Researchers Develop a Wi-fi Approach to Energy Human Implants
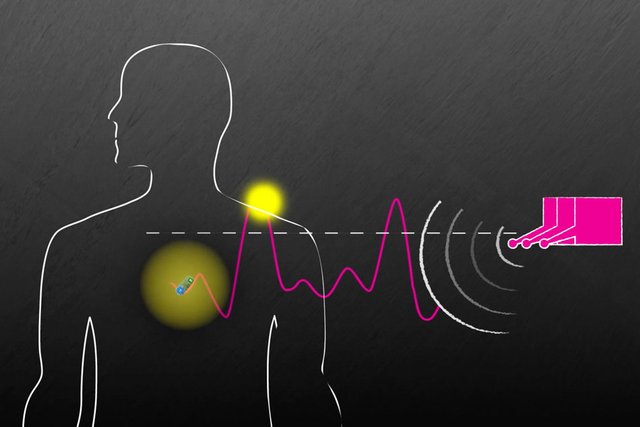
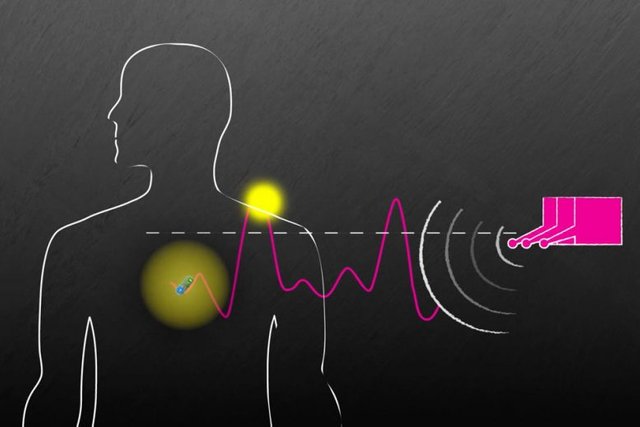
MIT researchers, working with scientists from Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital, have developed a brand new technique to energy and talk with units implanted deep inside the human physique. Picture: courtesy of the researchers
MIT researchers, working with scientists from Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital, have developed a brand new technique to energy and talk with units implanted deep inside the human physique. Such units might be used to ship medication, monitor circumstances contained in the physique, or deal with illness by stimulating the mind with electrical energy or mild.
The implants are powered by radio frequency waves, which might safely go by human tissues. In checks in animals, the researchers confirmed that the waves can energy units situated 10 centimeters deep in tissue, from a distance of 1 meter.
“Even though these tiny implantable devices have no batteries, we can now communicate with them from a distance outside the body. This opens up entirely new types of medical applications,” says Fadel Adib, an assistant professor in MIT’s Media Lab and a senior writer of the paper, which will likely be introduced on the Affiliation for Computing Equipment Particular Curiosity Group on Knowledge Communication (SIGCOMM) convention in August.
As a result of they don't require a battery, the units will be tiny. On this research, the researchers examined a prototype in regards to the measurement of a grain of rice, however they anticipate that it might be made even smaller.
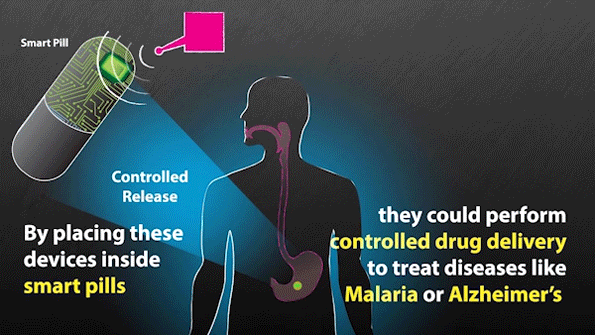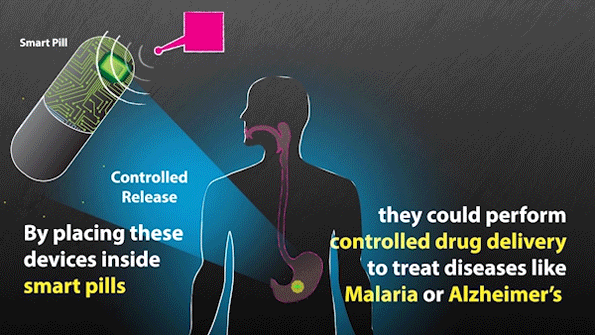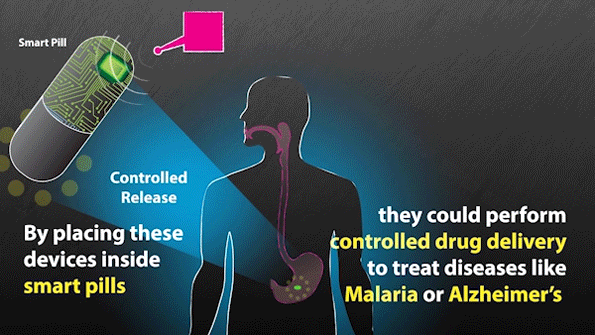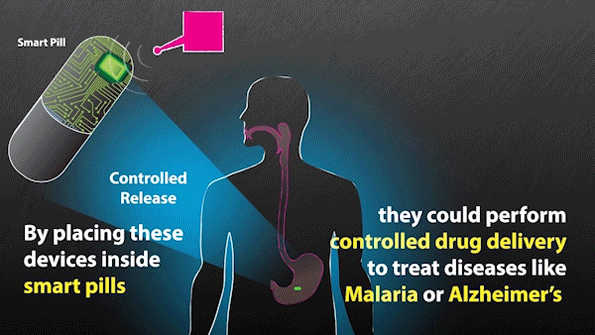
MIT researchers have developed expertise that might be used to remotely set off “smart pills” to ship medication.
