Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences 2|2019-03-15
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Harmonic Stability of Standing Water Waves (1903.05621v1)
Jon Wilkening
2019-03-13
A numerical method is developed to study the stability of standing water waves and other time-periodic solutions of the free-surface Euler equations using Floquet theory. A Fourier truncation of the monodromy operator is computed by solving the linearized Euler equations about the standing wave with initial conditions ranging over all Fourier modes up to a given wave number. The eigenvalues of the truncated monodromy operator are computed and ordered by the mean wave number of the corresponding eigenfunctions, which we introduce as a method of retaining only accurately computed Floquet multipliers. The mean wave number matches up with analytical results for the zero-amplitude standing wave and is helpful in identifying which Floquet multipliers collide and leave the unit circle to form unstable eigenmodes or rejoin the unit circle to regain stability. For standing waves in deep water, most waves with crest acceleration below
are found to be linearly stable to harmonic perturbations; however, we find several bubbles of instability at lower values of
that have not been reported previously in the literature. We also study the stability of several new or recently discovered time-periodic gravity-capillary or gravity waves in deep or shallow water, finding several examples of large-amplitude waves that are stable to harmonic perturbations and others that are not. A new method of matching the Floquet multipliers of two nearby standing waves by solving a linear assignment problem is also proposed to track individual eigenvalues via homotopy from the zero-amplitude state to large-amplitude standing waves.
Static structures of strained carbon chains:DFT-modeling vs classical modeling of the chain with Lennard-Jones potential (1903.05423v1)
George Chechin, Victoria Lapina
2019-03-13
We proved earlier that in the strained monoatomic chains with Lennard-Jones potential there can exist an equilibrium static bi-structure, which corresponds to N - 1 equal short interatomic bonds and one long bond with inversion in its center (N is the number of atoms of the chain). In the present work, we investigate with the aid of the density functional theory (DFT modeling) similar structures that can exist in the strained carbon chains. In contrast to the Lennard-Jones model, the bi-structures in this case are inhomogeneous (they have short bonds of different lengths) and appear abruptly when the strain exceeds a certain critical value
as a result of a hard bifurcation of the equilibrium state (an analogue of the first-order phase transition). Such a bifurcation is associated with two different parts of potential, in which the Lennard-Jones forces can be quite small (this is the vicinity of the potential minimum and the potential tail) and, therefore, the forces acting on the particle between the long and short bonds can be equal. Since practically all interatomic potentials possess such features, the above bifurcation is universal, i.e. it must occur for any monoatomic chain. We have studied in detail the properties of the above structures, in particular, the behavior of their parameters with increasing N. With the help of DFT-modeling, the electron density of the above structures near the bifurcation point is investigated.
Nonlinear management of topological solitons in a spin-orbit-coupled system (1903.05279v1)
H. Sakaguchi, B. A. Malomed
2019-03-13
We consider possibilities to control dynamics of solitons of two types, maintained by the combination of cubic attraction and spin-orbit coupling (SOC) in a two-component system, namely, semi-dipoles (SDs) and mixed modes (MMs), by making the relative strength of the cross-attraction, gamma, a function of time periodically oscillating around the critical value, gamma = 1, which is an SD/MM stability boundary in the static system. The structure of SDs is represented by the combination of a fundamental soliton in one component and localized dipole mode in the other, while MMs combine fundamental and dipole terms in each component. Systematic numerical analysis reveals a finite bistability region for the SDs and MMs around gamma = 1, which does not exist in the absence of the periodic temporal modulation ("management"), as well as emergence of specific instability troughs and stability tongues for the solitons of both types, which may be explained as manifestations of resonances between the time-periodic modulation and intrinsic modes of the solitons. The system can be implemented in Bose-Einstein condensates, and emulated in nonlinear optical waveguides.
Dynamics and stabilization of bright soliton stripes in the hyperbolic-dispersion nonlinear Schrödinger equation (1812.02260v2)
L. A. Cisneros-Ake, R. Carretero-Gonzalez, P. G. Kevrekidis, B. A. Malomed
2018-12-05
We consider the dynamics and stability of bright soliton stripes in the two-dimensional nonlinear Schr"odinger equation with hyperbolic dispersion, under the action of transverse perturbations. We start by discussing a recently proposed adiabatic-invariant approximation for transverse instabilities and its limitations in the bright soliton case. We then focus on a variational approximation used to reduce the dynamics of the bright-soliton stripe to effective equations of motion for its transverse shift. The reduction allows us to address the stripe's snaking instability, which is inherently present in the system, and follow the ensuing spatiotemporal undulation dynamics. Further, introducing a channel-shaped potential, we show that the instabilities (not only flexural, but also those of the necking type) can be attenuated, up to the point of complete stabilization of the soliton stripe.
