
With an Upvote
And
Resteem
If you find posts worthy of a nasty Splatin’ feel free and mention @splatz in your reply to their post. Call me out!!