Coagulation and Flocculation
.png)
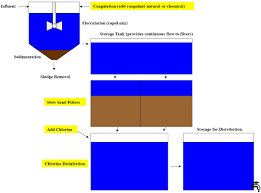
Water Treatment Plant Schematic ,source Wikipedia
Hello stemians,
In my previous article, i talked about standard water treatment (Drinking water and wastewater) , and the processes involved. Water treatment is quite broad and involves different processes. In this article, we will be looking at one of procedures which is the "coagulation and flocculation" process in water treatment .
So let's get started.....
Before I begin, I will start by explaining to us the meaning of "coagulation and flocculation". Coagulation is a procedure used in water treatment to destabilize colloidal particles by neutralizing their electrical charge. The material or substance used for the procedure is called a coagulant.
While flocculation is the merging together of particles as they are brought into contact by mechanical stirring .
Through this procedure, small suspended particles collide into heavier particles (flocs), settle down and are filtered out.
The first step to consider is to add a coagulant with rapid mixing and turbulence. In this procedure the particles are destabilized. After that we move to the next procedure which will take place in the same vessel or in a separate one, the rapid mixing continues and promotes the collision of particles to form larger aggregates.
The water then flows into the next vessel where slow mixing allows the aggregates to grow into flocs which are large enough that they can settle in the next chamber.
Coagulants in Common Use
The most common coagulant in use is the alum which reacts with the alkalinity in the water to form an aluminum hydroxide floc. If the water does not contain the required alkalinity, it may be necessary to introduce lime. (CaO) or soda ash in addition to the alum to get proper flocculation. Activated silica, sometimes added to the water, provides nuclei for floc formation. Other important coagulants include ferric chloride and ferric sulphate.For Alum and lime, treatment with lime produces non-carbonate hardness.
For Alum and soda ash, In this case, hardness is not produced but soda ash is more expensive than lime. A concentration of alum between 5-34 mg/l may be required for a successful coagulation with pre-settled waters.
For Ferric chloride, soft coloured waters are not effectively treated with alum. Here, iron III Chloride is used. About 5 - 150 g/m = is required for clarification.
With Iron sulphate, about 10-150g/m is required for clarification.
Water containing HS can be successfully treated with iron III chloride.
Please I want you to note that the the description only show how the reactions proceed and not actual amount of chemicals required.
Now let's look at the required chemical for this procedure.
Chemical Requirement
The quantity of chemicals required is found through trial by placing samples of the raw water into series of jars and adding different amounts of chemicals to each. After thorough mixing, the character of the flocs and their settleability are observed and the optimum dosage. Since water quality may change, i will advise the test should be conducted frequently.
Design of Secondary Settling Tanks with Mixers and Flocculators
Satisfactory coagulation requires that the chemicals and the raw water be thoroughly mixed. To achieve mixing, chemicals are added to the water in channels at hydraulic jumps or mixing basins where mixing is effected with rotating paddles or other devices. The depth of the mixing basins is usually about 1.5m whereas the detention time is 30-120 seconds.After mixing, the raw water together with the coagulants enter the flocculator. The flocculator is a chamber where the particles are allowed to collide together to form larger flocs. It precedes the settling tank and usually has the same width with the settling tank.
The water flows from the flocculator to the sedimentation tank where the flocs settle. The depth of the tank should be 0.6 to 1.2m more than the depth of the flocculating tank. Sedimentation with coagulation removes about 90% of the suspended solids. Now let's talk about flocculation.
Flocculation
There are different types of flocculators depending on the source of power. There are gravitational, pneumatic and mechanical flocculators. While the first is inflexible (like a baffled channel), the others are flexible.The baffled channels are examples of gravitational mixing devices. Velocity gradients are intentionally increased by changes in the direction of flow. As velocities increase turbulent condition is created which enhances mixing.
The pneumatic flocculators involve the injection or diffusion of compressed air into water. As the air is injected it expands isothermally, thereby effecting mixing. In the mechanical flocculators turbines, paddles or propellers are used to achieve mixing. Turbines consist of flat blades attached by a connecting radius arm to a vertical or horizontal shaft.
They operate at the speeds of 10 to 15 rpm. The paddles have blades which are attached directly to vertical or horizontal shafts and rotated at 2 to 15 rpm paddle flocculators are the most widely used in modern treatment plants. The shaft may be horizontal or vertical. In propellers, the blades are mounted on a vertical or inclined shaft and are rotated at 150 to 1500 rpm. Propellers are mainly used in flash mixers. The operate at the speed of 10 to 15 rpm.
Flocculation is affected by the total power input, properties of the turbulence field, and the residence time and distribution of the coagulants in water. It is directly proportional to velocity gradient (G ) produced in the treated water.
I believe we now know the concept of flocculation. Now let's see how the flocculant particles settle.
Settling of Flocculant Particles
The settling of properties of dilute suspension of flocculants differ from those of individual particles, in that the flocculating properties of the suspension must be considered along with the settling characteristics of the suspension. In flocculant sedimentation, the opportunity for particle contact increases as the depth of the settling vessel increases. As a result, the removed suspended matter depends not only on classification rate but on depth as well.The settling column of 130mm - 200mm diameter is constructed with sampling points at different heights. The column is filled with the suspension having uniform concentration (well mixed) throughout the depth. The suspension is allowed to settle under quiescent conditions. Samples are taken from a particular depth at different intervals of time and the concentration of particles in each case is determined. At any sampling depth, only those particles whose settling velocities are less than h/t will be found in suspension, where h = sampling depth and t is the settling time.
Conclusion
Coagulation and flocculation are important processes in water treatment (Drinking water and wastewater treatment), for a water to be treated thoroughly, it must pass through the process of coagulation and flocculation. With coagulation to destabilize particles through chemical reaction between coagulant and colloids, and flocculation to transport the destabilized particles that will cause collisions with floc.
Reference
[1] Flocculation
[2] Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment
[3] Flocculation and Sedimentation Water Treatment
[4] Flocculation/Clarification
[5] Coagulation and Flocculation -emis
[6] Coagulation ( water treatment) Wikipedia
[7] Difference between Coagulation and Flocculation
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpeg)
Also if i may add Coagulation and flocculation are used to remove colour, turbidity, algae and other micro- organisms from surface waters.
Thanks for sharing this.