Revealing Resistors | The must know about resistors..

image source
Preview
This is all about the ideas, concepts, and information regarding resistor. Resistor is a very common electronic component and most of the time it is neglected or undervalued in a circuit construction. Undervalued in a way that when we construct a circuit some of its parameters are neglected like the wattage value, type of resistor and its resistance value. I guess it happened because not like other electronics components, resistors are can be used even if its parameter is not exactly as the circuit design. Wrong application of parameter value of resistors most of the time will not result to fatal failure.
With this, I hope the readers will be enlightened about resistors and will give value to this little component. Readers will be expecting information of resistor like its:
- usage
- construction
- types
- how to read values
What is a resistor?
A resistor is a passive two-terminal device that implements a electrical resistance in a circuit. Electrical or electronic devices are categorize into passive and active devices. It is considered as active when a device needs something to operate or has a condition to operate. Best example of active device is the diode and other semiconductor devices. Diode need a 0.7 volts to operate. Also, the relationship between current and voltage in a active device is not linear. It means that when we increase the applied voltage, to output current will not follow the increment relating to the increase voltage. For a passive device, the device does not have condition to operate. It will conduct or operate as long as there is an applied voltage for example. A resistor is passive because there is no condition or scenario that a resistor will not to conduct. The relationship between current and voltage in a passive devices are linear. It means that the voltage and current increment are in uniform value.
The current through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage across the resistor's terminal. Thus, this relationship follows the concept of Ohm's law which states:
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship
Where I is the current through the conductor in units of amperes, V is the potential difference measured across the conductor in units of volts, and R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms. The ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's terminals to the intensity of current in the circuit is called its resistance.
How can we used the resistor?
Resistors have a multiple range of applications. Here are some applications of resistor.
- reduce current flow
- Adjust signal levels
- Provide voltage drops
- Provide bias to active elements
- Divide voltages
- terminate transmission lines
- impedance matching
- test loads
What are the types of resistor?
Generally resistors are classified into two category
- Fixed resistor
- Variable resistor
These categories have sub-categories in which if we map its categories it will look like this.
- Fixed resistor
1.1 Carbon Composition Resistors
1.2 Wire Wound Resistors
1.3 Thin Film Resistors
1.3.1 Carbon Film Resistor
1.3.2 Metal Film Resistor
1.4 Thick Film Resistors
- Fixed resistor
- Variable resistor
2.1 Potentiometers
2.2 Rheostats
2.3 Trimmers
- Variable resistor
Fixed Resistor
Fixed resistor as the name implies, it has a specified value of resistance and this resistance value is can not be change. Generally, this type is very cheap and small in size and occupy less space. These are also reliable and available in ohmic values and power rating.
Carbon Composition Resistors

image source
Its composition is made from the mixture of granulated or powdered carbon or graphite, insulation filler, or a resin binder. The actual resistance of this resistor in determined by the ratio of the insulation material. The insulating powder (binder) made in the shape of rods and there are two metal caps on the both ends of the rod.
Wire Wound Resistors

image source
Commonly made by winding a metal wire, usually nichrome, around a ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass core. The ends of the wire are soldered or welded to two caps or rings, attached to the ends of the core. The assembly of this resistor is protected with a layer of paint, molded plastic, or an enamel coating baked at high temperature. Wire wound resistors make lower noise than carbon composition resistors. They are reliable and flexible and can be used with DC and Audio frequency range. Disadvantage of wire wound resistor is that they are costly and can’t be used in high frequency equipments.
Carbon Film Resistors
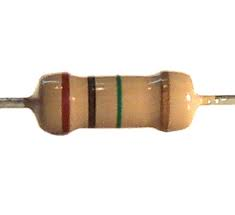
image source
This is the most common type of resistor that has been used. It contains an insulating material rod or core made from high grade ceramic material called substrate. These kinds of resistors are widely used in electronic circuits because of negligible noise and wide operating range and the stability as compared to solid carbon resistors.
Metal Film Resistors

image source
Same in construction like Carbon film resistors, but the main difference is that there is metal (or a mixture of the metal oxides, Nickel Chromium or mixture of metals and glass which is called metal glaze which is used as resistive film) instead of carbon. Metal film resistors are very tiny, cheap and reliable in operation.
Thick Film Resistors
image source
The production method of Thick film resistors is same like thin film resistors, but the difference is that there is a thick film instead of a thin film or layer of resistive material around. That’s why it is called Thick film resistors. There are two additional types of thick film resistors.
Variable resistor
This type is in contrast with fixed resistors. Variable resistors has a range value of resistance. Thus, its value can be change provided that it is under the range of variable resistor.
Potentiometers