“Having the capacity to communicate with these systems without the need for a battery would be a significant advance. These devices could be compatible with sensing conditions as well as aiding in the delivery of a drug,” says Giovanni Traverso, an assistant professor at Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital (BWH), Harvard Medical College, a analysis affiliate at MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Most cancers Analysis, and an writer of the paper.
Different authors of the paper are Media Lab postdoc Yunfei Ma, Media Lab graduate pupil Zhihong Luo, and Koch Institute and BWH affiliate postdoc Christoph Steiger.
<iframe width="777" height="437" src="
Researchers at MIT Media Lab, Harvard Medical College, and Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital have developed a brand new technique to wirelessly energy and talk with units implanted deep inside the human physique. Such units might be used to ship medication, monitor circumstances contained in the physique, or deal with illness by stimulating the mind with electrical energy or mild.
Wi-fi communication
Medical units that may be ingested or implanted within the physique might provide medical doctors new methods to diagnose, monitor, and deal with many illnesses. Traverso’s lab is now engaged on a wide range of ingestible techniques that can be utilized to ship medication, monitor very important indicators, and detect motion of the GI tract.
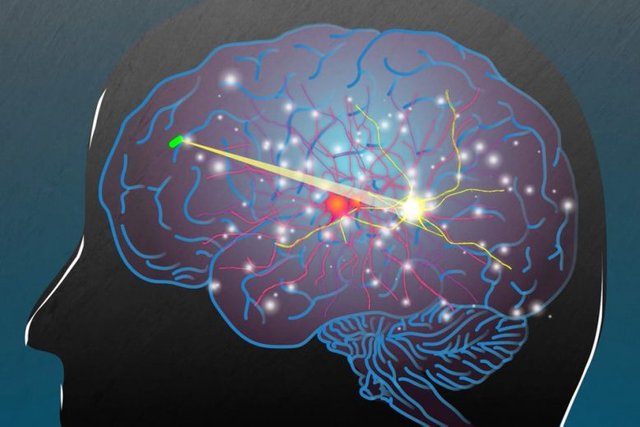
Within the mind, implantable electrodes that ship {an electrical} present are used for a way often known as deep mind stimulation, which is commonly used to deal with Parkinson’s illness or epilepsy. These electrodes at the moment are managed by a pacemaker-like machine implanted underneath the pores and skin, which might be eradicated if wi-fi energy is used. Wi-fi mind implants might additionally assist ship mild to stimulate or inhibit neuron exercise by optogenetics, which thus far has not been tailored to be used in people however might be helpful for treating many neurological problems.
At the moment, implantable medical units, corresponding to pacemakers, carry their very own batteries, which occupy many of the house on the machine and provide a restricted lifespan. Adib, who envisions a lot smaller, battery-free units, has been exploring the potential of wirelessly powering implantable units with radio waves emitted by antennas outdoors the physique.
Till now, this has been troublesome to attain as a result of radio waves are inclined to dissipate as they go by the physique, so that they find yourself being too weak to produce sufficient energy. To beat that, the researchers devised a system that they name “In Vivo Networking” (IVN). This method depends on an array of antennas that emit radio waves of barely totally different frequencies. Because the radio waves journey, they overlap and mix in numerous methods. At sure factors, the place the excessive factors of the waves overlap, they'll present sufficient power to energy an implanted sensor.
“We chose frequencies that are slightly different from each other, and in doing so, we know that at some point in time these are going to reach their highs at the same time. When they reach their highs at the same time, they are able to overcome the energy threshold needed to power the device,” Adib says.
With the brand new system, the researchers don’t have to know the precise location of the sensors within the physique, as the ability is transmitted over a big space. This additionally signifies that they'll energy a number of units without delay. On the identical time that the sensors obtain a burst of energy, in addition they obtain a sign telling them to relay info again to the antenna. This sign may be used to stimulate launch of a drug, a burst of electrical energy, or a pulse of sunshine, the researchers say.
On this research, the researchers examined a prototype in regards to the measurement of a grain of rice, however they anticipate that it might be made even smaller. Picture: courtesy of the researchers
Lengthy-distance energy
In checks in pigs, the researchers confirmed they may ship energy from as much as a meter outdoors the physique, to a sensor that was 10 centimeters deep within the physique. If the sensors are situated very near the pores and skin’s floor, they are often powered from as much as 38 meters away.
“There’s currently a tradeoff between how deep you can go and how far you can go outside the body,” Adib says.
The researchers at the moment are engaged on making the ability supply extra environment friendly and transferring it over better distances. This expertise additionally has the potential to enhance RFID functions in different areas corresponding to stock management, retail analytics, and “smart” environments, permitting for longer-distance object monitoring and communication, the researchers say.
The analysis was funded by the Media Lab Consortium and the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.
Paper: Enabling Deep-Tissue Networking for Miniature Medical Gadgets
Read my profile if want me to resteem your post to over 72,500 followers. @a-0-0
Hello, world!
Our develomers made best app for trading and checking cryptocurrency status in desktop mode - https://masscoinapp.com/