Learn about rainbows - physics explained
After doing this Physics explained series for a while, I have decided to ask you for topics you want to read about. @uniwhisp made a comment to my previous post how it would be fun to write about light refraction and rainbow formation. I am granting that wish and saying thank you for that lovely idea. Before we start talking about rainbows, here is the list of my previously published posts in this series:
DOPPLER EFFECT
COLD BOILING WATER
HOW DO WE SEE COLORS
EVERYTHING IS MAGNETIC!
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEAT AND TEMPERATURE
CALCULATE THE SPEED OF LIGHT USING CHOCOLATE
Since rainbow has a lot to do with light and colors, I suggest you read that post about how we see colors to get a head start. I will make some references to that post and remind you of things that we already talked about so you get a better understanding on rainbows and everything about them. Are you ready for another fun science post? Let's go!



As I mentioned, rainbows have a lot to do with light, they are made of it. The white light that comes from the Sun contains all the colors in it. HOW DO WE SEE COLORS post will explain this in detail to you. Since light is a wave (yes, it can be a particle too, do not get me started lol) we need to explain how waves behave. Reflection, refraction, and diffraction are those behaviors. A lot of "-ction's", I know, but they are fun-packed and very interesting.
Reflection
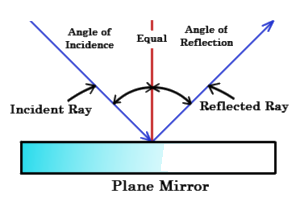
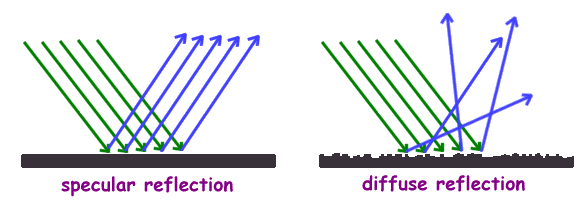
When light hits a surface and bounces off of it, we are talking about reflection. A light ray that is coming to the surface is called INCIDENT ray and the one that is bounced off is REFLECTED ray. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are the same. We have a specular reflection that happens on smooth surfaces, such as mirrors, where reflected rays all travel in the same direction, and we have a diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection happens on rough surfaces and reflected rays are scattered in different directions.
Refraction

The straw in this image is not broken or magical. It is normal straw but we see it as broken because of refraction of light. When waves pass from one medium to another, they change their direction, they bend. This happens because waves have a different speed and wavelength in different materials.
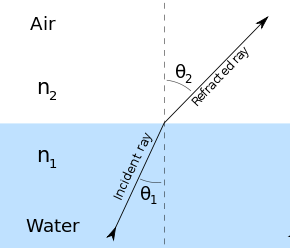
The change of direction is caused by a change in speed and here we have light traveling from air into water and slowing down because the water is a more dense substance. Water has a higher refractive index so the light bends towards the normal line.
Thanks to Snell's law, we know how the light will bend in different mediums.
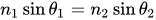
The n in this formula is the refractive index and it depends on the material. So n1 would be that of air and n2 of water in our example. The angle of refraction θ2 is less than the angle of incidence θ1. In this example, the light was going from air to water, from less dense to more dense medium. What do you think happens when it the other way around and the light goes from water to air?
As you probably guessed, the opposite thing would happen and the light would bend away from the normal line. Just remember:
- less dense to more dense medium, light bends towards the normal line
- more to less dense medium, light bends away from the normal line
Diffraction
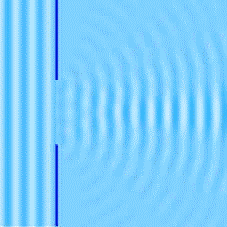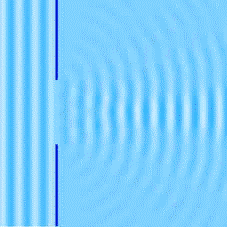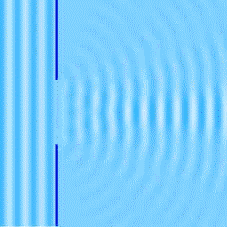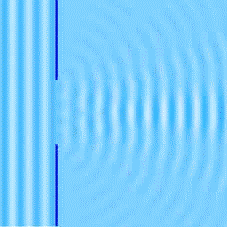
So far, we have learned that waves change direction when they bounce off a barrier (REFLECTION), and they change direction when they pass from one medium to another (REFRACTION). There is a third way for them to change their direction and it is called diffraction.
Diffraction happens when a wave passes through an opening or around a barrier in its path. In this gif image, you can see how water waves behave, light waves are very similar, they too bend after they pass through a slit.
When light passes through a slit, the longer waves spread out more than the shorter waves. If we have a monochromatic light its rays will break up into dark and light bands and if we have a white light it will break into colors of the spectrum.

Now that we know how light behaves, we can go on to rainbows and see how they form. We will even discuss some things about them that you probably did not know. Not only double rainbows but upside down rainbows and Moon rainbows but first thing's first, let's start with their formation.