image source
Potentiometer is a three terminal device which is used for controlling the level of voltage in the circuit. The resistance between two external terminals is constant while the third terminal is connected with moving contact (Wiper) which is variable. The value of resistance can be changed by rotating the wiper which is connected to the control shaft.
Rheoetats

image source
Rheostats are a two or three terminal device which is used for the current limiting purpose by hand or manual operation. Rheostats are also known as tapped resistors or variable wire wound resistors.
Trimmers

image source
There is an additional screw with Potentiometer or variable resistors for better efficiency and operation and they are known as Trimmers. The value of resistance can be changed by changing the position of screw to rotate by a small screwdriver.
How to read resistance value of resistor?
There are type of resistor that its resistance value is already printed in the surface. But, for the most common resistor type (carbon and metal film) it is not printed. Indicators are provided for the users to know the value like the color bands. In this case, i will show to methods of identifying the resistance value of carbon and metal film resistor.
Measuring resistance value using ohmmeter.
Ohmmeter is a electrical measuring device that can measure resistance value. Not only in resistor, but it can measure resistance in most devices. In most cases, ohmmeter is associated with other measuring devices like voltmeter and ammeter called multimeter or VOM meter.
To use it, set it to ohmmeter setting and put the two probes of ohmmeter to the terminals of resistor. Take a look in picture below to know the proper positioning of ohmmeter.

Measuring resistance with ohmmeter
Resistance using color coding.
Carbon film and metal film resistors are printed with color is its surface. These colors are called color bands which is use to identify the value of resistance. Every color represents a numerical value that can be use as a digital, multiplier and tolerance. Here are the colors with numerical value.

For the information on how to use the color codes, here is a chart that serve as a guide and reference.
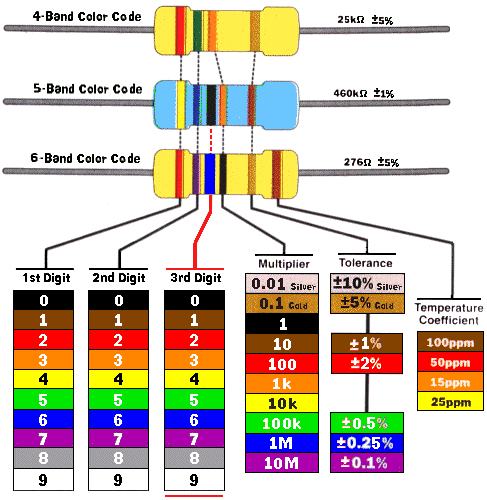
Color Coding Chart
As we see in the picture there are three options in the chart. It has 4-band, 5-band and 6-band chart that need to understand on how to use.
4-Band Color Code
This is use to identify the resistance value of resistors having four (4) color bands. The first two bands represent the digit, the third band represents multiplier and the fourth band represents the tolerance.
- 1st band - digit
- 2nd band - digit
- 3rd band - multiplier
- 4th band - tolerance
For example this resistor 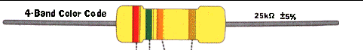
Its color bands are Red, Green, Orange and Gold. Here is the corresponding value.
- Red = 2 (digit)
- Green = 5 (digit)
- Orange = 3 (multiplier)
- Gold = (+/-) 5% (tolerance)
For final result, take not that the numerical number in multiplier means the number of zero (0). If orange as multiplier is
3, it means 1000.
[2] [5] x [1000] [(+/-) 5%]
= 25,000 or 25k (+/-) 5% ohms
5-Band Color Code
It is the same concept and process with 4-band color code. The difference now is in 5-band there are 3 digits instead of 2 digits.
- 1st band - digit
- 2nd band - digit
- 3rd band - digit
- 4th band - multiplier
- 5th band - tolerance
6-Band Color Code
There are resistor with 6 color bands. The additional color band is intended for temperature coefficient information of a resistor. Again, it is still with the same process.
- 1st band - digit
- 2nd band - digit
- 3rd band - digit
- 4th band - multiplier
- 5th band - tolerance
- 6th band - temperature coefficient
Here are my sources, these links may help you understand more about resistors.
- https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2015/01/resistor-types-resistors-fixed-variable-linear-non-linear.html
- https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-2/resistors/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistor
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ohm%27s_law
- http://www.resistorguide.com/power-rating/
- http://www.resistorguide.com/resistor-color-code/
Best Regards,
@thinkingmind
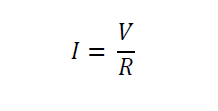
You have been upvoted by the @sndbox-alpha! Our curation team is currently formed by @jeffbernst, @bitrocker2020, @jrswab & @teachblogger . We are seeking posts of the highest quality and we deem your endeavour as one of them. If you want to get to know more, feel free to check our blog.
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by thinkingmind from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.