Statistical properties of nonlinear stage of modulation instability in fiber optics (1903.05190v1)
Adrien Kraych, Dmitry Agafontsev, Stephane Randoux, Pierre Suret
2019-03-12
We present an optical fiber experiment in which we examine the space-time evolution of a modulationally unstable plane wave initially perturbed by a small noise. Using a recirculating fiber loop as experimental platform, we report the single-shot observation of the noise-driven development of breather structures from the early stage to the long-term evolution of modulation instability. Performing single-point statistical analysis of optical power recorded in the experiments, we observe decaying oscillations of the second-order moment together with the exponential distribution in the long term evolution, as predicted in [D.,S. Agafontsev and V.,E. Zakharov, Nonlinearity {\bf 28}, 2791 (2015)]. Finally, we demonstrate experimentally and numerically that the autocorrelation of the optical power
exhibits some unique oscillatory features typifying the nonlinear stage of the noise-driven modulation instability and of integrable turbulence
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
Quantum Critical Dynamics of a Heisenberg-Ising Chain in a Longitudinal Field: Many-Body Strings versus Fractional Excitations (1903.05492v1)
Zhe Wang, M. Schmidt, A. Loidl, Jianda Wu, Haiyuan Zou, Wang Yang, Chao Dong, Y. Kohama, K. Kindo, D. I. Gorbunov, S. Niesen, O. Breunig, J. Engelmayer, T. Lorenz
2019-03-13
We report a high-resolution terahertz spectroscopic study of quantum spin dynamics in the antiferromagnetic Heisenberg-Ising spin-chain compound BaCo
V
O
as a function of temperature and longitudinal magnetic field. Confined spinon excitations are observed in an antiferromagnetic phase below
K. In a field-induced gapless phase above
T, we identify many-body string excitations as well as low-energy fractional psinon/antipsinon excitations by comparing to Bethe-Ansatz calculations. In the vicinity of
, the high-energy string excitations are found to be dynamically dominant over the fractional excitations.
Exact 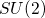 symmetry and
symmetry and  -pairing ground states in interacting fermion models with spin-orbit coupling (1901.06914v2)
-pairing ground states in interacting fermion models with spin-orbit coupling (1901.06914v2)
Kai Li
2019-01-21
We generalize the
-pairing theory in Hubbard models to the ones with spin-orbit coupling (SOC). Despite the broken
spin symmetry, the
pairing reveals an
pseudospin symmetry in our spin-orbit coupled Hubbard model. In particular, we find that our exact results can be applied to a variety of spin-orbit coupled systems, whose noninteracting limit can be a Dirac semimetal, a Weyl semimetal, a nodal-line semimetal, and a Chern insulator. We then focus on a Dirac-semimetal Hubbard model with additional interactions and establish the stability regions in parameter space where the
-pairing states as well as charge-density-wave states can be constructed as exact ground states. The basic idea of the exact solution is to make the Hamiltonian frustration-free in some parameter regions. Our work uncovers an exact
symmetry and establishes the exact superconducting ground states in spin-orbit coupled interacting systems, which may shed new light on the physics of strongly correlated systems with SOC.
Asymptotics for the Sasa--Satsuma equation in terms of a modified Painlevé II transcendent (1903.04857v1)
Lin Huang, Jonatan Lenells
2019-03-12
We consider the initial-value problem for the Sasa-Satsuma equation on the line with decaying initial data. Using a Riemann-Hilbert formulation and steepest descent arguments, we compute the long-time asymptotics of the solution in the sector
,
constant. It turns out that the asymptotics can be expressed in terms of the solution of a modified Painlev'e II equation. Whereas the standard Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann-Hilbert problem, this modified Painlev'e II equation is related to a
matrix Riemann--Hilbert problem.
Boundary matrices for the higher spin six vertex model (1903.00274v2)
Vladimir V. Mangazeev, Xilin Lu
2019-03-01
In this paper we consider solutions to the reflection equation related to the higher spin stochastic six vertex model. The corresponding higher spin
-matrix is associated with the affine quantum algebra
. The explicit formulas for boundary
-matrices for spins
are well known. We derive difference equations for the generating function of matrix elements of the
-matrix for any spin
and solve them in terms of hypergeometric functions. As a result we derive the explicit formula for matrix elements of the
-matrix for arbitrary spin. In the lower- and upper- triangular cases, the
-matrix simplifies and reduces to simple products of
-Pochhammer symbols.
Search for CAC-integrable homogeneous quadratic triplets of quad equations and their classification by BT and Lax (1806.08511v2)
Jarmo Hietarinta
2018-06-22
We consider two-dimensional lattice equations defined on an elementary square of the Cartesian lattice and depending on the variables at the corners of the quadrilateral. For such equations the property often associated with integrability is that of "multidimensional consistency" (MDC): it should be possible to extend the equation from two to higher dimensions so that the embedded two-dimensional lattice equations are compatible. Usually compatibility is checked using "Consistency-Around-a-Cube" (CAC). In this context it is often assumed that the equations on the six sides of the cube are the same (up to lattice parameters), but this assumption was relaxed in the classification of Boll \cite{Boll2011}. We present here the results of a search and classification of homogeneous quadratic triplets of multidimensionally consistent lattice equations, allowing different equations on the three orthogonal planes (hence triplets) but using the same equation on parallel planes. No assumptions are made about symmetry or tetrahedron property. The results are then grouped by subset/limit properties, and analyzed by the effectiveness of their B"acklund transformations, or equivalently, by the quality of their Lax pair (fake or not).

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.
You got a 64.52% upvote from @brupvoter courtesy of @complexcity!