Bipolar Junction Transistor or BJT
In 1947 J. Barden, W. Bratterin and W. Shockley imagined transistor. The term transistor was given by John R. Penetrate. Through at first it was known as the strong state form of the vacuum triode, yet the term transistor has survived. As we will experience the subject, we will think about the transistor, basically bipolar junction transistor or BJT. These days the utilization of BJT's has declined towards CMOS innovation in the plan of IC's. The word transistor is gotten from the words "Exchange" and "Resistor" it portrays the task of a BJT i.e. the exchange of an info motion from a low resistance circuit to a high obstruction circuit. This sort of transistor is comprised of semiconductors. We realize that silicon (Si) and Germanium (Ge) are the cases of semiconductors.
Image of a printed circuit board. From PIXABAY
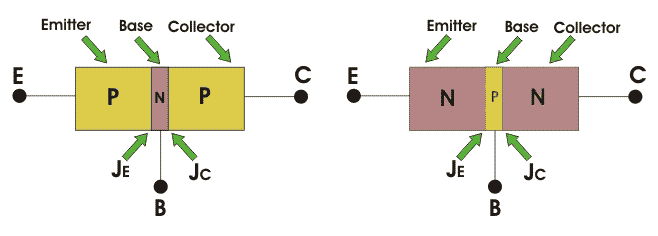
Presently, in this kind of transistor any one sort of semiconductors is sandwiched between the other kind of semiconductor. For instance, a n - sort can be sandwiched between two p-type semiconductors or comparably one p-sort can be sandwiched between two n-type semiconductors. These are called p-n-p and n-p-n transistors individually. We will talk about them later. Presently as there are two intersections of various sorts of semiconductors, this is called intersection transistor. It's called bipolar on the grounds that the conduction happens because of the two electrons and gaps.
Meaning of BJT
A bipolar intersection transistor is a three terminal semiconductor gadget comprising of two p-n intersections which can open up or amplify a flag. It is a current controlled gadget. The three terminals of the BJT are the base, the gatherer and the producer. A flag of little plentifulness if connected to the base is accessible in the enhanced frame at the gatherer of the transistor. This is the enhancement gave by the BJT. Note that it requires an outer wellspring of DC control supply to do the intensification procedure.
The essential outlines of the two sorts of bipolar junction transistors said above are given beneath.
This Image Was Created By @helen001
N-P-N Bipolar Intersection Transistor
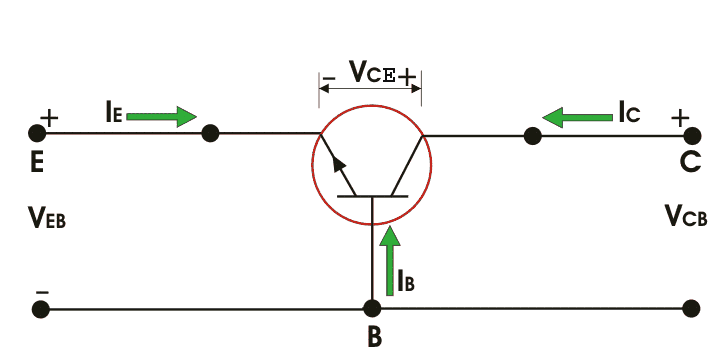
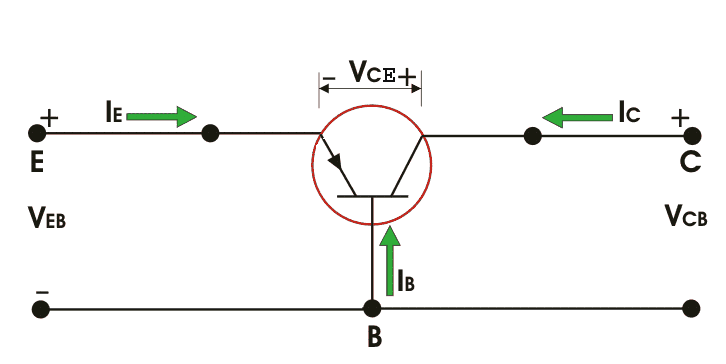
As began before in n-p-n bipolar transistor one p-type semiconductor dwells between two n-type semiconductors the outline beneath a n-p-n transistor is appearedNow IE, IC is emitter current and collect current respectively and VEB and VCB are emitter base voltage and collector base voltage respectively. According to convention if for the emitter, base and collector current IE, IB and IC current goes into the transistor the sign of the current is taken as positive and if current goes out from the transistor then the sign is taken as negative. We can tabulate the different currents and voltages inside the n-p-n transistor.
