Thermodynamics Review Problems for Mechanical Engineering Students | Series 2
Hi folks!
This is the 2nd series of my "Thermodynamics Review Problems for Mechanical Engineering Students" and without further ado, allow me to present two review problems for today's series.
Review Problem 1
A 2 kilogram mass of oxygen expands at a constant pressure of 172 kilo-pascal (kPa) in a piston cylinder system from a temperature of 32 degree Celsius to a final temperature of 182 degree Celsius. Determine the work done.
For this review problem, the formula for obtaining the work done at constant pressure is expressed in terms of W = P (change in volume).And since we're not provided with the values of the volume during the initial and final state of the gas, we would be using the relation from the universal gas constant which is mathematically expressed by the formula PV = mRT wherein; P is pressure, V is volume, m is either in terms of mol or in terms of kilograms for SI units or pounds for English units, R is the universal gas constant of a gas and lastly T is the absolute temperature which is expressed in terms of degree Kelvin (K) for SI units or degree Rankine (R) for English units. With that the formula for obtaining the work done by the gas would be simplified to W = mR (change in Temperature).
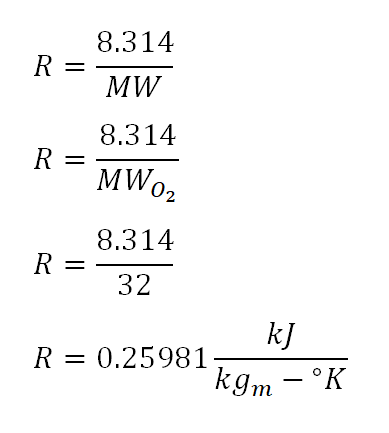
Since we've obtained the R for oxygen gas, we can now obtain the work done by the gas during change of state. In the photo below, the computed work done by the oxygen gas is equal to 77.94 kilo-joule (kJ).
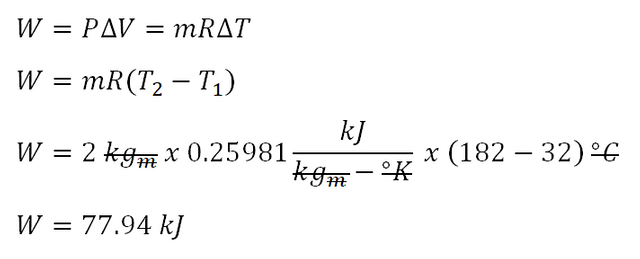
Review Problem 2
While the pressure remains constant at 689.5 kilo-pascal (kPa) the volume of a system of air changes from 0.567 cubic meters (m3) to 0.283 cubic meters (m3). Determine the heat that is added/rejected.
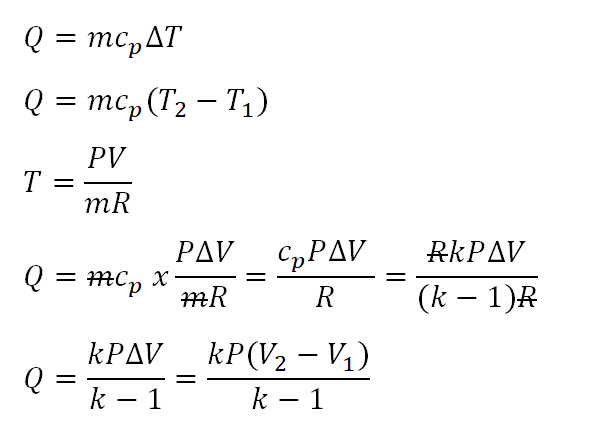
With the above derived formula, we can now obtain the heat that is either added/rejected by the air. In the photo below, the heat was found to be - 685.36 kJ and that signifies that the heat is rejected by the air.
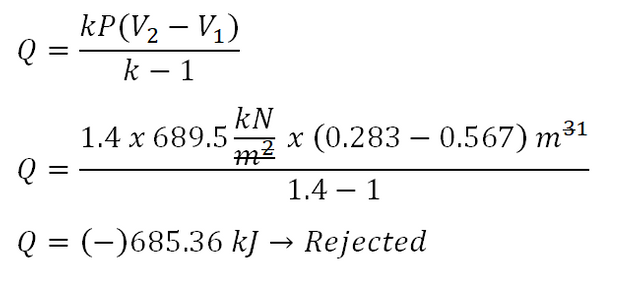
For previous series, see:
