Decentralized Applications Steemit Crypto Academy Season 4 - Homework Post for Task 8
I'll be giving answers to question 1 of task 8
What are dApps? Explain the working system of dApps? What are the differences between dApps and other applications? Explain the advantages and disadvantages of dApps? How can dApps developers promote their apps? What should we pay attention to when using dApps? How do we find the information of a DApp that we want to know? Provide the steps (Screenshot required).
What are dApps

Decentralized applications, or Dapps, are applications that are not centralized. They look and work like regular apps, but they're run on a peer-to-peer network like a blockchain.
Decentralized operations (dApps) are digital operations or programs that live and performance on a blockchain or peer-to- peer network of computers rather of one computer, and are independent of a single authority's oversight and control.
This means that the network is not controlled by any single person or entity. Other important characteristics includes;
- It must be open-source and self-contained.
- Its records and data must be accessible to the general public.
- To keep the network safe, it must employ a cryptographic token.
Unlike traditional programs, DApps run their backend law on a decentralized peer-to- peer network. A DApp's frontend law and stoner interfaces can be developed in any language that can communicate with the backend. Its frontend can also be hosted on decentralized storehouse systems similar as Swarm or IPFS.
DApps are often open-source, decentralized, rewarded by offering tokens to people that validate the DApp, and adhere to a community-defined protocol.
DApps can run on distributed computing platforms like Ethereum or Bitcoin. Applications that are not centralized are referred to as decentralized. A blockchain system keeps track of decentralized apps and executes them.
Working System of dApps
DApps can run on either a peer-to- peer (P2P) or a blockchain network. BitTorrent, Tor, and Popcorn Time, for illustration, are software that run on computers that are part of a peer-to- peer (P2P) network, where multitudinous actors are consuming, feeding, or sowing content, or doing both places at the same time.
In the terrain of cryptocurrencies, decentralized operations (dApps) run on a blockchain network during a public, open source, decentralized terrain, freed from any single authority's control or intervention
A inventor, for illustration, could design a Twitter-such like dApp and emplace it on a blockchain, allowing any stoner to post dispatches. No bone, including the app's makers, can cancel the dispatches once they have been uploaded.
The front-end and back-end aspects of dApps are identical, with the exception that the back end is built on a blockchain, with data spread over several hosting nodes.
Data is fed into the system only after all of the hosting nodes have reached an agreement (i.e. an agreement).
Because of its dispersed structure, pulling down a blockchain back-end becomes difficult in the event of malicious activities.
Differences between dApp and other Applications
Other apps have central nodes that control the application system, whereas decentralized apps do not have a central authority to control the program.
Decentralized apps are transparent and open source, making them more secure than centralized apps, which are less secure since nodes or authorities have access to everything you do.
Decentralized apps operate more quickly than centralized apps. Transactions in Dapps, for example, are lightning fast.
When developing a dApp, decent apps are more expensive than other apps.
Dapps, unlike apps, employ a variety of revenue mechanisms. Dapps aren't based on the exchange of money. Instead, they keep value in the app itself, allowing developers to issue currencies as tokens, produce value through app work, and trade the tokens on financial markets.
Internal finance models are used by Dapps not just as a means of transaction, but also as a motivator for putting in effort. This isn't to say that Dapps exist solely for the aim of making money. In fact, many Dapp development efforts are focused on finding new ways to establish user networks, such as supply chains, without relying on a large number of middlemen.Dapps run on a peer-to-peer network, obviating the need for a central server and its security issues. Hackers are more likely to attack a single central point, putting the entire program at danger. Dapps, on the other hand, have distributed security and are therefore less vulnerable to assaults.
As a new type of corporate organization, dapps have the potential to transform the way we trade currency, buy goods and services, and exchange value in general.Every business person uses an application to reach out to additional users and consumers, even through mobile phones, in order to expand their business.
However, a Dapp, or decentralized application, is one that uses the decentralization principle. i.e., there will never be a single point of control in a dapp, and authority will be diffused to everyone.To link people with an app, an intermediary is required.
However, a dapp does not require an intermediary and automatically communicates with users.An app is always under the control of its creators or owners, who can only make modifications to the code and functionality. However, a dapp alters codes and functionalities on its own, avoiding the need for developers' input.
Advantages of dApps
Censorship resistance: Because Dapps aren't under the control of any authority, it's extremely difficult for any authority or government to limit access to them.
P2P network: Dapps don't believe one point of failure within the system, like a hosting server. As a result, there are not any limitations or downtime in hosting it.
Dapps become more safe and faster inside the ecosystem as a results of open source development.
Inherent Safety: Because they often keep sensitive data on a blockchain, dApps are built to withstand any attempt to modify that data in order to steal money or censor content. Because each entry is included into the hashed value of the subsequent entry, a blockchain maintains information in a way that cannot be modified unless all of its hosts agree that the change is valid.
