Maintenance Engineering - An insight on Failure Pattern and How to Choose the Suitable Maintenance Technique
I welcome you once again to my blog. I appreciate your contributions and support so far. I'm glad to be back writing a STEM-related post after some days of poetry. Forgive the diverse nature of my blog, I had to finish up a poetry challenge I entered a long while ago. Well, you could treat yourself to some lines if you don't mind, you might find it interesting.
Today, I will be revisiting my hood, Engineering - specifically a very important topic in Production Engineering.
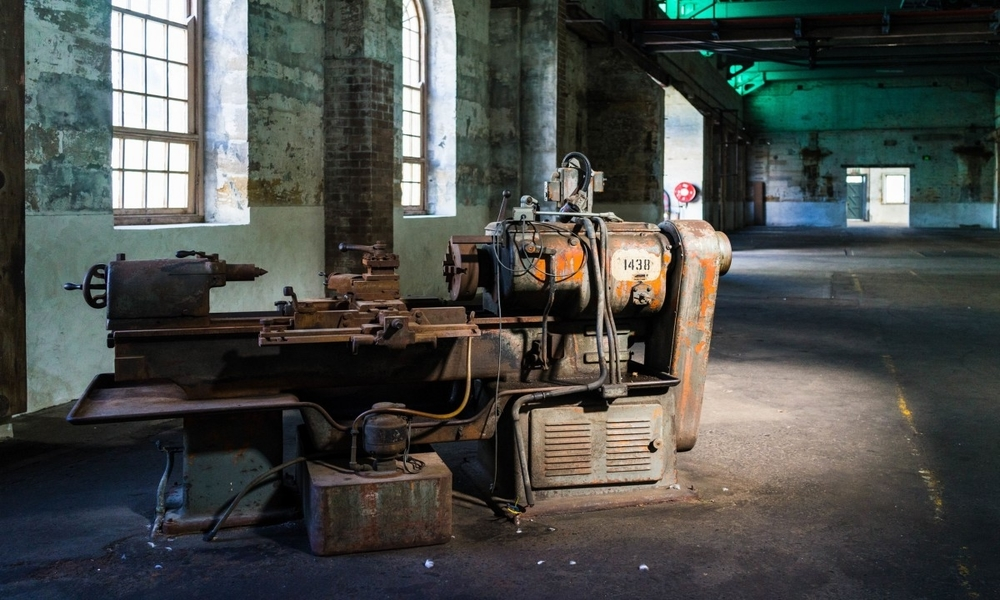
Some days ago, I spoke about my experience at a workshop I visited where they had quite an impressive number of machines in their compact layout. The only problem I noted was the lack of a functioning Maintenance routine which left them with more than half non-functioning machines lying in the workshop. Most of them are crying from the attack of corrosion as they look rusty.
In this post, I explained in details the meaning of Maintenance from a production engineer's perspective and as well the reasons why we need to have a maintenance routine in place if we are to cut down losses resulting from lack of maintenance on our machines.
I was able to explain that maintenance isn't just about "repair" as many understand it but rather a comprehensive activity that either help restore a facility to an acceptable working condition or help retain the facility in a good working condition.
An important aspect that I talked about which will form the basis of my discussion of today are the forms of Maintenance that a production engineer can employ on his facilities. I mentioned that he can either practice a planned or an unplanned maintenance routine.
I highlighted the types of Unplanned Maintenance which could prove economical in the initial stages as costs related to setting up a prior maintenance schedule would be eliminated. However, on a long run, when there are breakdowns and delays, the recurred costs may be way higher as compared to what was initially saved.
Today, my focus would be on the various types of planned Maintenance routine which is the backbone of the industries of today.
Haven't we wondered how those big machines and equipment of various industries stay in operation for a long time with minimal failure?
Don't you ever imagine the big loss that would be incurred if any of them just suddenly breakdown with no or less recovery alternative in place?
Well, I believe they are only able to keep up because their maintenance department isn't on a codeine diet.
What? Codeine?
Forgive me, I only meant that the maintenance department isn't on a "slow" but rather active and up to their task.
So, stay with me as I explain the concepts of planned maintenance and its relevance to the developing industrial world of today.
.png)
Corroded Lathe Machine - Pxhere Creative Commons CC0
Before I proceed, I will like to explain the concepts of Planned Maintenance as related to production engineering.
A Planned Maintenance routine is a comprehensive activity that includes monitoring and controlling activities enabled with the use of sensors and other monitoring means to ensure that a facility operates at a good and acceptable working condition.
The processes employed in planned maintenance involves an intentional monitoring, scheduled maintenance routines, and condition monitoring techniques so as to prevent any breakdown or failure in the system
Now that we are familiar with what planned maintenance really entails. I'll like to outline to us the need to consider planned maintenance over the unplanned maintenance.
So, why adopt Planned Maintenance?
In the previous post, I highlighted the main advantages of unplanned maintenance to be majorly initial reservation of resources such as time and cost that maintenance will take. The view from unplanned maintenance is that we would save money if we wait on the machine to deteriorate to some extent after use rather than planting a maintenance equipment right from day one when it is still considerably new. The view is that during that period when the facility is quite new, the maintenance facility employed is just a waste of resources.
But, you'll agree with me that on a long run, when this facility begins to fail, it would be difficult to measure the rate of failure, parts that need more attention and of course, big shutdown might be impending and in the end, more time and cost will be needed to save the hullabaloo.
So, a planned maintenance routine would prove more useful and significant for facilities in that:
- It saves us from the scenario of emergency shutdown and delay in production
- It assures that our machine is operated in the allowable range of operational condition
- It keeps the maintenance engineer busy and in that way, we wouldn't be losing money on an inactive workforce
- It saves us from the exorbitant carrying cost that comes with inventory stocking of spare parts for the sake of emergency breakdown
- It saves us from the loss in production level that may arise from breakdown to a critical machine.
Enough of the "why"..I'm not here to advertise. Let's move to the HOW's - the different ways of implementing planned maintenance.