| Transistor type | IE | IB | IC | VEB | VCB | VCE |
| n-p-n | - | + | + | - | + | + |
P-N-P Bipolar Junction Transistor
Essentially for p-n-p bipolar intersection transistor a n-type semiconductors is sandwiched between two p-type semiconductors. The outline of a p-n-p transistor is demonstrated as followsFor p-n-p transistors, current goes into the transistor through the producer terminal. Like any bipolar junctiontransistor, the producer base intersection is forward one-sided and the authority base intersection is switch one-sided. We can classify the producer, base and gatherer current, and also the producer base, authority base and authority producer voltage for p-n-p transistors moreover.
| Transistor type | IE | IB | IC | VEB | VCB | VCE |
| p - n - p | + | - | - | + | - | - |
Working Principle of BJT
Figure demonstrates a n-p-n transistor one-sided in the dynamic area (See transistor biasing), the BE intersection is forward one-sided though the CB intersection is switched one-sided. The width of the consumption locale of the BE intersection is little when contrasted with that of the CB intersection. The forward predisposition at the BE intersection decreases the boundary potential and makes the electrons spill out of the producer to base. As the base is thin and daintily doped it comprises of not very many openings so a portion of the electrons from the producer (around 2%) recombine with the gaps introduce in the base locale and stream out of the base terminal. This constitutes the base current, it streams because of recombination of electrons and gaps (Note that the course of customary current stream is inverse to that of stream of electrons). The staying vast number of electrons will cross the turn around one-sided authority intersection to constitute the gatherer current. Consequently by KCL,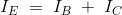
The base current is little when contrasted with producer and authority current.
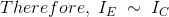
Here, the majority charge bearers are electrons. The task of a p-n-p transistor is same as of the n-p-n, the main distinction is that the lion's share charge transporters are gaps rather than electrons. Just a little part current streams because of greater part bearers and the majority of the present streams because of minority charge transporters in a BJT. Subsequently, they are called as minority transporter gadgets.
Comparable Circuit of BJT
A p-n intersection is spoken to by a diode. As a transistor has two p-n intersections, it is comparable to two diodes associated consecutive. This is called as the two diode similarity of the BJT.
Bipolar Junction Transistors Qualities
The three sections of a BJT are authority, producer and base. Before thinking about the bipolar intersection transistor attributes, we need to think about the methods of activity for this sort of transistors. The modes are- Basic Base (CB) mode
- Basic Producer (CE) mode
- Regular Gatherer (CC) mode
Every one of the three sorts of modes are demonstrated as follows
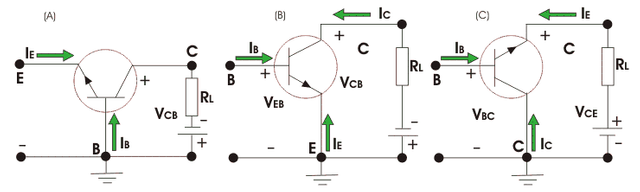
Presently going to the attributes of BJT there are distinctive qualities for various methods of activity. Qualities is only the graphical types of connections among various current and voltage factors of the transistor. The qualities for p-n-p transistors are given for various modes and diverse parameters.
Normal Base Attributes
input Attributes
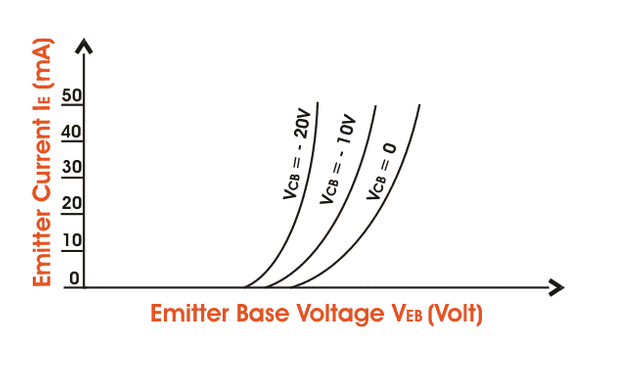
For p-n-p transistor, the input current is the emitter current (IE) and the input voltage is the collector base voltage (VCB). As the emitter - base junction is forward biased, therefore the graph of IE Vs VEB is similar to the forward characteristics of a p-n diode. IE increases for fixed VEB when VCB increases.Output Characteristics
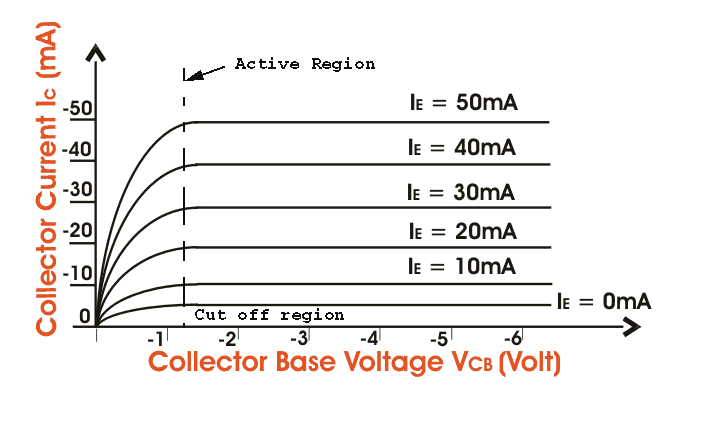
The output characteristics shows the relation between output voltage and output current IC is the output current and collector-base voltage and the emitter current IE is the input current and works as the parameters. The figure below shows the output characteristics for a p-n-p transistor in CB mode. As we know for p-n-p transistors IE and VEB are positive and IC, IB, VCB are negative. These are three regions in the curve, active region saturation region and the cut off region. The active region is the region where the transistor operates normally. Here the emitter junction is reverse biased. Now the saturation region is the region where both the emitter collector junctions are forward biased. And finally the cut off region is the region where both emitter and the collector junctions are reverse biased.Common Emitter Characteristics
Input characteristics
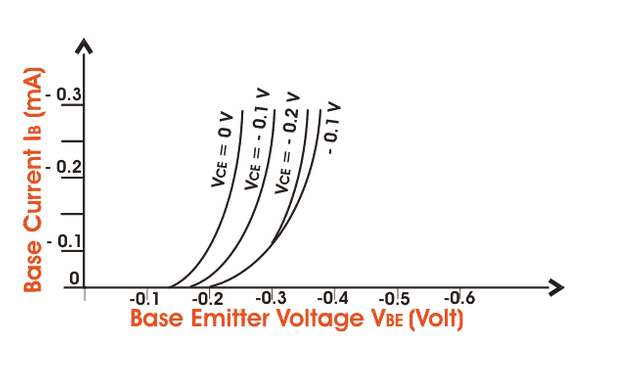
IB (Base Current) is the input current, VBE (Base - Emitter Voltage) is the input voltage for CE (Common Emitter) mode. So, the input characteristics for CE mode will be the relation between IB and VBE with VCE as parameter. The characteristics are shown belowThe typical CE input characteristics are similar to that of a forward biased of p-n diode. But as VCB increases the base width decreases.