Effortless Cryptocurrency Integration: Many dApps use cryptocurrencies; Bitcoins launched blockchains, the technology that dApps rely on, and cryptocurrency transactions remain the most common use of the technology. By compensating content providers and incentivizing specific users to host a "full node" - a duplicate of the dApp's whole blockchain that accepts incoming transactions and possibly verifies them through "mining," cryptocurrencies can help to boost activity on the platform.
Many dApps that use cryptocurrencies build their own internal token that is unique to the platform; these are frequently based on Ethereum and integrated with its blockchain, because Ethereum's ERC-20 standard makes creating a unique token fairly simple.Corporate Intervention Resistant: Most traditional applications rely on their creators or some other central authority to handle transactions and make choices about the platform's structure, but once launched, dApps are completely self-contained.
This implies they are free of outside influence, whether it comes from developers, corporations, or the government. Because each individual user has a stake in the data and platform's management, penetrating it would require manipulating a majority of them; there are no known examples of this.Innovation Potential And Novelty: While the inherent freedom from outside intervention has made dApps increasingly popular among many of the same libertarians who first championed cryptocurrencies, they have also been used to create applications that do not require privacy or security, such as games and networks for sharing entertainment content. It will be exciting to watch how the technology develops as more software developers get interested in dApps.
Disadvantages of dApps
It's tough to fix faults or update DApps because each peer in the network must upgrade their node software.
Some applications require user identification verification (known as KYC), and because there is no central authority to validate user identity, this poses a problem when designing such apps.
They're tough to create since they rely on extremely sophisticated protocols to obtain consensus, and they have to be created from the ground up to be scalable. As a result, we can't merely build an idea and then add more features and scale it afterwards.
Because many dApps rely on open source smart contracts, hackers can exploit and hack the weaker ones. It's best to have all of your money in your wallet under your control.
When it comes to worng transactions, dapps have no authority to aid. The application's transactions are irreversible, and there is no one who can assist you. Many users will find it impossible to recover their payments as a result of this.
The dApp ecosystem contains many new ideas that consumers must learn, resulting in poor usability. Many of the Dapps that are now available are still difficult to find.
How Developers can Promote their Apps
Developers can advertise their application in a variety of ways, some of which are included below:
To advertise new dapps being built, one might post them on social media channels. Use Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, and other social media platforms, for example.
Several Dapp directories are also used to promote Dapps, such as DappRadar, dappbag, dappclap, and so on.
Decentralized applications can also benefit from airdrops, bounties, ICOs, IEOs, and STOs.
What One Should Pay Attention to When Using dApps
Crypto has a lot of amazing prospects, but it also has a lot of danger, which most people are unaware of before investing in it. There are a number of phony Dapps out there that have nice and convincing terms and conditions. High-risk Dapps are what they're called.
The majority of high-risk Dapps promise to be transparent, decentralized, and to work with well-known exchanges, but in fact they do not. They also claim to award and distribute tokens to users who join through your link.
Before investing in any of these dApp projects, thorough research is required.
How to Find Information of a dApp we want to Know
Step one: I accessed the site via this link.
Link
Step two: It directed to where i was able to access the page of the site
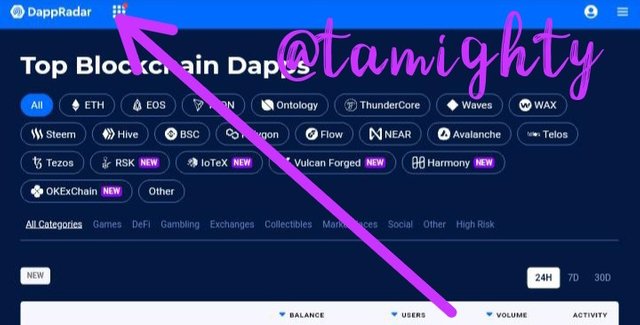
Step three: I clicked on the topmost left which brought out some list including Rankings where i could access dApps
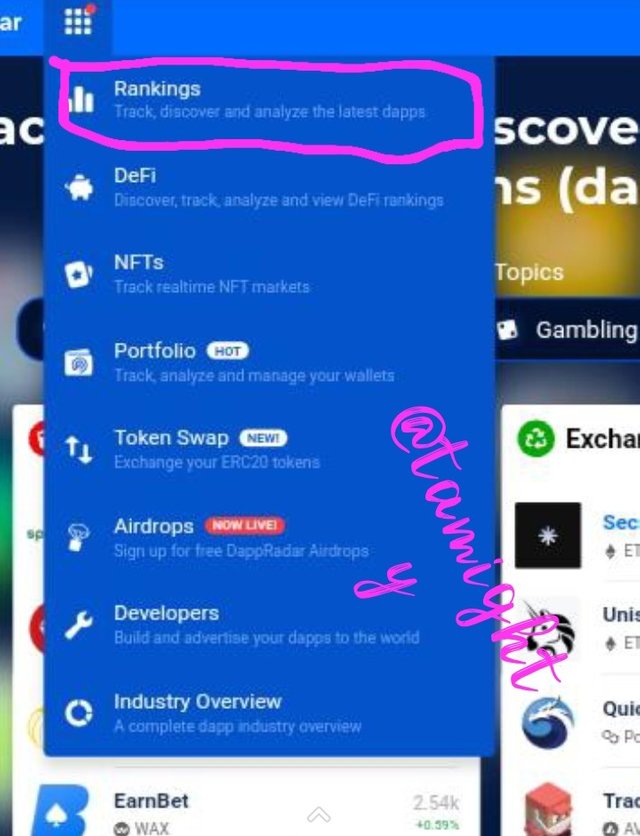
Step four: i accessed the topmost app
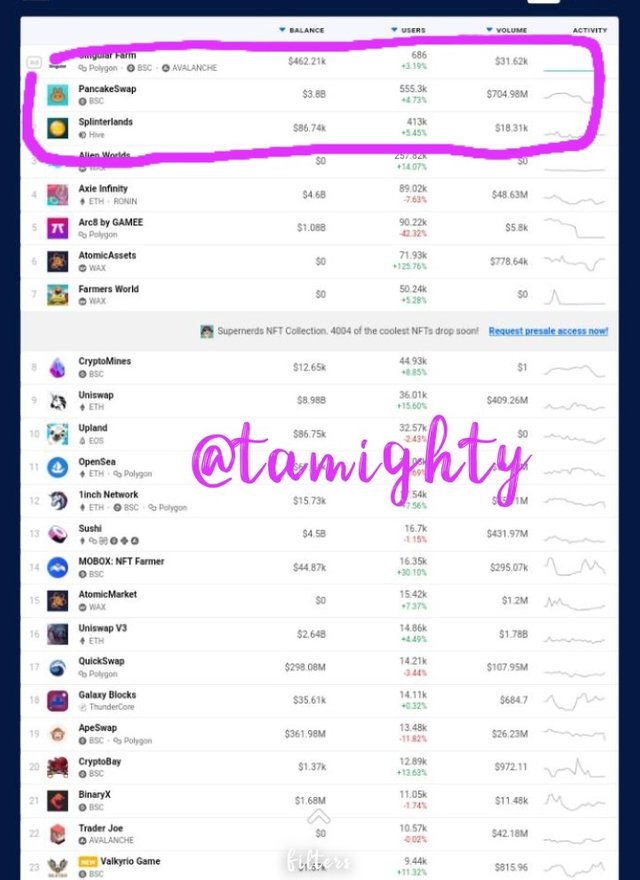
Step five: I chose the pancakeswap App and clicked open dApp button to open
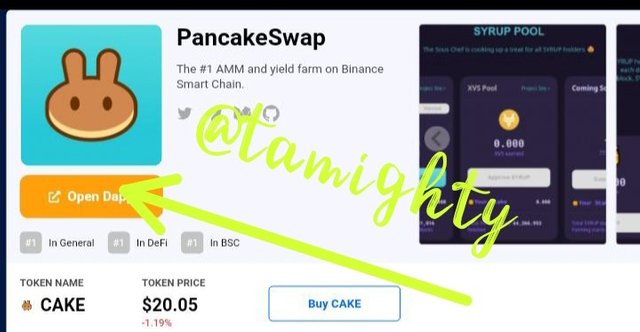
Step six:
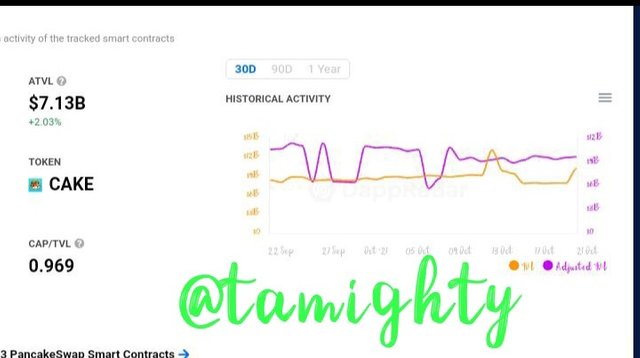
The chart above shows the rate at which it is now
Step seven:

As of present, the number of users, trades, and stake market for Pancakeswap are depicted in the graphic above.
Conclusion
This has been a while lot of research. It is indeed tasking but it worth it.
I await your response and corrections about your observations.