So, what are the types of Planned Maintenance available to a Production Engineer
There are various ways by which planned maintenance can be implemented. There is time-based, condition based and combined maintenance available to a production engineer. The decision on which he uses is based on the type of facility and industry they exist as cost and many other factors determines which maintenance technique an industry should adopt.
So, let's talk about the various maintenance techniques we have.
Preventive Maintenance
This type of maintenance is a time-based maintenance(TBM) that focuses on using a scheduled interval of performing maintenance on the facilities. Here, after a predefined time, say, after a machine run time, a calendar time or a custom defined schedule, the machine is subjected to some maintenance activities.
This could be a daily cleaning, re-oiling, re-tightening of fasteners or other simple activities that can help keep a facility in good working conditions. The maintenance is also based on usage as much as it is based on time. One of the examples of common preventive maintenance near us is the servicing of our Air- conditioners.

Air Conditioner Servicing - Wikimedia Creative Commons CC-BY-SA-4.0 [Authored by JDCooling]
Before the end of my training, I had two maintenance sessions with a particular company which was one of our clients. We helped them service their Air-conditioner within a 3 months intervals.
Another common Preventive maintenance we do is on our cars, where we do change the lubricating oil after a specified or recommended time by the manufacturers. Small generator owners practice a preventive maintenance based on usage. After a long use of the generator, it is required of the owner to do some servicing on it to prevent a major breakdown of the generator.
If we keep looking around, we would see a lot of preventive type of maintenances which we perform on some regular interval. The main aim of Preventive maintenance is to help prevent any sudden failure. Such interval-based checks and maintenance ensures fewer breakdown and help increase the lifespan of facilities.
As important as this technique might look, we have to be sure it is the best choice for our facilities as it might actually be a waste of money and other resources for some scenario (or equipment). Hence, a production engineer needs to mind the applications with which he employs this type of maintenance.
So, what are the Suitable and Unsuitable applications of Preventive Maintenance technique?
The major decider here is cost. We have to be certain that the application we deploy this technique is actually cost-effective before adopting it.
Preventive maintenance is best suited to applications whereby there is a high likelihood of failure with increasing use. That is a facility that has critical operating functions. Here, preventive maintenance would help extend the facility lifespan as it would prevent failure of a part through regular and scheduled maintenance. Thus, such facility must be one with which the failure mode can be improved or prevented through maintenance.
On the other hand, it is not advisable to employ preventive maintenance of facilities that have a random failure mode especially failure that doesn't have to do with lack of maintenance. Such case would definitely be a waste of resources and misutilization of manpower.
So, it is of great importance to analyze the need for a maintenance technique before adopting it.