Output Characteristics
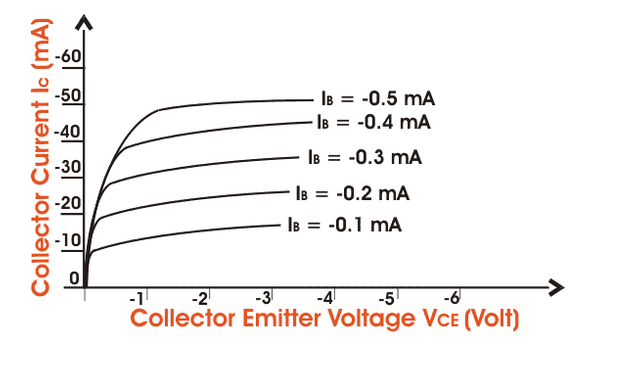
Output characteristics for CE mode is the curve or graph between collector current (IC) and collector - emitter voltage (VCE) when the base current IB is the parameter. The characteristics is shown below in the figure. Like the yield qualities of regular - base transistor CE mode has likewise three areas named (I) Active locale, (ii) cut-off districts, (iii) immersion area. The dynamic district has gatherer area switch one-sided and the producer intersection forward one-sided. For cut-off locale the producer intersection is marginally invert one-sided and the gatherer current isn't completely cut-off. Lastly for immersion district both the authority and the producer intersection are forward one-sided.
Utilization of BJT
BJT's are utilized as a part of discrete circuit composed because of accessibility of numerous kinds, and clearly due to its high transconductane and output resistance which is superior to MOSFET. BJT's are reasonable for high recurrence application moreover. That is the reason they are utilized as a part of radio recurrence for remote frameworks. Another utilization of BJT can be expressed as little flag intensifier, metal closeness photocell, and so on.
Bipolar Junction Transistor Amplifier
To comprehend the idea of Bipolar Junction Transistor Amplifier, we should look through the chart of a p-n-p transistor first.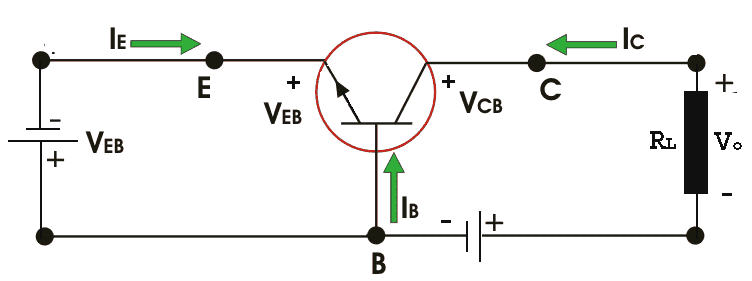
This Image Was Created By @helen001
Now as the input voltage is changed a little, say ΔVi of the emitter-base voltage changes the barrier height and the emitter current by ΔIE. This change in emitter current develops a voltage drop ΔVO across the load resistance RL, where,
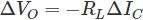
ΔVO gives the output voltage of the amplifier. There is a negative sign because of the collector current gives a voltage drop across RL with polarity opposite to the reference polarity. The voltage gain AV for the amplifier is given the ratio between the output voltages ΔVO to the input voltage ΔVi, so,
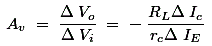
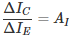
this is known as the present pick up proportion of the transistor. From the figure chart appeared above we can see that an expansion in the producer voltage diminishes the forward inclination at the producer intersection along these lines diminishes the authority current. It demonstrates that the yield voltage and the information voltage are in stage. Presently, at long last the power pick up Ap of the transistor is the proportion between the yield control and the information control
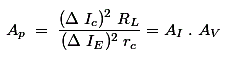
References
the creation of transistors

The guidelines I told u can be found here
oh thanks alot
though i created this post using the guideline i was given by my mentor
Who is your mentor if I may ask?
samminator
Really, he's a boss now. Anyway lemme just add a few things too. Make your post conversational and extemporaneous. Don't make it to straight forward. You need to reference your materials. You didn't write all of those from head, did you? There are a few other things I'll like to tell u. Message me on discord.