Distributed Generation Lecture 2 [Part 2]
Hello Steemians!!!
Hope you all are doing well and enjoying the bounties of life.Today i am gonna continue Introduction to Distributed generation with you guys.

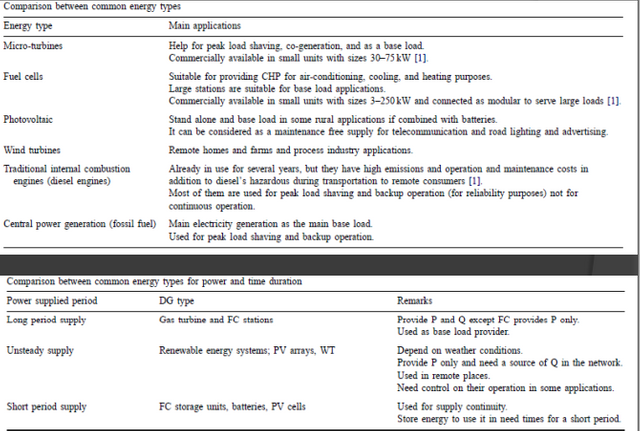
Fuel Cell :
- The fuel cell is a device used to generate electric power and provide thermal energy from chemical energy through electrochemical processes. It can be considered as a battery supplying electric energy as long as its fuels are continued to supply.
- Unlike batteries, FC does not need to be charged for the consumed materials during the electrochemical process since these materials are continuously supplied.
- FC capacities vary from kW to MW for portable and stationary units, respectively. It provides clean power and heat for several applications by using gaseous and liquid fuels.
Advantages of Fuel Cell :
- FCs transform the fuel chemical energy to electric power with a 60% efficiency, which is considered to be twice of that of the traditional generating stations.
- The absence of moving parts in FCs operation, except for air blowers (for O2) and fuel (for H2) and/or water pumps, results in very low noise levels, relatively higher efficiencies and emits lower air pollutants.
- No combustion is involved in the FC operation make it environmental friendly generation with approximately negligible emissions (low CO2)
- Also, due to the output bi-product (electricity and heat as a result of high fuel conversion efficiency) and their prices, small size FCs in the coming recent years are expected to be implemented in commercial and residential buildings for both purposes of lighting and heating at the same time.
Disadvantages of Fuel Cell :
- From the electrical point of view, as a result of aging the FC internal impedance slowly increases, therefore, we need a power electronic interface to regulate the output voltage.
Storage Devices :
- It consists of batteries, flywheels, and other devices, which are charged during low load demand and used when required. It is usually combined with other kinds of DG types to supply the required peak load demand.
- These batteries are called “deep cycle”. Unlike car batteries, “shallow cycle” which will be damaged if they have several times of deep discharging, deep cycle batteries can be charged and discharged a large number of times without any failure or damage.
- These batteries have a charging controller for protection from overcharge and over discharge as it disconnects the charging process when the batteries have full charge. The sizes of these batteries determine the battery discharge period. However, flywheels systems can charge and provide 700kW in 5 s.
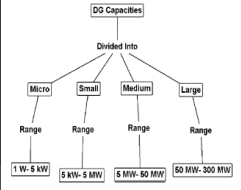
Classification of DGs :
• Standby
• Stand alone
• Peak load shaving
• Rural and remote application
• Providing combined heat and power (CHP)
• Base load
• Supply duration and power type
• DG capacities
• Generated power type
Comparison:
DG Operational Constraints:
The operational constraints differ according to the DG type as follows:
• Gas turbine, combustion engines, and hydro generation DGs: These types of DG generations can be considered
alike, though not identical to, the traditional central generation, which has the ability to be dispatched. But they
have two additional constraints.
• (a) The output generated power: The DG output power (Pg) has minimum and maximum power limits. The minimum output generated power of some DG is essential in the case of co-generation required for some applications, like heating purposes. The maximum power generation limit is
for thermal and overloading capabilities.
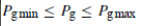
• (b) The ramp rate: This ramp is due to the natural delay taken by DGs to increase the amount of output generated power in a certain defined duration. 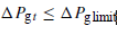
• Renewable energy DGs: This kind of energy resource includes WTs and PV arrays. The main characteristic of this generation is that it cannot be dispatched in emergency situations as its outputs are mainly affected by
environmental conditions such as wind speed and sunlight, respectively. In some kinds of this generation, the output power generated is related to the system frequency (f) and voltage at the bus where DGs are connected (Vg) .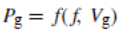
• Storage devices: Some kinds like batteries can be dispatched to control the output power and their period of duration. However, each kind has different characteristics. 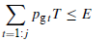
• Where Pgt is the released output power at time t; E, the total available storage energy; and T is the time elapsed.
• FCs, renewable, and storage devices: They produce active power only. Therefore, the required reactive power can be obtained from the system by one of the following methods: a fixed capacitor, a controllable capacitor with a fixed power factor or interfacing with the network through power electronic devices. The three possibilities can be described as follows:


Hope you like my article and if you do please

Excellent,this is great post...thanks a lot sharing this valuable educative post...
that's pretty cool to know....
Splendid! nicely written. Thanks enlightening us