Predictive Maintenance
Forecasted Data - Wikimedia Creative Commons Public Domain
It is a condition based maintenance (CBM) that analyzes the condition of parts of a facility through inspection and diagnosis, collect the data and predict when failure might occur in the system and then devise corrective means to prevent this failure from occurring.
The major advantage of this technique is that there would be reduced maintenance schedules as it would be based on the forecasted time of failure rather than a set scheduled interval of maintenance as in preventive maintenance. Its implication thus is reduced cost and time spent on maintenance even without impending failure detected. It saves us money and time, helps predict likely failure time (from data of course, not the Oracle).
The big task in this type of maintenance will then be the cost of setting up monitoring equipment, sensors and the eventual data analysis for prediction of failure of parts so as to carry out the corresponding corrective maintenance. Specialists, as well as special machines, are required to make this happen. Thus, the Production engineer must analyze the situation well before employing this technique.
So, what are the Suitable and Unsuitable applications of Predictive Maintenance technique?
Well, as in the preventive technique, we must be clear about the effectiveness and suitability of the applications that we decide to adopt a particular maintenance technique.
Majorly, this technique is a cost-driven technique for the level of technology it requires, so, the production engineer must ensure that it is adopted only in applications where failure will be cost-effective - that is, where regular maintenance isn't necessary. It should be an application where the machine doesn't have a critical operational function whereby deterioration of parts is highly inclined to the time of usage.

Now this is where it gets more interesting
Proactive Maintenance
This is quite an interesting maintenance technique that has an entirely different approach to maintenance of a facility. Unlike the preventive and predictive techniques that are based on usage time and condition of facilities respectively, proactive maintenance focus on the root causes of failure. It tends to analyze why failure actually occurs in a facility.
It analyzes failure and it roots causes to know how to not just correct the failure or predict a failure pattern, but to perform maintenance on the processes, methods, and manner of handling of such facility right before it is put into working. We can call it maintenance of the maintenance processes.
Proactive Maintenance will analyze a facility in terms of what it is made of, where it is of the standard quality required. It analyzes the human error, which could be a poorly fixed joint or failure to carry out recommended maintenance. It also analyzes the use time of a facility - whether it is within its specified limits.
All these are put together to detect why the machine fails and is being worked on from the base stage rather than performing reactive maintenance or condition-based maintenance later.
It could be a design pattern, a wrongly executed production process or use of fake materials that results in quick deterioration of the facility, hence, causing a breakdown. So, proactive maintenance, as the name implies is an early bird that makes a stitch in time.
This technique hence helps to not just prevent the need for maintenance but to also help extend the wear-out age of the facility, thus, increasing its lifespan.
What Opportunities does the Proactive Maintenance bring to the table?
Well, without mincing words, we would agree that the proactive maintenance technique will be more favorable for an industry on a long run. It will help eliminate the need for scheduled maintenance which could be tedious and costly in a long run. It also helps to reduce the big money that would be used on facility monitoring the condition of a facility in the predictive technique.
So, basically, what the Proactive maintenance technique brings to the table is a general reduction in the cost of maintenance. It cut down costs related to the reactive or preventive methods of maintenance. Man-power and other maintenance resources are also saved and can be used in another aspect of production.

