Primary lymphoma located in the mediastinum
We will start by referring to the lymphomas that are known as malignant neoplastic lesions, whose origin lies in B cells located in the thymus. Epidemiologically most frequently affects the female sex, between 15 to 30 years of age, with its highest peak in adolescence.
When the clinical presentation of these cases is expressed as a large mediastinal mass and rapid growth represents an oncological emergency, since it severely compromises the physical, functional and life of the patient. Mainly affected via the area and generating the secondary vein syndrome to the compression of the large tumor mass.
Other symptoms associated with large mediastinal tumors are dyspnea at small and moderate efforts, cough or hemoptysis, dysphagia chest pain and volume increase in one or both upper limbs due to compression.
Thorax anatomy. Free medical illustrations under Creative Commons License

Clinic history
She is a 30-year-old female patient, with no significant medical history, who presents with an evolving clinical course of two months, characterized by dyspnea at moderate and small efforts, and subsequently pain is associated in left hemithorax accompanied by mucopurulent cough with 3 episodes of hemoptysis, go to multiple practitioner in your locality where it is treated as a low respiratory process, receiving oral antibiotic therapy for 7 days (levofloxacin 500mg tablets), without any improvement and exacerbation of symptoms, evidenced by 1 week of evolution of volume increase upper left limb, and orthopnea, so he goes to the emergency room of his nearby hospital where it is requested for clinic and in view of finding is entered.
Laboratory tests (Initial):
| CB | 7000 |
| Sec | 65% |
| Lymphocytes | 32% |
| Hb | 11 |
| Plaq | 450,000 |
| Urea | 21 |
| Creatinine | 0.8 |
An initial chest x-ray is requested, showing massive left pleural effusion, which required the placement of a chest tube.
However, in view of clinical and paraclinical findings initially, the patient was treated as a pleural effusion of etiology to be determined.
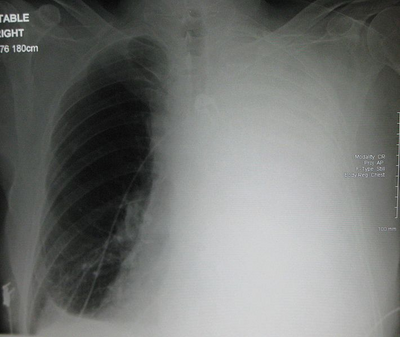
Massive left-sided pleural effusion in a patient with lung cancer. Public domain image under license CC BY-SA 3.0.
In the previous image it shows a clear example of what our patient presented in the chest X-ray, where massive left pleural effusion is evidenced, similar to that presented by the patient of the clinical case. I do not own images of the radiological exam, that is why I take an example that I found on the web.
In view of certain results, based on the age of the patient, with no known pathological history, being the main cause of etiology of pleural effusions in this age group, of infectious origin, followed by neoplastic pathologies.
It is for this reason that samples are taken for culture, cytology and cytochemistry of pleural fluid, as well as culture, antibiogram, gram, BK, KOH of sputum. The results obtained were negative for bacterial growth and presence of neoplastic cells in pleural fluid culture, with respect to the sputum study was negative for bacterial growth.
After 2 weeks and chest radiographs, with a decrease in the pleural fluid, a large mass with irregular edges is seen, which is impressive and is located throughout the mediastinal space and extends into the thoracic cavity and displaces the lung.
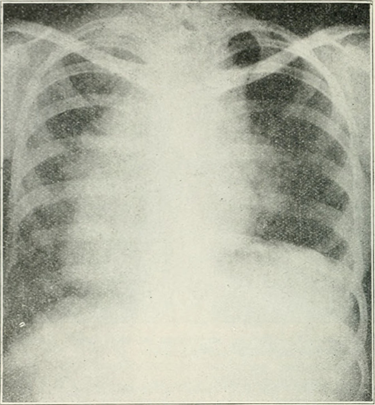
Chest x-ray, where important mediastinal mass similar to that of our patient is evidenced. Public domain image. FLICKR source
Simultaneously, the increase in left arm volume progresses, as well as the presence of a venous network in the anterior thorax, compatible with the presence of:
Vena Cava Superior Syndrome
The description of this syndrome was made in 1757, being a dangerous clinical entity, product of the extrinsic or intrinsic obstruction and compression of the superior vena cava, clinical evidence of facial, cervical edema, volume increase in upper limb secondary to the presence of DVT in said limb, headache, facial cyanosis and chest pain, neck and even shoulders. In severe cases, neurological manifestations can be observed due to drowsiness, obtundation and hemodynamic deterioration that compromises the patient's life.
The etiology of this syndrome is varied, being the most frequent one of neoplastic origin, especially lung cancer, as well as those triggered by infectious processes such is the case of syphilitic aneurysms, tuberculous mediastinitis among others, and finally those cases of vena cava syndrome, product of manipulation or minimally invasive procedures that involve the anterior thorax or upper extremities or central venous access.
In view of the patient's clinical findings, it was decided to perform a chest Tomography with contrast or in the absence of chest NMR, observing the following:
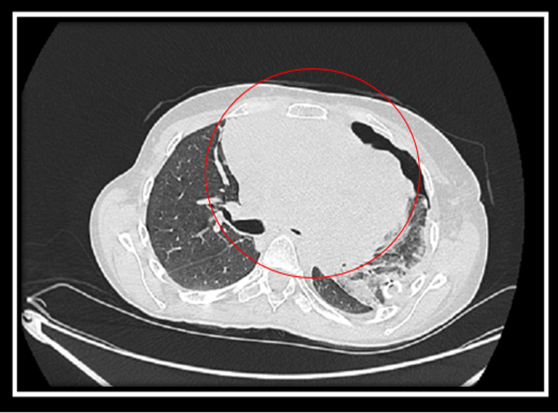
Image by @anestrada12
Video by @anaestrada12
Conclusion:
Large tumor mass from the mediastinum, which by its large size displaces vital structures such as the lung, compresses important blood vessels.

