THE SUN AS THE MOST IMPORTANT STAR IN THE UNIVERSE: THE SCIENCE AND THE BENEFITS

Source: https://goo.gl/images/hDS46L
I once heard this proverb in BBC "Focus on Africa" that says "It is only the Sun that does not fail to show up in the morning".
How true is that. In Africa we celebrate and welcome the rising sun and gaze at the beautiful sunset after a long sunny day. From the North to the south of Africa, the East to the West, the sun has its own significance to the people. Some worship the sun as their god and source of life making oblation to it.

The Tiv people in Nigeria consider the Sun to be the son of the supreme being Awondo and the Moon as Awondo's daughter. The Barotse tribe believes that the Sun is inhabited by the sky god Nyambi and the Moon is his wife. Some Sara people also worship the sun. There are many places around the world where the sun was worshiped.
There are references in the Bible where the Sun was mentioned as God or the son of God.
Jesus spoke to the Pharisees again. “I am the light of the world,” he said. “Whoever follows me will have the light of life and will never walk in darkness.” John 8: 12
The Word was the source of life, and this life brought light to people. 5 The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness has never put it out.
4 The Word was the source of life, and this life brought light to people. 5 The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness has never put it out. 6 God sent his messenger, a man named John, 7 who came to tell people about the light, so that all should hear the message and believe. 8 He himself was not the light; he came to tell about the light. 9 This was the real light—the light that comes into the world and shines on all people. John 1: 4-9
11For the LORD God is a sun and shield:... Psalm 84: 11
These are figure of speec in the bible to tell us how important the sun can be.
THE SUN AND SCIENCE
The continuous cyrcle of the sun rising, setting, and rising again became the primary cycle to life on Earth and called that a “day.” Our prehistoric ancestors imprinted this pattern into our very nature. The first rays of light at sunrise made a welcome sight and led to a day of hunting, gathering, farming and fishing. Ancient observers took time to monitor the way light fell at different times of the day and how cast shadows moved, shortened, and lengthened. As the sun set, they noted the emergence of different animals and wondered how long it would be before the sun would return. After a few thousand days, they could comprehend the sun’s longer pattern—call that a “year”—and from then on, every day of every year, the first astronomers could predict when and where the morning sun would rise and the evening sun would set. The sun taught us to be scientists in the firs place.
It is the sun that is refered to as the life-giving star at the center of our solar system.
Comparing the sun with the billions of other stars in the universe, the sun is remarkably unique. But for Earth and the other planets that revolve around it, the sun is a powerful center of attention or attraction. It holds the entire solar system together; pours life-giving light, heat, and energy on Earth; and generates space weather.
The sun is believed to have "burned" for more than 4.5 billion years. It is a massive collection of gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. Because it is so massive, it has this immense gravity, enough gravitational force to hold all of that hydrogen and helium together in place (and to hold all of the planets in their orbits around the sun).
We say the sun burns, but it doesn’t burn out like wood burns. Instead, the sun is a gigantic nuclear reactor on its own.
Plants and the Sun
Plants are called autotrophs because they can use energy fromthe sun light to synthesize, or make their own food source. When you are not actually “feeding” a plant when you put it in soil, water it, or place it outside in the Sun, because none of these things are considered food. Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air (carbondioxide) to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
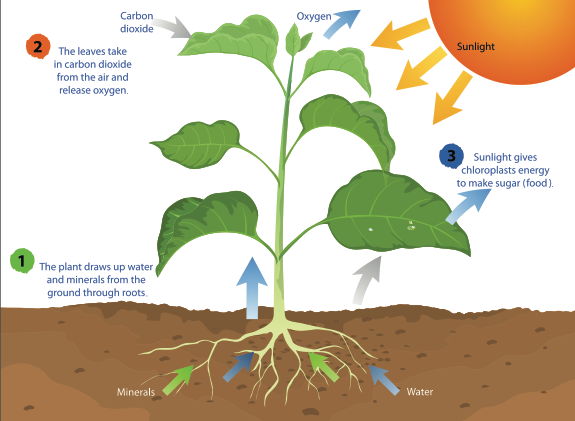
It is from these plants we have our food source, hence the plants help us to synthesize glucose energy from the sun before it can be made available for animals to utilize.
Internal structure and atmosphere
The sun and its atmosphere
These are divided into several zones and layers. They are solar interior, from the inside out is made up of the core, radiative zone and the convective zone.
The solar atmosphere above that consists of the photosphere, chromosphere, a transition region and the corona. Beyond that is the solar wind, an outflow of gas that exudes from the corona.
.jpg)
Source: https://goo.gl/images/GqrNnV
Magnetic field
The strength of the sun's magnetic field is typically only about twice as strong as the Earth's field. It however becomes highly concentrated in small areas, reaching up to 3,000 times stronger than the usual. These kinks and twists in the magnetic field develop because the sun spins more rapidly at the earth's equatorial region than at the higher latitudes and because the inner parts of the sun rotates more quickly than the surface. These distortions create features ranging from sunspots to spectacular eruptions known as flares and coronal mass ejections. Flares are the most violent eruptions in the solar system, while coronal mass ejections are much less violent but involve extraordinary amounts of matter — a single ejection can spout roughly 20 billion tons (18 billion metric tons) of matter into space.
Chemical composition
Like most other stars in the universe, the sun is made up mostly of hydrogen, followed by helium. Nearly all the remaining matter consists of seven other elements which are; oxygen, carbon, neon, nitrogen, magnesium, iron and silicon. For every 1 million atoms of hydrogen in the sun, there are 98,000 of helium, 850 of oxygen, 360 of carbon, 120 of neon, 110 of nitrogen, 40 of magnesium, 35 of iron and 35 of silicon. Still, hydrogen remains the lightest of all elements, so it only accounts for roughly 72 percent of the sun's mass, while helium makes up about 26 percent.
Sun and Energy*
Sunbeams are turned into useful electrical energy or electricity. The sun's light (and all light) contains energy. Usually, when light hits an object or a surface, the energy turns into heat, like the warmth you feel while sitting in the sun. But when light hits certain materials due to their properties the energy turns into an electrical current instead, which we can then harness for power.
Renewables have overtaken coal as the world’s largest source of electricity generation capacity with about 30% of that capacity is due to silicon solar cells.
How do silicon cells work
Simply put, a silicon cell is like a four-part sandwich having the bread on either side consists of thin strips of metallic electrodes. They extract the power generated within the solar cell and conduct it to an external circuit.
Just like a sandwich, it’s the filling which is the most interesting part – this is where photons from the sun are converted into usable electricity. The filling of a solar cell consists of two different layers of silicon: negative and positive silicon, or n- and p-type silicon.
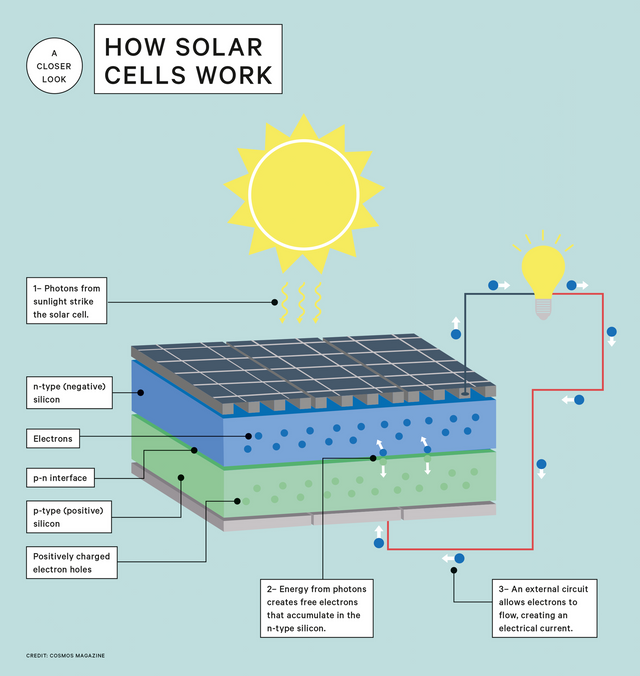
To create a positive or negative types of silicon is relatively easy. The silicon is impregnated with elements known as dopants. These dopants replaces some of the silicon atoms in the crystal structure, allowing the number of electrons present in each layer to be manipulated.
Take for instance, phosphorus is used to create n-type silicon while boron is used to create p-type silicon respectively. Phosphorus has one more electron than silicon and when substituted into the silicon structure, the electron is so weakly bound tobether to the phosphorus that it can move freely within the crystal, creating a negative charge.
But on the other hand, boron has fewer electrons than silicon and sucks up silicon’s electrons. This creates “electron holes” – regions of mobile positive charge in the crystal structure.
At the interface of the p- and n- type silicon, the positive electron holes and the electrons combine. It’s not a simple electrostatic interaction, but the upshot is that you get a slightly positive charge in the n-type silicon and a slightly negative charge in the p-type silicon at the interface of the n- and p- type silicon which is the opposite of what you might expect.
Photons from the sun passes between the strips of the top electrode and strike silicon atoms in the crystal structure. Like the strike of a cue ball, the colliding photon itself gives some of the silicon electrons enough energy to escape from their parent silicon atom.

