This Post Is About Nothing (The Number Zero)
Zero. Zip. Zilch. Nada. Nought. Nil. Diddly squat. A great big goose egg.
This post is literally about nothing.
Zero plays a big role in our society. Without it our computers simply could not work as one half of the binary system is made of the number zero.
We are used to the number zero as a concept and as a mathematical tool but this was not always so. In fact, its invention was a very major breakthrough in both mathematics as well as philosophy.
The History of Zero
Many ancient civilizations such as the Ancient Egyptians, pre-Columbian Mesoamericans and the Chinese had some rudimentary or rough concepts of the number zero. However it was in India in the 2nd/3rd century BC that the number zero came into its true modern use and conceptual understanding.
The earliest text to use a decimal number value system with a zero as a placeholder is the Lokavibhāga which is a Jain text on cosmology dated to AD 458. The symbol for zero at that time was a dot. It is also around this time that the decimal-based numbering system notation was developed and can be traced to the Aryabhatiya (circa 500) as follows:
"from place to place each is ten times the preceding."
So, the concept of using a zero as a placeholder in the decimal numbering scheme came to life.
This math system spread from India to Arabic culture (and later Islamic culture) as they were traders and found this new math it to be incredibly useful in commerce.
The number zero however met resistance in Europe because the Romans already had their own well-established numbering system (I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, and so on). Maybe it was Empire hubris and superiority complex that caused them to dismiss this wonderful mathematical tool. Too bad for them.
The number zero eventually did get transmitted to Europe via the Moors in Spain and for this reason the numbering system has come to be known as Arabic numerals in the West.
The Roles Of Zero
The number zero has two primary roles. The first is as a placeholder in our positional numbering system.
Take the familiar base 10 numbering system in which there are ten symbols as follows, 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and 9. Once you hit 9 there is a problem as you have run out of numbers so the Indian invention to just add a 0 after the 1 to get 10 saves us from our quandary. Repeat this for every power of ten to get 100, 1000, 10000 and so on.
The second role of zero is to act as a sort of middleman in between the positive numbers and the negative numbers. Zero is neither positive, nor is it negative and in this role it acts as the number that represents nil (as in you have no money, or no sheep etc.).
Zero Can Be Dangerous!
Multiplication is just fancy addition. Three times five is just adding up the number three to itself five times over.
Conversely, division is just fancy subtraction. Thirty divided by six is just subtracting six from thirty five times in a row until nothing is left.
However any number divided by zero is a big problem and in mathematics it is not formally defined.
To illustrate this let's try to divide the number 1 by the number 0. If division is just fancy subtraction then you subtract zero from one to get one. Then you subtract zero from one to get one. Then you subtract zero from one to get one. Then you subtract zero from one to get one and so on and so forth without end.
You would be tempted to then say one divided zero is infinity because it never ends but you would be wrong and there are good reasons for this.
The first is that infinity is simply not a number, it is just a concept. Mathematicians can manipulate processes or functions that approach infinity but can never manipulate never infinity itself.
Okay, if you don't believe this then let's say we divide one by zero and equate it to infinity. Fair enough.
Let's now divide two by zero. We also get infinity. If infinity were a real bonafide number then this implies that one equals two which is a nonsensical mathematical result.
Another good example is to use calculus to determine the value of 1 divided by zero. If we take the limit of 1/x as x approaches zero from the positive side of the number scale, we will evaluate the answer to be positive infinity as can be seen in the equation below:
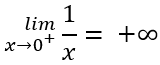
However it is equally valid to evaluate this same limit approaching from the negative side of the number scale as shown in the equation below:
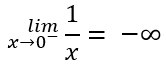
In this second case we get an answer of negative infinity. Two different answers using two different and valid approaches.
These two examples are good illustrations of why anything divided by zero is simply not definable.
Zero, Binary and Computers
The reliable old decimal number system.
It has had a good long run and is still very popular with those pesky humans but in terms of the number of digits being used on a day-to-day basis it has simply been overwhelmingly replaced by that upstart, the binary number system.
