Internal Combustion Engine
Internal combustion Engine:

Systems that constitute an engine

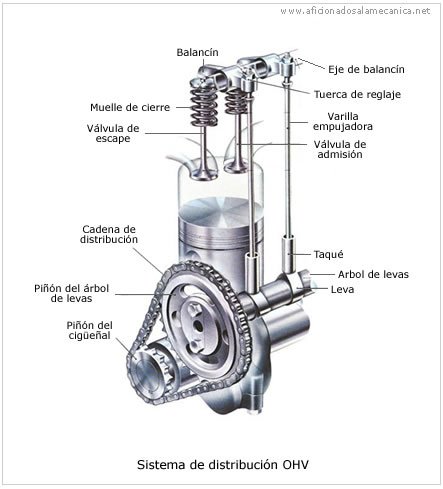
Distribution system: It is a set of parts that regulate the entry and exit of gases in cylinder.
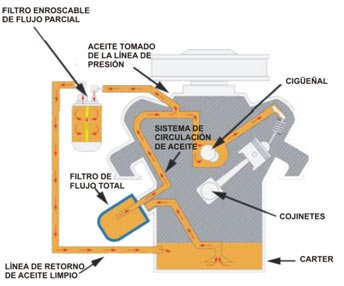
Lubrication system: The main function of this is the reduce the friction between the engine parts through the application of a lubricant.
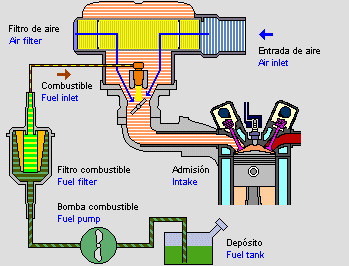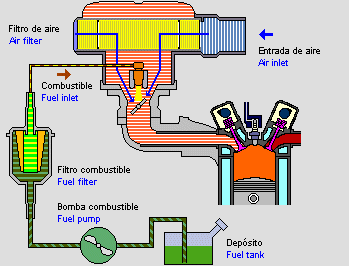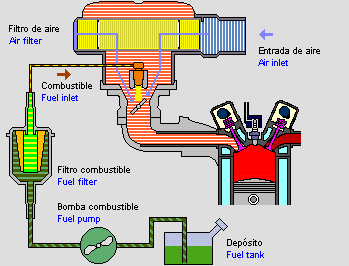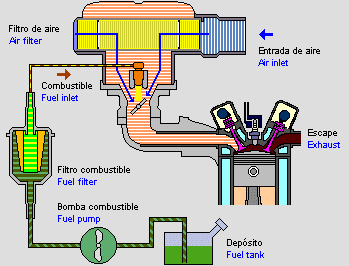
Power supply: is in charge of supplying the quantity of fuel required by the engine according to the requirements of the same.
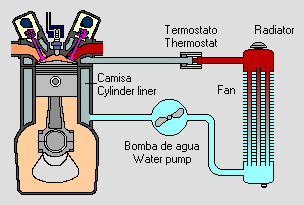
Cooling system: is in charge of evacuating the heat produced in the engine which prevents the motor from overheating.
Ignition system: is in charge of giving the first movements with the help of one electric motor.