The “free” electrons move to and accumulate within the n-type silicon like a store.
Once free electrons have accumulated in the n-type silicon, it’s time to put all the free electrons to work. In order to use their energy, the electrodes must be connected via an external circuit. Electrons flow through the electrodes and the external electric circuit from the n-type to the p-type. The p-type silicon acts as an electron sink. Without it, the electron flow would clog up.
It is this flow of electrons that creates the electrical current we can use to power our appliances or charge batteries for when the sun is not shining.
The knowledge is good, the sight is beautiful. In Africa countries likes South Africa, Morocco, Algeria, Ghana and Egypt are having the largest and continuously growing solar markets in Africa and are taking advantage of its rich possibilities. Hopping more countries like Nigeria see the need for this free gift of nature and source of all energies.
Thank you for reading.
References
https://cosmosmagazine.com/technology/how-solar-cells-turn-sunlight-into-electricity
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/solar-system/the-sun/
https://www.space.com/58-the-sun-formation-facts-and-characteristics.html
I am @gloeze

Hi! This is jlk.news intelligent bot. I just upvoted your post based on my criteria for quality. Keep on writing nice posts on Steemit and follow me @jlkreiss to get premium world news updates round the clock! 🦄🦄🦄
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! @wafrica is now following you! ALWAYs follow @wafrica and use the wafrica tag!
Your post is high quality , keep steeming, if you love engineering and sports , you can join our steemit F1 Team,
And steem your way to power greatness and glory, see you at the finish line!