The decimal system has ten symbols but electronic circuits work best when applying only two voltages such as +5 volts or 0 volts (other voltages are used and it depends on the circuit board technology i.e TTL vs LVTTL).
So digital circuits only like two levels which corresponds to two numbers, 0 and 1.
Since there are only 2 numbers you run out of symbols very fast so the placeholder technique invented so long ago in India becomes handy, very quickly. For example the following table illustrates how you build up numbers using only ones and zeroes:
| Decimal | Binary |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 11 |
| 4 | 100 |
| 5 | 101 |
| 6 | 110 |
| 7 | 111 |
| 8 | 1000 |
| 9 | 1001 |
| 10 | 1010 |
| 11 | 1011 |
| 12 | 1100 |
| 13 | 1101 |
| 14 | 1110 |
| 15 | 1111 |
| 16 | 10000 |
| and so on | and so forth. |
In binary, every doubling needs an extra digit so the lack of symbols in binary is actually not that big of a problem. Computers also have perfect mechanical memory and do not mind performing tedious tasks so using binary really is not a showstopper.
Brief aside: Ternary computers - Digital circuits also work well with both a positive voltage, a negative voltage and a zero voltage to represent a ternary number system (i.e. 0, 1 and 2). In fact some computers like this have been developed as research projects and are thought to be more elegant but they have never caught on.
Closing Words
Imagine it was 2000 years ago and before the invention of the number zero in your local area. Let's say that the concept of zero dawns on you one day (maybe you were smoking weed) and then you starting telling people about this new thing. They would have looked at you like you were crazy.
Imagine that trying to explain to people that there is this symbol that means nothing or not having anything. Most people would think, "you can have a sheep all right but why even bother talking about not having sheep when there aren't any around. Zero sheep? What kind of nonsense is this."
However the concept of zero has proven its worth and it is the reason I can post this article using my computer and you can read it using yours.
That was a lot of words about nothing however in the end it was worth it.
Thank you for reading my post.
Post Sources
[1] What is Zero? Getting Something from Nothing - with Hannah Fry Royal Institute
[2] Problems with Zero - Numberphile
[3] The History of Zero
[4] Zero - Wikipedia
[5] Common DC Voltage Levels
[6] Ternary Computer
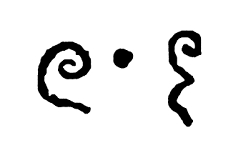
Hi @procrastilearner
We have selected your post as post of the day for our DaVinci Times. Our goal is to help the scientific community of Steemit, and even if our vote is still small we hope to grow in quickly! You will soon receive our sincere upvote! If you are interested in science follow us sto learn more about our project.
Immagine CC0 Creative Commons, si ringrazia @mrazura per il logo ITASTEM.
CLICK HERE AND VOTE FOR DAVINCI.WITNESS
Keep in mind that for organizational reasons it’s necessary to use the “steemstem” and “davinci-times” tags to be voted again.
Greetings from @davinci.witness and the itaSTEM team.
Keep up the good work and good luck with your science community project davinci.
0 is the naught-tiest number
I can always count on mathowl for the best comments.
I think another important aspect of zero are math modells. Mathematicians always need zeros. They need the zero as neutral element in groups. For example zero vector, zero matrix ...
Good point. For every post there is a natural stopping point or you lose your audience.
In addition to null sets, I wanted to also wanted to do 0^0, zero to the power of zero (hint: it too is undefined).
Not everybody stepped their nose deep into math XD.
0^0 is an interesting topic. In some models it is defined (for example polynoms) in other models not for example x^y.
Interesting subject. I never thought I would learn something from a post about nothing...Nice work!
Thank you for the nice comment.
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 6 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 12 SBD worth and should receive 101 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigNice to see you are still alive truffle pig bot. Keep up the good work.
There are much to learn from nothing, I guess.
Zerois in fact notnothing. Without it, there wouldn't be computer system as the computer is on functional thanks to programs and the language this so called machine understands iszeroandone. Its benefit goes beyond that. Think of electric circuit too.So in a nutshell;
I am @teekingtv and I write STEM.
You know nothing John Snow.
Apologies for the Game of Thrones reference.
This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!