Rainbows are formatted by a combination of refraction and reflection and have the dispersion of sunlight into a continuous distribution of colors. It is not a coincidence that they appear after the rain. Water is needed as much as the light source, there would be no rainbows without these two things.
After the rain, there are a lot of suspended water droplets in the atmosphere that are the medium with a different optical density than the surrounding air. Those droplets are refractors of light. They cause a deviation in the path of light as it enters and exits each drop.
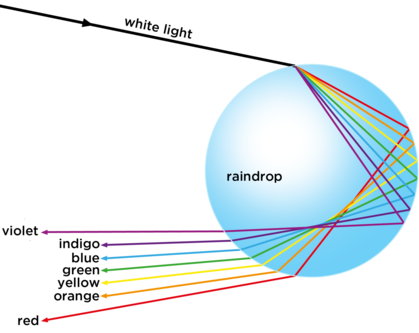
The rainbow that we usually see is called the primary rainbow. It is formed when light rays go through one internal reflection in drops of water. There are actually 3 things that happen, two refractions and one reflection. First is the refraction when light enters the drop, then the reflection inside the drop and finally, another refraction when the light leaves the drop.
The angle between the incoming light rays from the sun and the refracted rays directed to the observer's eyes is called angle of deviation and is approximately 42 degrees for the red light. Shorter wavelengths refract more so their angle is smaller. For violet is approximately 40 degrees. This is why we see red on the top of the rainbow and violet at the bottom.
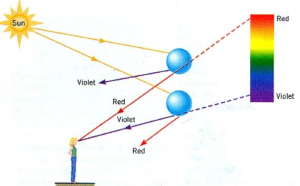
Rainbow is a circle. We see it as an arch from the ground but it is in fact a circular. You can see the whole circle if you are looking at the rainbow from the plane. Every droplet within the arc is refracting and dispersing the entire visible light spectrum. You can create your own rainbow with a water sprinkler and even see rainbows at waterfalls.
To be able to see a rainbow, you have to have your back to the Sun. When the Sun is too high in the sky, the rainbow will be below the horizon and you will not see it. The best time to see it is early morning and late afternoon when the Sun is closer to the horizon.



Probably the most interesting thing about rainbows is how whenever you see a rainow there are actually thousands of them. If you move just a little left or right you are not seeing the same rainbow from a different angle but a completely new rainbow.
A rainbow is never static.
The rainbow is not in any particular place in the sky. When you move, you will look at different raindrops and see a different rainbow. Each observer receives scattered light from different sets of raindrops so if there are nine people around you, the ten of you are seeing ten different rainbows.
There are actually more than a thousand rainbows, more than we can count because you will see one from one position and a different one from any other position.


Have you ever seen a double rainbow? It is a gorgeous thing to see and very interesting. Remember when we talked about two refractions and one reflection inside a water drop? For a double rainbow to appear there needs to be a second reflection inside a drop for that second rainbow to form.
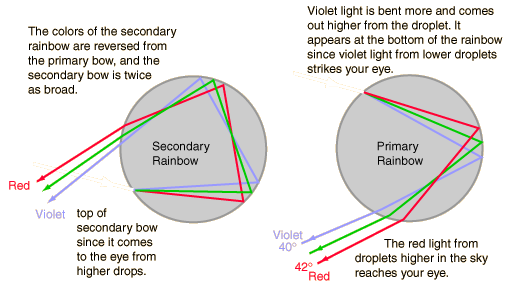
When you look at that second rainbow, its colors are reversed. Red is not at the bottom and violet is at the top. You will also notice that the second rainbow is twice as broad and not as bright as the first one. If you take a closer look, you will see that the sky between two rainbows is darker than the rest of it. This is called Alexander’s dark band after the Alexander of Aphrodisias, who described it in the early 3rd century. This part of the sky is darker because that area is devoid of rays which have passed through water drops. Light reflected from the surface of drops reaches the band but is faint and the area is darker.



Sometimes, when you look at the rainbow, you will see that it has smaller rainbows inside it. This happens when raindrops are small and their numbers and spacing change from minute to minute. Slightly different ray paths through a raindrop produce slightly different path lengths and slightly larger exit angles of those rays. There is constructive and destructive interference of each color in the spectrum as a function of that ray exit angle, and a set of bows become visible inside the primary rainbow.



Did you know that the sky sometimes smiles? Well, at least it looks like it smiles. Upside down rainbows are called circumzenithal arcs and they are more common in cold climates. These rainbows are caused by ice crystals in the air. They are not real rainbows. Circumzenithal arc is an optical phenomenon arising from refraction of sunlight through ice crystals.



Yes, there can be rainbows at night too. Remember how I explained that Moon is not a primary source of light in my post HOW DO WE SEE COLORS? Light that comes from the Sun is reflected off of Moon but that does not stop it to create rainbows just as the Sun. For the Lunar rainbow to be seen the Moon has to be full or almost full and very low in the sky. Since the sky has to be pretty dark, this all leads to Lunar rainbows being visible 2 to 3 hours before sunrise, or 2 to 3 hours after sunset.


And there you go, now you know almost everything about rainbows. I hope you found this post interesting and if you want to learn more, check out the following links.
References:
On the Physics of Rainbow, by Federica Volpi
Lunar rainbows from wiki
Rainbow Light Paths
Dispersion: The Rainbow and Prisms
Refraction of light
Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction
Color - Diffraction And Interference
Rainbow Formation
Weird rainbows
Until next time,
KEEP YOUR SMILE ON
and respect your inner genius!

If you are interested in something physics (or science in general) related, tell me and I would be happy to make a post about it and explained it. Promoting science and making it understandable gives me great joy, I would be happy to help you.

Image sources:
- cover image is from unsplash.com and made by alaindphoto
- lunar rainbow is from wikipedia and can be found here
- upside down rainbow is from physics.org <a href="http://www.physics.org/article-questions.asp?id=58>here
- image of two raindrops is from Rainbow Light Paths cites in the list of references
- small rainbow image in my titles is from Free Clip Art Library
- blue sky with rainbow is from pixabay and made by Kevin_John_Mauricio
- reflection off of plane mirror is from wikimedia and can be seen here
- glass with a straw is from Index of Refraction
- specular and diffuse reflection is from Behavior of Light as a Wave
- Snell law is from wikipedia and can be found here
- blue raindrop is from The Physics Behind Rainbow Formation
- gif image of waves is from wikipedia and can be found here
- supernumerary rainbow is from wikipedia and can be found here
- rainbow formation is from Dispersion
- dffraction of light is from Diffraction of light and separation of its colors
- the bitmoji is well... my bitmoji. Get yours at https://www.bitmoji.com/
PROUD MEMBER OF:



@steemitbloggers
- lunar rainbow is from wikipedia and can be found here
- upside down rainbow is from physics.org <a href="http://www.physics.org/article-questions.asp?id=58>here
- image of two raindrops is from Rainbow Light Paths cites in the list of references
- small rainbow image in my titles is from Free Clip Art Library
- blue sky with rainbow is from pixabay and made by Kevin_John_Mauricio
- reflection off of plane mirror is from wikimedia and can be seen here
- glass with a straw is from Index of Refraction
- specular and diffuse reflection is from Behavior of Light as a Wave
- Snell law is from wikipedia and can be found here
- blue raindrop is from The Physics Behind Rainbow Formation
- gif image of waves is from wikipedia and can be found here
- supernumerary rainbow is from wikipedia and can be found here
- rainbow formation is from Dispersion
- dffraction of light is from Diffraction of light and separation of its colors
- the bitmoji is well... my bitmoji. Get yours at https://www.bitmoji.com/
PROUD MEMBER OF:



@steemitbloggers

Why are there so many songs about rainbows?
Rainbows are visions but only illustions and
rainbows have nothing to hide...
Someday you'll find it
the rainbow connection
the lovers, the dreamers and me
Again a lovely post and loved the scientific approach this time
What a lovely poem, thank you for sharing such a beauty 💚
Wow so many facts about rainbows.
Something I didn't know was about the double rainbows and how the colors are reversed.
This comment was made from https://ulogs.org
I am glad you found it interesting, thanks for reading 💚
By the way I don't know you've ever seen the double rainbow viral video from some years ago... What does it meeeaan? It went viral all over youtube and even songs were spawned from it
A man saw and filmed a double rainbow, he was so happy and excited and screaming. It seemed to me he had a rainbowgasm lol. Cute, check it out :D
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 4 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 17 SBD worth and should receive 185 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigHey @zen-art, I wish you had been my science teacher growing up :)
That was a lovely thing to read this morning. I was just drinking my coffee and wow, you just made my day honey 💚💚💚
awww @zen-art, I'm so glad. That's very sweet of you to say! ❤️
Following you.

I stumbled upon you by following a link from @yidneth.
I saw all you science posts. Finally, someone here that makes sense after seeing all that bullshit from flat-earthers and the rest of the kranks.
I know this stuff you post, but it's always refreshing to see someone explaining the "magic" in physics.
Keep it up.
Joe
@joe.nobel
science fiction, fantasy, erotica
Hihihihi, flat-earthers hihihihi. Have you seen this?
I can't stop laughing!
Does rainbow really have seven colour?? I know its silly question but i really have doubt.
There are actually about a million separate colors in a rainbow and how many of them can you see depends on your eyes (the cones in your eyes). There are no clear boundaries between the colors so we can not really count them. We say seven (some say six) but that is not a precise answer. You can even answer yourself. How many colors are in this picture? Seven? Nope :D

Yay! Thank you for doing this! Refraction is one of my favorite physics topics. :)
Thank you for making me do it 💚
Very nice explanation! I remember someone asking if understanding how something like a rainbow is created ruins the beauty of the thing itself. I would have to say, the beauty of the rainbow leads us to discover the underlying elegance of the universe and physics that govern it. It remains beautiful but shows us the path to something even more elegant!
Why would it ruin the beauty? This way I can know where that beauty comes from and admire that too. And I have to say, that one sentence of yours, with the underlying elegance, is the phrase of the day. 💚
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by zen-art 💚 from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.