Water Treatment Process
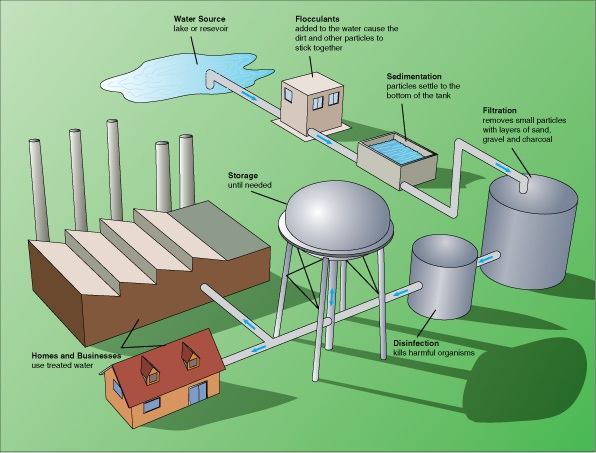
Illustration of a typical drinking water treatment process, source : Wikimedia commons
Water treatment is essentially a process of water purification and it is often very necessary because water naturally occurs in contaminated form. Potable water must be free of pathogenic organisms, toxic substances and an excess of mineral and organic material. The impurities in water must be below certain limits or be removed before using the water for domestic or industrial purposes. This means that with the exception of unusual situations, water must be treated. To be attractive to customers, water should be free from colour, turbidity and odour, it should contain sufficient oxygen and be acceptable in taste.
Provision of water supply sufficient to meet the daily needs of customers will greatly help decrease the incidence and most worm infections.
Method of Treatment
Water is subjected to treatment depending on its intended use such as domestic, industrial, agricultural, recreational or navigational uses. In addition, the level of treatment is affected by the nature and extent of contaminants in the water. Groundwater, for example, which is often free from suspended solids and bacteria may need only disinfection and aeration-disinfection to counteract possible pollution of the water along the the distribution, and aeration for odour and colour removal. River water, on the other hand, which may be subjected to heavy pollution (high bacteria content, high suspended solids, etc) will require elaborate treatment. An impounded reservoir water can be used after disinfection only if the catchment area is well managed and proper sanitary control is exercised.
Water Treatment Units and Applications
Water treatment units or processes are the screen, plain sedimentation, coagulation and flocculation, secondary sedimentation, filtration ,disinfection, aeration, chemical precipitation and ion exchange(e.g zeolite bed).The screen is used for removal of floating matter. Water from lakes, rivers or the ground passes through a screen as it enters the water treatment plant. If the water source is from the river or lake, the screen keeps out plants, wood and fish.
The plain sedimentation is used for the removal of fine discrete particles which are allowed to settle under gravity and then be removed.
The coagulation and flocculation is used for the addition of some chemicals to coagulate the finer and lighter flocculent materials which cannot settle under plain sedimentation. By allowing them to form a larger mass (flocs) they can settle. The water treatment plant workers add alum and other chemicals to the water, which cause tiny sticky particles, or floc, to form.
The secondary sedimentation is used for the settling of tank with short detention time where the flocculent materials that have come together in coagulation and flocculation process, settle down and are then removed.
Filtration is employed to remove very fine particles and colloidal matters which might have escaped from the sedimentation tank. Some microorganisms are also removed by filtration. The filter is usually constructed of porous materials such as zoned graded sand and gravel.
The disinfection process is necessary because the effluent from the filter may still contain some bacterial. Disinfection may be achieved by chlorination, ozonation or sonozone process. And also the use of UV radiation to kill potentially harmful microorganisms and pathogens in the water.
Aeration process is introduced because water which has been treated by sedimentation, filtration and disinfection will be safe but not necessarily attractive. Aeration unit removes odour and colour (iron and manganese) by mixing and exposing water to air. Aeration can be created through hydraulic jump.
The chemical precipitation is used to remove such chemicals in water like iron, manganese and hardness.
The Ion exchange process also achieves the removal of hardness by exchange of ion.
There also some other treatment processes that might be applied; for example, fluoridation (addition of fluorides in solution) for teeth care.
The unit operations designed here are aimed at successively removing smaller suspended matters and sand from the wastewater. Leaves, coarse solids and other sizeable clogging substances are removed by screening.
Water Treatment Plant Failure
Water treatment plants can stop functioning, as a result of poor maintenance, power shutdown, inability to withstand and treat high flow of water. When it fails the impact reaches a large number of persons.When a water treatment plant fails the users of the water can only deal with the situation by purchasing water filtration systems or tablets.
Modern engineers often design larger volume than expected as to avoid plant failure due to high flow of water for treatment. And carry out routine check up as to ascertain when the plant is due for maintenance, an as well provide the needed auxiliary devices and machines that can be replaced immediately while they carry out maintenance. As to avoid total failure.
Conclusion
Clean, safe water is essential for health, hygiene and the productivity of our community.
The basic principles of water treatment are the same. Though water treatment process or procedure may vary slightly based on the technology of plant and the water it needs to process (Drinking water or wastewater).
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it more acceptable for a specific intended purpose. The intended purpose could be for drinking, industrial water supply, river flow maintenance, irrigation, water recreation or many other uses. The essence of water treatment is to remove contaminants and unpleasant components, or to reduce their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its intended purpose.
Reference
[2] Water Treatment -Wikipedia
[3] five steps of water purification
[5] Water Treatment Plant Process -canon city
[6] Wastewater Treatment Fact Sheet
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here

.png)
Good info brother. I like this info and post. Regard forum Indonesia
This is very educative and informative.
I will like to know what it would cost to have this sort of setup in the home
Setting up a water treatment plant at home is expensive. I can't say the exact cost. But I know water filtration systems or tablets are not expensive. It is used when there is no water treatment plant. And is affordable.
Thanks for your feedback!
I know after boiling water it is free from every impurities.... Can it be compared to the method explained above?
No