What's the next step?
After knowing the techniques to adapt to maintain our machines, what else do we need to know? I bet it is the types of failure or failure pattern possible, is the best option. This enables the production engineer to know the best way to approach the situation and decide which of the technique is more suitable.
As reported from a study by Nolan and Heap on an airline industry in 1978 where they described six possible failure pattern. It was noted that a large part of failure witnessed in a facility is usually a random one rather than dependent on the age and rate of use of the facility like we would expect.
The Failure Patterns
As reported, the common failure patterns that are possible in a system are:
- Bathtub Curve
- Wear Out Curve
- Fatigue Curve
- Initial Break-In Curve
- Random Pattern
- Infant Mortality Curve
Bathtub Curve - by @mrbreeziewrites
The bathtub curve initial stage describes a high probability of failure in the infant mortality stage when the facility is quite new. Failure here is usually due to manufacturing error, improper testing before use or use of low-quality materials. So, the failure rate is usually high before dropping as the usage increases.
This is followed, in the curve, by the Useful life period of the material that is usually characterized by a constant failure rate. Here, the facility witnesses the lowest failure probability and forms the main period where the functions of the facility are best enjoyed.
Followed by it in the curve is the Wear out Period which represents the later days of the facility usage. It is another point when the facility witnesses a progressive failure pattern owing to the wear out from usage.
The Bathtub Curve accounts for approximately 4% of failure witnessed in a facility
Wear Out Curve - by @mrbreeziewrites
This is characterized by two stages which are - a steady or constant failure rate stage whereby the facility witnesses a very low failure rate as it is considered new and less susceptible to failure.
This is followed by the wear out stage which represents the later days of the facility where failure increases progressively as a result of old age and wear out.
The Wear Out Curve accounts for approximately 2% of failure witnessed in a facility
Fatigue Curve - by @mrbreeziewrites
This is usually represented in a linear and positively increasing graph showing the transition of the failure from a low-level stage to a gradually increasing high-level failure rate.
The Fatigue Curve accounts for approximately 5% of failure witnessed in a facility
Initial Break-in Curve - by @mrbreeziewrites
The initial stage is usually a steep curve of low failure then a high jump before a constant rate of failure is reached.
The Initial Break-in Curve accounts for approximately 7% of failure witnessed in a facility
Random Pattern - by @mrbreeziewrites
Here, failure can occur at any stage of the facility lifespan.
The Random Pattern accounts for approximately 11% of failure witnessed in a facility
Infant Mortality Curve - by @mrbreeziewrites
It is characterized by an initially sharp failure rate when it is still quite new owing to some design error or installation error followed by a constant (or random) failure pattern throughout the remaining lifespan of the facility.
The Infant mortality curve accounts for approximately 68% of failure witnessed in a facility
In summary, we would see that failure in a facility can be grouped into three different headings which are;
- Age-related failures
- Random failures
- and Infant Mortality failures
So, all the Production Engineer need do is to understand which of this failure pattern is most likely to face his facilities so as to know the appropriate maintenance technique to favor at the expense of others.
Ok, I wouldn't be selfish, I'll tell us the Maintenance technique to pick for each kind of failure that exists
For Age-related failures, which are usually a result of erosion, wear or corrosion attack as the usage increases, the best maintenance techniques to keep a facility in good condition are the fixed time maintenance (say Preventive Maintenance) that includes basic cleaning and oiling, replacements, or overhauling of some parts. This will help extend the life of such facility which is susceptible to an age-related failure.
For Random failures which can't be predicted or based on a particular usage time, maintenance techniques which would detect such failure through monitoring would best suit. Some specific failure must be monitored using predictive or condition-based equipment so as to detect and diagnose the equipment for failure and corrective means are applied. Here, predictive or condition-based maintenance is best suited for this kind of failures.
For Infant Mortality failures, which accounts for the majority of failure existing, failure need not be predicted or prevented through fixed time maintenance but rather, a root failure cause must be corrected. The infant mortality failure is a function of either improper installation, below standard material usage or other design error which can be fixed before being put in operation.
When all these initial problems are eliminated, the probability of failure is greatly reduced leaving us with a facility with a constant failure rate after the elimination of the high infant mortality failure stage that existed for the facility.
So, that's it, we have our full aid in choosing a suiting maintenance technique for our facilities as related to the failure pattern inclined to it

CONCLUSION
Maintenance is undoubtedly the backbone of the industries of today. Without maintenance, many machines that enhance work for us wouldn't stay too long in operation leaving us with a constant breakdown and big loss in production level.
We have witnessed a great aspect of Production Engineering together, in terms of Planned Maintenance techniques which is the most practiced maintenance type in industries as compared to unplanned maintenance. With the failure patterns highlighted and the best suiting techniques for each failure pattern available to a Production Engineer, it shouldn't be hard for him to set up an effective Maintenance strategy for his facilities.
Thanks for your time. You're well appreciated.