Mediastinum
Controversies exist when defining what the mediastinum represents, initially this structure is defined anatomically as a well-defined space, laterally by the pleurae and lungs, anterior by the posterior side of the external, in its posterior part by vertebral bodies (column thoracic), superiorly delimited by the base of the neck and finally in its lower part by the diaphragm.
However, there are other literatures that establish that the mediastinum is not just a space because it contains anatomical elements inside, it is for this reason that it has been defined as follows:
"Mediastinum means that set of organs and anatomical elements that occupy the middle part of the thorax and are tangible because they are real."
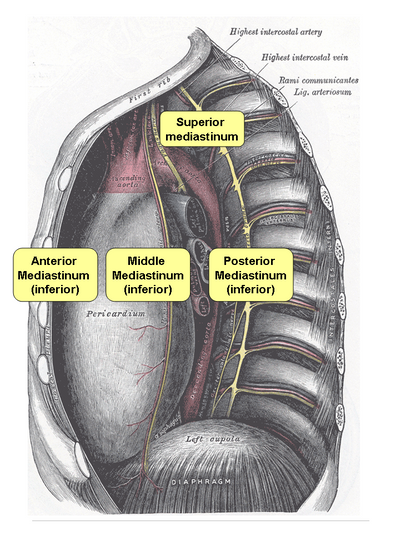
Mediastinum open, seen from the right side. Public domain image licensed CC BY-SA 3.0.

Tumors of the mediastinum
Benign cysts: Bronchogenic, Pericardial, Mesothelial, Enteric and Duplication.
The growth of tumors both in the mediastinum and in any anatomical area can be presented in two ways based on their characteristics, such as benign or malignant, whose consistency can be cystic or solid, and which according to their origin are primary or metastatic.
Age, sex and genetic predisposition play a very important role, with respect to the incidence and prevalence of these cases.
According to its growth and location we can establish the following:
| Timo: |
| Teratoma (germ cells): |
| Thyroid (Endocrine tissue): |
| Mesenchymal: |
Others:
Based on what was established by the literature and its wide range of mediastinal tumor lesions, it was decided to take a biopsy of this mass, which reports the following:
Findings compatible with nodular sclerosis variety Hodgkin disease.
Taking into account that only a biopsy is taken, the ideal would be to carry out immunohistochemistry, awaiting results.

