Nuclear Science (Part:7).
INTRODUCTION:
Nuclear Science is the study of the world of atoms, the term "nuclear" meaning ‘of or relating to or constituting the nucleus of an atom’. The field of particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics. Nuclear science studies how energy is released by the nuclei of atoms when they undergo certain changes, and nuclear technology is concerned with the applications of the findings to various fields— such as agriculture, industry, medicine, etc.
1:NUCLEAR POWER:
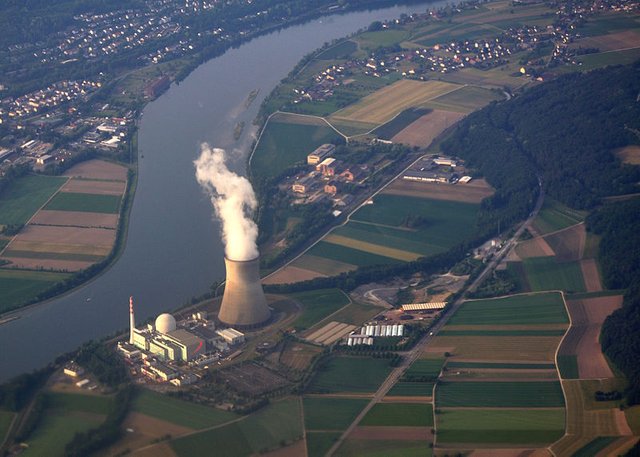

Source_Wikipedia by Hansueli Krapf
Licenec under: CREATIVE COMMONS.
Nuclear energy results from changes in the nucleus of atoms. Scientists and Engineers have found many uses for this energy, espically in producing electricity. But they do not yet have the ability to make full use of Nuclear Power. If nuclear energy were fully developed, it could supply all the world's electricity for millions of years.
A nucleus make up most of the mass of every atom and this nucleus is held together by an extremely powerful force. A huge amount of energy is concentrated in the nucleus because of this force.
Scientists first released nuclear energy on a large scale at the University of Chicago in 1942,three years after World War 2 began. This achievement led to the development of thr atomic bomc. It is since 1945 that nuclear energy has been put to peaceful uses such as production of electricity.
Einstein pointed out that if the energy of a body changes by an amount E, its mass changes by an amount "m",given by the equation,
E=mc².
The implication is that any reaction in which there is a decrease of mass, called a mass defect, is a source of energy. The energy and mass changes in physical and chemical changes are very small; those in some nuclear reactions, such as radioactive decay, are millions of times greater. The sum of the masses of the products of a nuclear reaction is less than the sum of the masses of the reacting particles. This lost mass is converted into energy.
Electricity generated from nuclear means is unique in that it inherently addresses many of the short-comings of the other means for power generation. The use of nuclear power provides answers for many problems in the areas of the environment, safety, economics, reliability, sustainability, and even waste.
➡REFERANCE:
1.Nuclear power Britannica technology.
2.Nuclear power encyclopedia energy education.
3.Nuclear power wikipedia.
2:NUCLEAR FISSION:
Source_Wikipedia by Andel License Under-Public Domain.
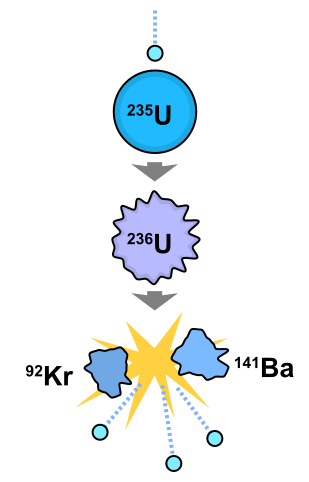
Nuclear fission is the process whereby an atomic nucleus breaks up into two or more major fragments with the emission of two or three neutrons. It is accompanied by the release of energy in the form of gamma radiation and the kinetic energy of the emitted particles.
Fission occurs spontaneously in nuclei of Uranium-235, the main fuel used in nuclear reactors. However, the process can also be induced by bombarding nuclei with neutrons becauses a nucleus that has absorbed a neutron becomes unstable and soon splits.
The mass defect is large and appears mostly as kinetic energy of the fission fragments. These fly apart at great speed, colliding with surrounding atoms and raising their average kinetic energy, that is, their temperature. Heat is therefore produced.
If the fission neutrons split other Uranium-235 nuclei, a chain reaction is set up. In practice, some fission neutrons are lost by escaping from the surface of the Uranium before this happens. The ratio of those escaping to those causing fission decreases as the mass of Uranium-235 increases. This must exceed a certain critical mass for a chain reaction to start. Critical mass is thus the minimum mass of fissile material that can undergo a continuous chain reaction. Above the critical mass, the reaction may accelerate into nuclear explosion if uncontrolled.
The Uranium-238 isotope would make an ideal nuclear reactor fuel because it is abundant in nature. But Uranium-238 nuclei usually absorbs free neutrons without fissioning. An absorbed neutron simply becomes part of nucleus. The scarce Uranium isotope U-235 is the only natural material that nuclear reactors can use to produce a chain reaction. Uranium with an abundant amount of U-235 is called enriched uranium.
➡REFERANCE:
1.Nuclear fission-wikipedia.
2.Nuclear fission-Hyperphysics_concept
3.Nuclear fission-study.com
4.What is Nuclear fission.
Read more articles related to this posts:
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Part 4
Part 5
Part 6