Engines can be classified as follows:
According to the form of causing ignition or ignition of the mixture
• Ignition caused by: are the Otto cycle or gasoline.
• Using compression-ignition: are the Diesel cycle
According to the way of making the renewal of the load
• Four-stroke cycle, or in which the working cycle is completed in four races the plunger and two turns of the crank. In these engines, the renewal of the load is controlled by opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
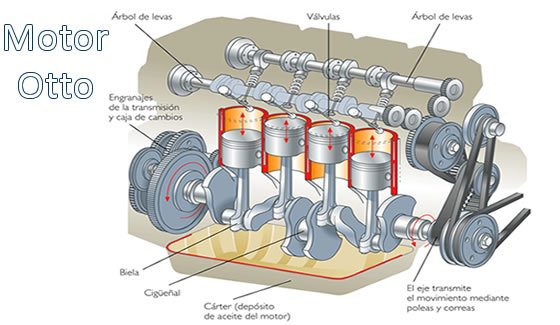
Otto engine
Cyclic Otto, whose name comes from the German technician who invented it, Nikolaus August Otto, conventional gasoline engine four-stroke used in automotive and aeronautics but also engine is known as Beau de Rochas cycle due to the inventor engine Frenchman who patented it (August, 1862)
Advantages
- efficient
2 Middleweight
Disadvantages
1 complex - highly refined fuel
Operation
- admission time - mixed air and fuel enter through the intake valve.
- compression time - the mixture air/fuel is compressed and ignited by the spark plug.
- time of combustion - the fuel ignites and the piston is pushed downwards.
- time of exhaust - exhaust gases are led out through the exhaust valve.
Diesel engine
Named in honor of the German engineer born in France Rudolf Diesel, it works with a different principle and usually consume diesel. A diesel engine is an engine in which the power is produced by a high temperature which allows the compression of the air inside the cylinder of this.
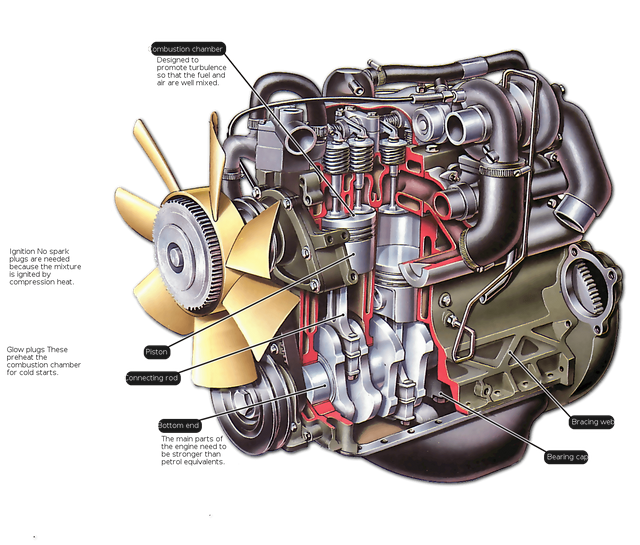
A diesel engine works by ignition of the mixture air-gas no spark. Temperature that starts combustion comes from the rise of pressure that occurs in the second engine time, compression. Diesel fuel is injected into the top of the compression chamber at high pressure, in such a way that it atomizes and mixed with air at high temperature and pressure. As a result, the mixture Burns very quickly. This combustion causes the gas contained in the Chamber to expand, pushing the piston down. Connecting rod transmits this movement to the crankshaft, which spins, transforming the linear motion of the piston into a rotational movement.
This engine is internal combustion and it can operate under two or four-stroke cycle. Its Foundation is based on the entry of air, which is compressed to high ratios of the order of 16 to 22:1, which causes the combustion"(Diesel, 1893). That described in detail the operation of the engine. However, it was not until 1898 when finally Diesel saw fulfilled his dream, personally presenting his first four-stroke engine diesel-powered and cooled by water in Munich. It was globally presented by own Diesel at the international fair in Paris in 1900.
Advantages
- low emission
- high torque
- lower fuel consumption
Disadvantages - noisy
- high cost of maintenance
- best at low speeds
Working cycles
- time of aspiration - fresh air enters the cylinder by the downward movement of the piston.
- time of compression - the piston compresses the air very strong and reaches a very high temperature.
3 stroke - diesel fuel is injected, and this turns on immediately because of the high temperature. - exhaust race - the piston pushes the combustion to exhaust gases.
Engine 2-stroke
The general principle of the two-stroke engine is the reduction of the duration of the absorption of fuel and expulsion of gases at a fraction of the times, rather than each operation requires a full time.
In two-stroke engines the mixture of fuel and air enters the cylinder through the intake port when the piston is positioned away from the cylinder head.
The first phase is the compression, which turns the burden of mixture when the piston reaches the end of the phase. Then, the piston moves backwards in the phase of explosion, opening the eject hole and allowing the gases leaving the camera.
Advantages
- simple
2 light - economic
Disadvantages
1 burning oil
2 inefficient - high vibration
The Wankel engine or rotary (4-stroke)
It was invented by Félix Wankel, this engine instead of Pistons used rotors particularly has a way of working, it is so smooth, silent and reliable, thanks to the simplicity of its design.
Like a piston engine, the newspaper uses the pressure produced by the combustion of the mixture air fuel. The difference is that this pressure is contained in the Chamber consisting of a part of the casing or stator and closed by one of the sides of the triangular rotor, which in this type of engine in lieu of the Pistons.
Advantages
- less vibration
- greater reliability
- less moving parts
Disadvantages
- reduced efficiency
- increased cost of maintenance
3 synchronization and sealing
CONCLUSION
The internal combustion engine obtains mechanical energy directly from the chemical energy produced by a fuel that burns within a combustion chamber.
Each engine acts differently from the others both so have different cycles of work that makes them more efficient and better performance to one another. Internal combustion engines causing increased pollution of the environment are gasoline engines.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
• Internal combustion engines; (www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motor_de_combusti%C3%B3n_interna.
• Types of engines; (www.slideshare.net/linkin_po/motores-de-combustion-interna-presentation
• Parts of an internal combustion engine; http://es.scribd.com/doc/7329814/Motor-de-Combustion-Interna-y-Sus-Sistemas-Presentacion.
• Performance Diesel engine; (www.lym.com.mx/t4.html);.
• Motor wankel; (www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motor_Wankel);
• Phases of Wankel engine operation; (www.bestcars.uol.com.br/tecprep/wankel-1.htm);
Greetings, see you soon! @borcast
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by borcast from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.