REFERENCES
Ismaila, O. S., "Mechanical Maintenance". Lecture note for MCE509, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria
Adejuyigbe, S.B. (2002). "Production Management (Design, Planning, Implementation, and Control)". Topfun Publications, Akure, Nigeria
World Class Maintenance Management, Terry Wireman, Industrial Press Inc., 1990, pp. 7, 73.

If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details.

I'm a proud member of @promo-mentors where you get mentored and guided on how to make quality posts on steemit amongst other benefits. Do join us on discord
. We anticipate your arrival.


Nice writeup about maintenance routine, Maintenance is indeed a neccessity in the field of engineering especially in a workshop, All machines should have a planned maintenance routine in its design specifications so as to allow such equipment to have and extended useful life rather than total life. It is generally known that corrosion is a deteriorating factor that render the useful life of a machine low and also proper maintenance routine helps to reduce corrosion rate. nice one, from a big Fan .👍
Thanks for this insightful comments, I appreciate your input and it's nice to hear from a mate in the field.
You're well appreciated.
This post could make a series of lectures on machine maintenance. I think you outdid yourself on this one. Well done.
As they say, a stitch in time saves nine. Most of our infrastructures in Nigeria need excellent maintenance culture which is currently lacking. At the end we spend so much buying new machines when we could have kept the old ones in good working conditions through good maintenance practice... Thanks for sharing.
Thanks for the encouraging comments, I could have made another series but it's already a sequel to a previous post. I just had to type and type.. Guess I enjoyed letting it out.
Exactly what we lack. We are just too bad at maintaining things. I would look at classes and many infrastructures in my Alma mater and wonder why they actually erected them if they wouldn't maintain them. It's just one of our major problems. I hope this orientation get changed soon.
Thanks for coming around Bro. I appreciate your kind gesture.
I have always respected the way you craft your articles. I really learnt more on the art of maintenance. You have done more than enough sir.
Thanks for the warm comments..I am motivated to do more...
You are welcome
This is a long interesting and well detailed post. Fantastic as usual.
I really learnt a lot about maintenance
Happy it was helpful. Thanks for the warm comments. I appreciate your time here.
Okay.. 👏👏👏👏. Thank you for being detailed. Care and maintenance is very important even to our household equipment and to the production company. I hope those companies will place the maintenance department higher in their scale of preference as they always see the department as one who "takes money away" from the organization and not "bring in the money" directly. Indirectly, however, the department saves the company a lot of money.
Now I have to thank you for the detailed comments.
As I've stated earlier, companies must pay more attention to the maintenance dept. and quit the believe that they waste resources as the are actually the backbone of every industry...
I appreciate your time and input.
Aside machines, I guess human deserves planned or predictive maintenance to last long. Nice one Engineer Breezie
You said it right though. Maintenance cuts across many aspects of our lives.
Thanks for your comments.
The Pleasure is all mine
💪
You have done well explaining what maintenance engineering is about.. Especially the part where you mentioned codeine diet
So, it's only codeine diet you saw.. That was just to describe the activeness of maintenance engineers...
Thanks for dropping by, I always appreciate your presence
What have you not said, I think you have said it all. I might be a maintenance engineer already by reading your post alone. You have explained in such an explicit manner and for that I must applaud you.
Thanks for the motivating comments. I'm motivated to do more...
Thanks or dropping by
Or? I get sha.
You are most welcome.
I kept my "f"....😂
Or uture purposes?
uck! You just a ucking crook or this.
😂 😂 😂
winks
permit me to say you "killed it".
maintenance of machinery is as important as the machinery itself.
Exactly, so important.
Thanks for the comments.
Maintenance is just to vital but then with you telling me about preventive measures and troubleshooting... Mayb you don't like me
But you hit the nail on the head bruv
I don't quite get you....
Don't like me?