Primary mediastinal lymphoma
This pathology called lymphoma whose origin lies in large cells of B lymphocytes. It usually occurs as a single lesion, whose epidemiology affects more often the female sex during adolescence and young adulthood.
Lymphomas are characterized by malignant neoplasms of the lymphocytes and their precursor cells. This pathology represents more than 30% of mediastinal lesions, increasing their frequency index in childhood.
At present, histopathologically, lymphomas are classified according to their immunological characteristics, morphology and molecular biology, based on what is established by the WHO, they are:
In general, this type of primary mediastinal tumors are those of Hodgkin lymphomas, in more than 60% of cases. This pathological entity was first described in 1970 by Dr. Van Heerden.
Primary mediastinal Hodgkin lymphomas are divided into two histological subtypes, which helps us determine the aggressiveness and behavior of the same. The two forms are;
Where the latter has an aggressive, rapidly growing neoplastic behavior, they tend to be of poor prognosis, with a high rate of dissemination.
However, we must bear in mind that the thymus has the capacity to transform, as it were, from its lymphoid cells into a Thymoma, being known as its histological type in Hodgkin's lymphoma in its scleronodular and finally lymphoblastic variety.
The incidence of this pathology increases with the passage of time, and which has taken more force, with its association with the acquired human immunodeficiency virus, obtaining devastating results.
Clinical manifestations
They will be the product of the presence of the lesion or tumor mass, which will be directly proportional to its size.
Complications, most feared total obstruction due to compression of the airway, pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade and death.

Diagnostic
It is based on the identification of the tumor mass, either by several methods, such as chest X-ray, chest CT with contrast or chest NMR with contrast. It is very useful in these cases to request a complete tomographic scan that involves the abdomen, pelvis and neck, for this way, to determine whether or not the presence of more neoplastic lesions, if metastatic lesions are observed or not, the integrity of the ganglion chains and determine its stage in cases of lymphoma such as the classification of Ann-Arbor Classification, based on the tomographic studies.
We must not forget that the request for laboratory tests, such as complete hematology or blood count in order to determine spinal infiltration are very useful, kidney and liver function are essential, and of course the determination of indirect markers (calcium, urea acid , LDH, Alkaline Phosphatase) play an important role in the study of all patients with neoplastic lesions.
Whose definitive diagnostic is based on the biopsy of the lesion and its respective immunohistochemistry.

Conclusions
Based on those described during the development of the clinical case, our patient was asymptomatic for many years, and it was not until then that she presented a pleural effusion that was able to determine the presence of a large mediastinal mass, without previous clinical examination during all her youth, even calls attention, that our patient arrives at happy terms two previous pregnancies without any complication.
Epidemiologically, our patient is in the age group and sex that is mostly affected, its clinical evolution has been florid, presenting all the clinical manifestations from chest pain, to a superior vena cava syndrome due to the large size of its tumor mass, for which an arterial and venous Doppler echo of the left upper limb, which was the largest, was performed as a protocol for this condition, evidencing the presence of a thrombus in the humoral veins, which is why I need treatment with oral anticoagulants.
It is noteworthy that during a routine pelvic abdominal ultrasound, a cystic lesion is seen in the right kidney, it is evaluated by urology service, which suggests after the complete tomographic scan evaluation, the biopsy of said lesion. suspected renal, but due to clinical conditions of the patient, it has been impossible to take her to complete sedation.
Currently, it is treated by the hemato-oncology service, and received its debulking scheme based on chemotherapy with Vincristine, Cyclophosphamide and prednisone. Waiting to initiate complete chemo therapy scheme of 8 cycles.

Sources of support in the publication
Mediastinoscopy in the Treatment of Mediastinal Cysts
Congenital mediastinal cysts: imaging findings
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome with Malignant Causes
Chapter 18: Thoracic Wall, Pleura, Mediastinum, & Lung
Management of large mediastinal masses: surgical and anesthesiological considerations
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA: AN UPDATE ON ITS BIOLOGY WITH NEWER INSIGHTS INTO CLASSIFICATION
Sclerosing mediastinitis in the differential diagnosis of mediastinal tumors
Pediatric Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Changing trends of adult lymphoma in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia - comparison of data sources.


steemSTEM is a project of the chain of blocks that supports the scientific content in different areas of science. If you want to know more about this wonderful project you can join the server in discord
This article will be published at https://www.steemstem.io/
I hope you enjoyed my content.
Congratulations @anaestrada12! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @utopian-io.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness and utopian-io witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Thanks for having added @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post. This granted you a stronger support from SteemSTEM.
Thanks for having used the steemstem.io app. You got a stronger support!
Hi @anaestrada12!
Your post was upvoted by Utopian.io in cooperation with @steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV