CELL SUSTENANCE #2: Albumin; meet the workaholic polypeptide.
The blood is a collection of cells in a liquid, apart from cells, the blood also consists of other inorganic and organic molecules suspended on this fluid. The blood cells includes the white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes) and platelets (thrombocytes); they perform different functions in the body. Organic molecules suspended on this fluid part of the blood are compounds obtained from the foods and drugs we take (such as carbohydrates, fats and cholestrols), hormones and antibodies, the inorganic molecules includes sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium, chloride and other minerals which are vital to the body. These compounds are transported via blood to the the target organs and tissues.
credit: pxhere. CC0 creative commons license. Unknown author
When blood is collected in an anticoagulant bottle, centrifuged and examined, a clear straw colored fluid is observed to be separated from another division which looks like a stack of cells; these are actually stacks of cells which constitutes about 45% of the whole blood volume, this is also known as the hematocrit or packed-cell volume.
The straw colored fluid part of the blood is known as the plasma, this accounts for the remaining part of the centrifuged blood and it contains blood clotting factors, suspensions of the blood such as the inorganic and organic molecules, the major constituent of the plasma is water ( about 90%) and solids (10%); in addition to these gases such as carbon dioxide, oxygen and nitrogen are also suspended on the plasma. The plasma also contains the blood clotting factors Fibrinogen and prothrombin, when these clotting factors are removed, the plasma is known as serum.
The major solids contained in the plasma are proteins, they account for about 7% of the plasma the normal value of plasma proteins is 7.4mg%, however, there is a reference range of 6.4-8.3mg% and a deviation from this range is an Indication of protein malnutrition and/or liver disease.
Plasma proteins includes:
In the clinical laboratory, these proteins are precipitated using salts. At certain percentage or saturation of these salts, the proteins are precipitated. Albumins are precipitated at full saturation of ammonium sulphate while the Globulins are precipitated at half saturation of the ammonium salts. Fibrinogens are precipitated by 10% saturation of sodium sulphate while Globulins can be precipitated by 22% saturation of sodium sulphate.
))
Blood clothing process. Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author: GrahamColm
Fibrinogen is a very important part of the secondary blood coagulation system, during the blood clotting process; the prothrombin converted the Fibrinogen which is an unstable protein to a more stable form known as fibrin.
Accumulation of these fibrins (fibrin scaffolding ) is the major action which helps the blood vessels to cover the openings created as a result of trauma or injury to the vessels, this helps to prevent excess blood loss due to injury and to maintain the integrity of the blood vessels. Normal fibrinogen level is 300mg/dl With a reference range of 200-400mg/dl, a deviation from this value impairs The blood clotting process and is an indication of a liver problems as the fibrinogens are also synthesized by the liver.
Albumin is the major plasma protein produced by the liver, making up about 60% of the plasma proteins.
The albumin is a single chainpolypeptide of about 584 amino acid residues, it has a molecular weight of about 66Kda (66,300Da). Albumin is negatively charged due to the fact that it consist of more acidic amino acid residues than the basic amino acids, hence it’s inability to escape the filtration barrier of the renal glomerulus.
The renal glomerulus also carries a net negative charge due to proteoglycans and collages which Linea the glomerular membrane, this the albumin which is also negatively charge can not pass through them even though they are below the size range if substances which can pass through this membrane. When albumin is detected in the urine, it is an indication of glomerular nephritis. Glomerular nephritis is a pathological disorder where the glomerular membrane loses it negative charge, allowing the passage of albumin.
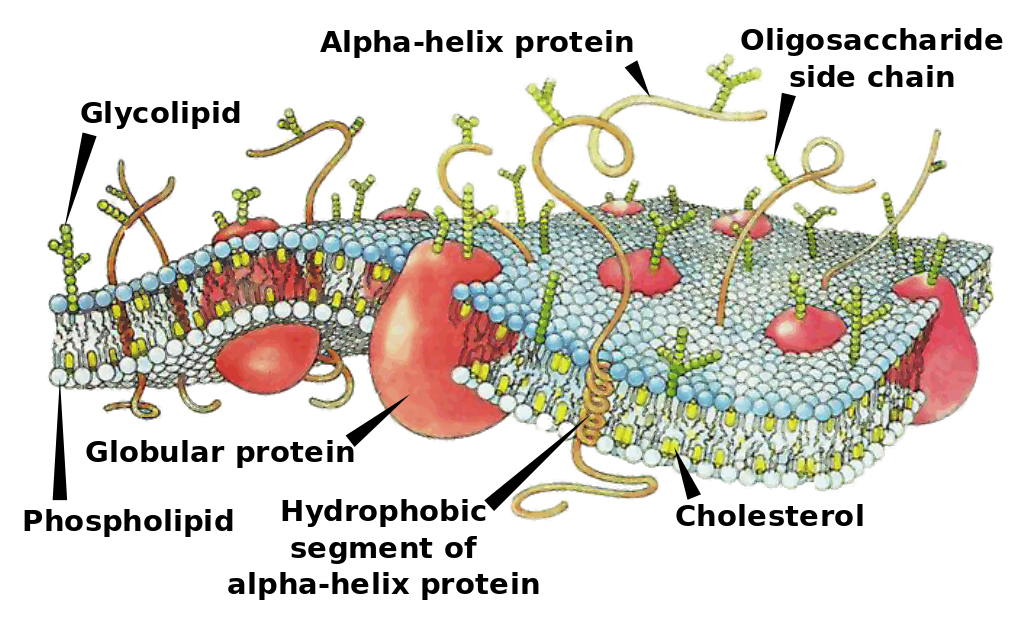
image credit: wikimedia. CC4.0 license. Medium69
The secondary structure or the albumin is usually an α-helical (alpha helical) conformation and less commonly as β-plated structure and in a lesser frequency as a random coil formation, it has a globular tertiary structure with the hydrophobic amino acids in its interior and hydrophilic amino acids in its exterior, this accounts for it’s high solubility.
The liver produces about 11g of albumin daily; this represents about 25% of the total hepatic protein synthesis, albumin is thus the major protein produced by the liver. It’s normal level is 3.4-4.7g/dl. Albumin can be found in cerebrospinal fluid and in the interstitial fluid because it can come out of the vascular compartments. It has a half life of 20 days. Hence the body cycle of Albumins is on a minimum of 20 days interval.
The body synthesizes much amount of albumin, this is because the albumin performs many functions in the body; these functions are very important in cell sustenance as the cells resultantly dies off when these actions are impaired or not occurring at all.
These functions includes:
Transport:
Transportation in the human body is much similar to our everyday orientation of what transportation means, the only difference being that this is done on a molecular level and very much smaller and often microscopic molecules are conveyed from the point of synthesis or any part of the body to the point of action or target cells.
))
credit: credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author: OpenStax College
These substances includes hormones, chemicals such as drugs and nutritional substances such as monosaccharides, amino acids and lipids, these substances are loaded into transport molecules, more popularly the carrier molecules which travels via the blood or other body fluids to deposit these substances to the area where they are needed.
The albumin is a very important transport molecule, it transports fatty acids from the adipose tissues to the liver; it can bind with hydrophobic substances such as drugs and bilirubin produced during the destruction of red blood cells, albumin helps to transport these substances to the required parts if the body where they are utilized and excreted respectively.
Albumin can also transport hormones which are hydrophobic, this includes sex hormones such as testosterone and estrogens, thyroid hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4) and glucocorticoids. An impaired albumin metabolism will affect the action of these hormones which includes the development of sexual organs and characteristics, normal body growth is also impaired due to decreased thyroid hormone transport and supply, glucocorticoids inhibits inflammation reactions, this action may he affected as well
Regulation of osmotic pressure:
Osmosis is defined as the movement of water from area of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration, this is to balance the osmolarity at both ends. At the arterial end of blood vessels, hydrostatic pressure is produced which causes an outflow of fluid, this outflow is balanced by an equivalent oncotic pressure produce in the venous end of the blood vessels, hence only a little amount fluid leaves the blood vessels.
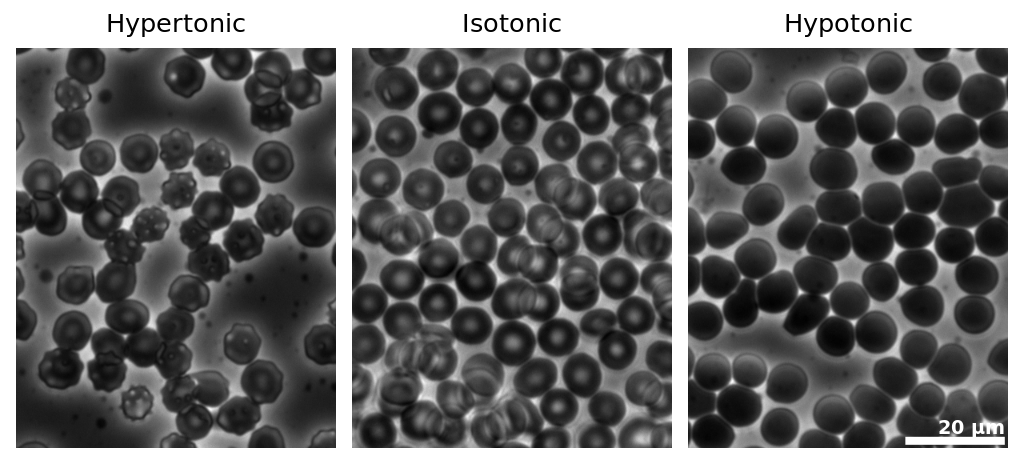
osmotic pressures in human red blood cells. Credit: wikimedia. CC3.0 creative commons license. Author: Zephris
This oncotic pressure is known as the effective osmotic pressure and is exerted by proteins because they cannot easily move out of the vascular space. Albumins account for about 80% of this effective osmotic pressure (about 25mmHg) this ensuring that only a little amount of fluid leaves the vascular space. Albumin can hold about 18ml of fluid in the blood stream; this ability helps it to perform this action.
Decrease in the plasma level of albumin causes these fluids to accumulate in the extravascular compartments, this conditions is known as edema. It is characterized by pooling of fluid in the distal compartments of the body such as the feet and hands this is due force of gravity forcing these fluid to the distal parts of the body.
Buffer action:
During normal metabolic actions, the human body produces large amount of acids, you’d wonder why the effect of these acids are not felt in the body as acids are very toxic to the cells. Fortunately; the body contains buffers, a buffer is a substance which mops up hydrogen ions and thus prevents the toxic action of acids as a higher concentration of these hydrogen causes more acidity. Proteins are able to perform this action, albumin have the highest buffering action amongst all proteins, this action is due to the imidazole group of histidine. Albumins has sixteen (16) histidine residues, this contributes to its buffering action.
Source of food:
Eggs are good source of proteins, egg white has a very good concentration of albumin protein, just like other proteins, albumin is a source of nutrient to the cells, the cells through pinocytosis can take in albumin, this is broken down into amino acids just as other proteins and serves as a source of energy to the cell.

credit: pixabay. CC0 creative commons license. Contributed by Congerdesigna
Albumin also acts as a reservoir for calcium in the plasma. The normal range of albumin concentration in the plasma is 3.5-5.0g/dl, this range should be kept in check as hyperalbuminemia or hypoalbuminemia may result from excess protein diet and low protein diet respectively. Egg white has high albumin value, this should be kept in mind while preparing individual and/or family meals. Globulins are the third class of plasma proteins, this will however be a topic for the next part of this series…
REFERENCES
- Plasma proteins -biochemden
- Albumin -wikipedia
- Fibrinogens-wikipedia
- Globulin -wikipedia
- The Role of Albumin and Fluids in the Body -vetfolio
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.
